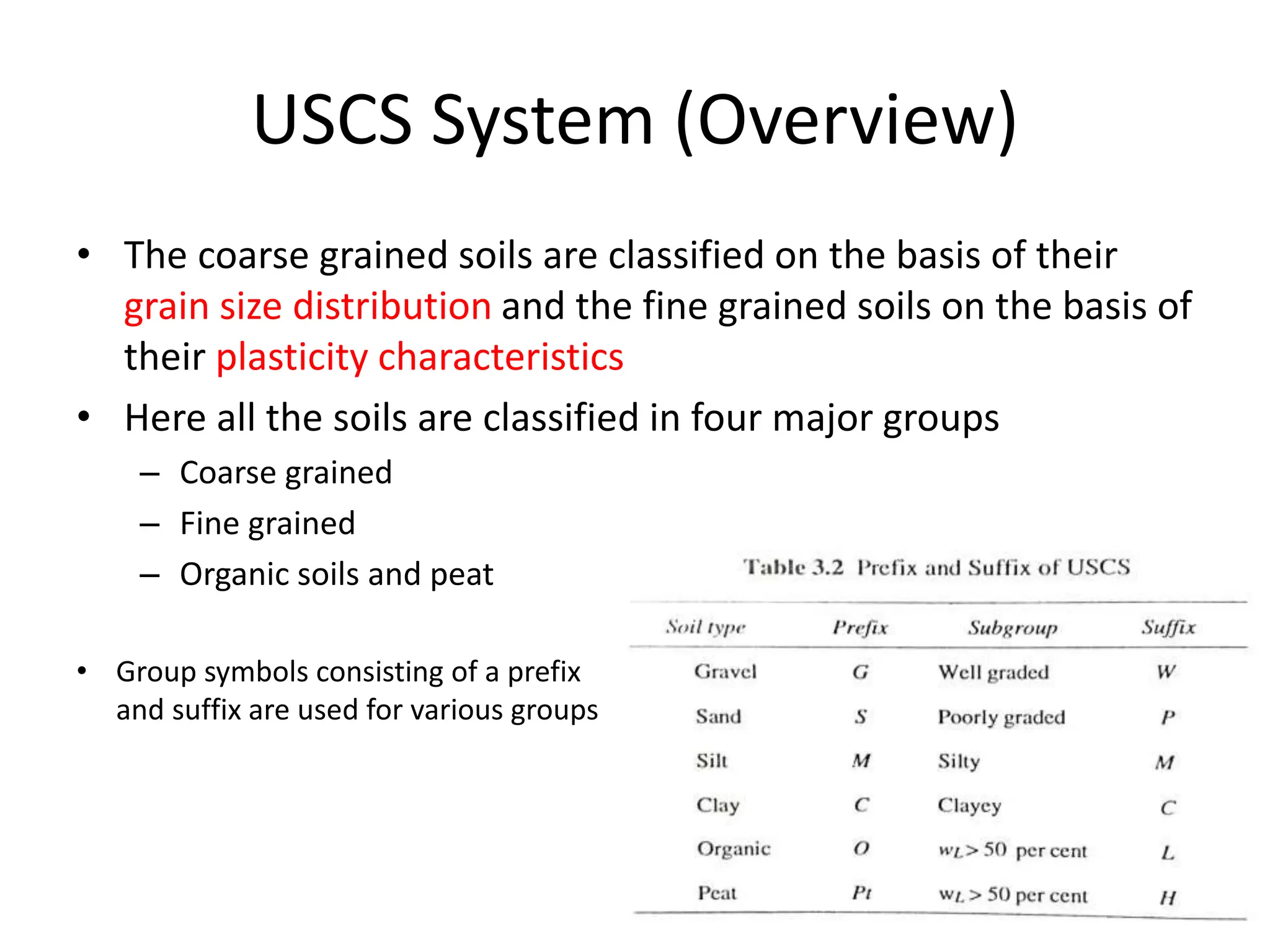
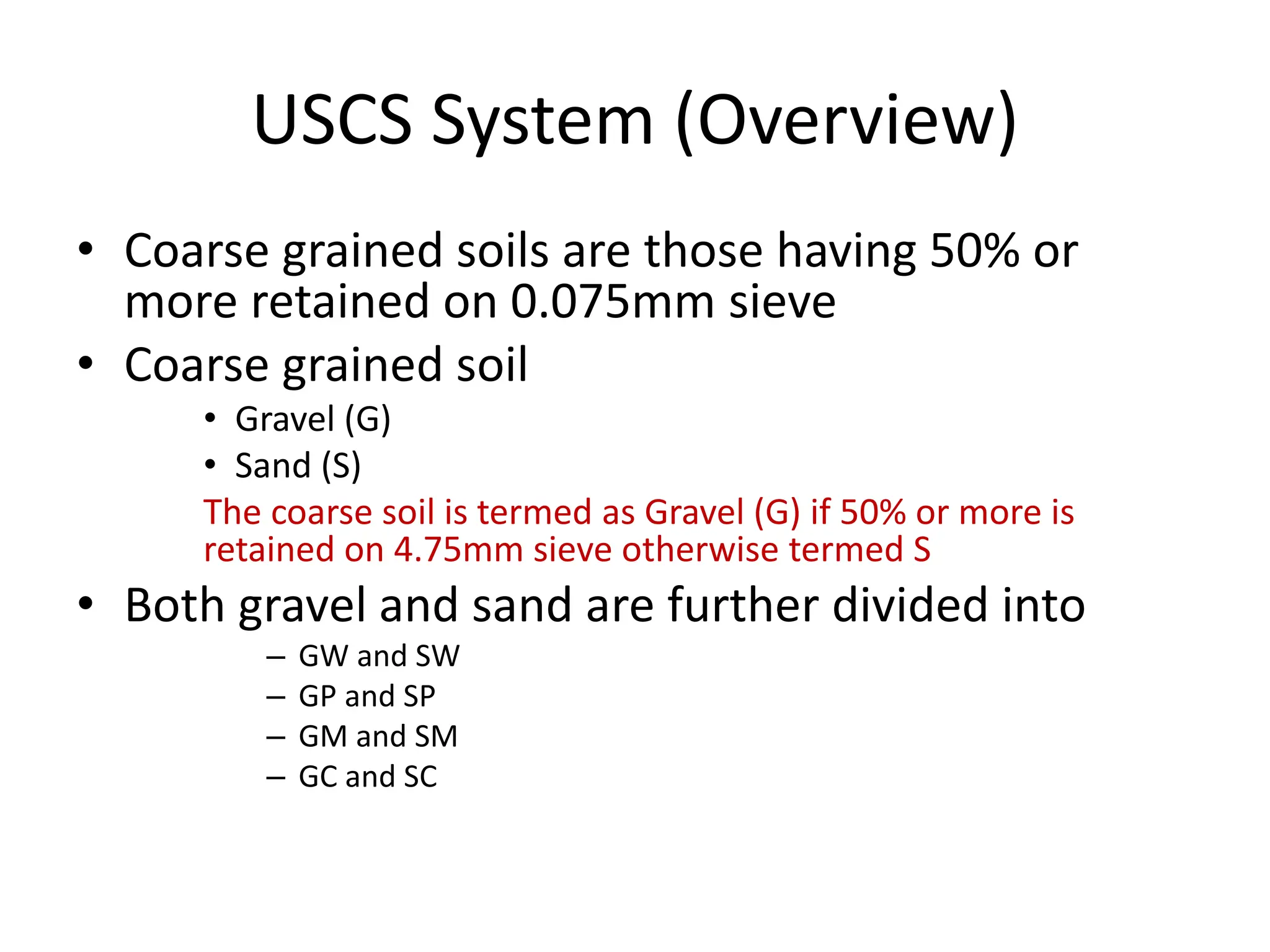
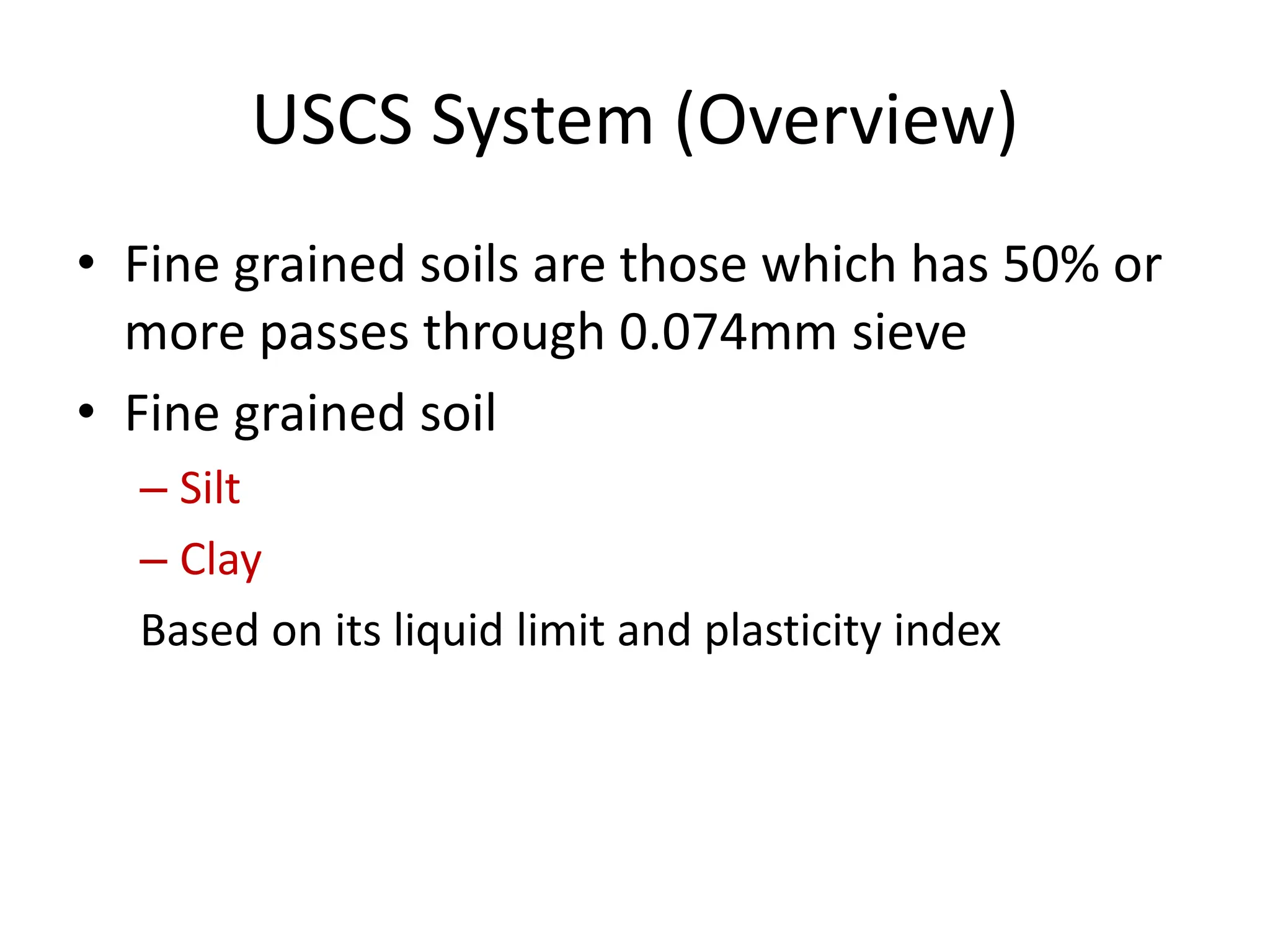
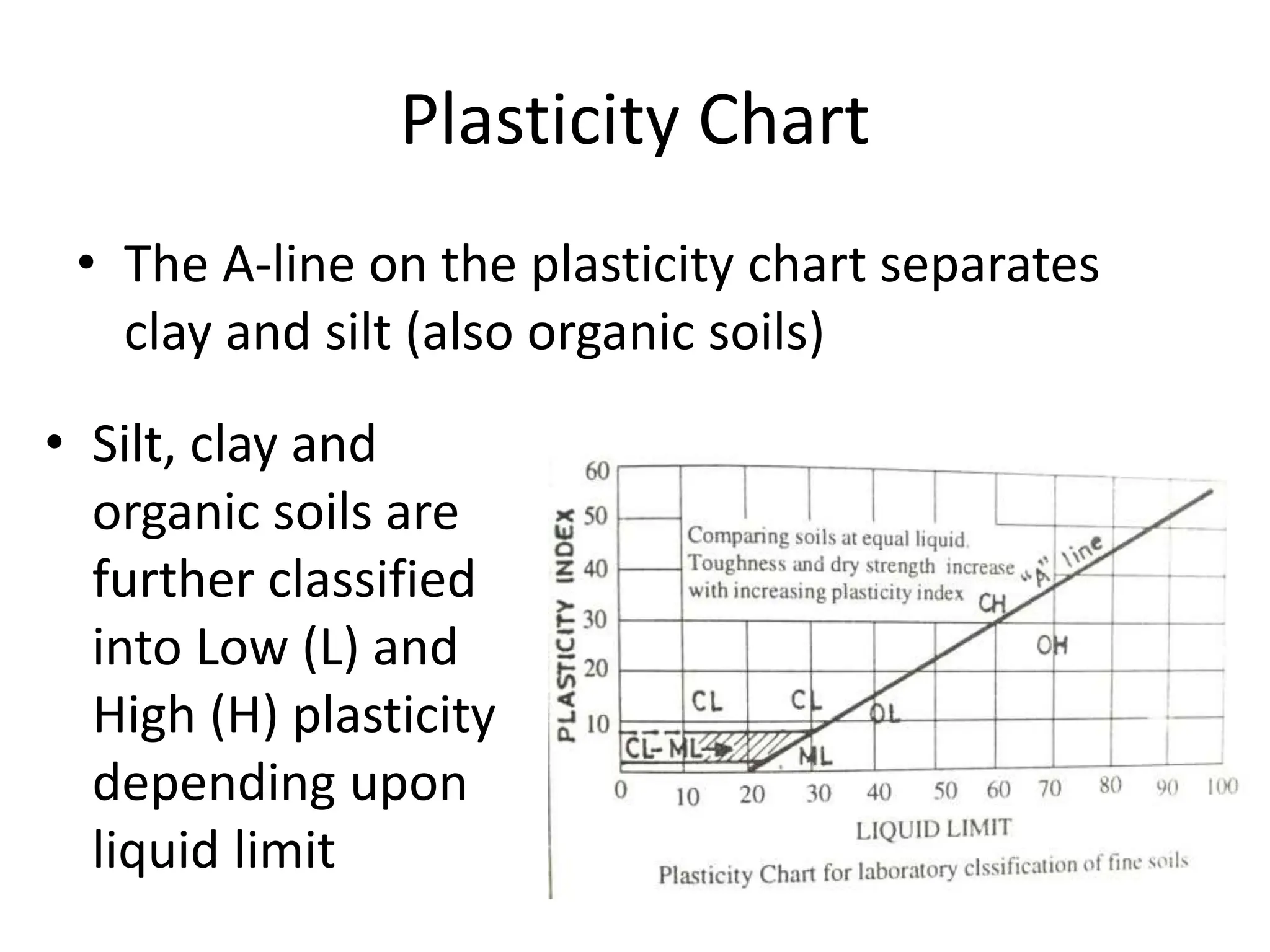
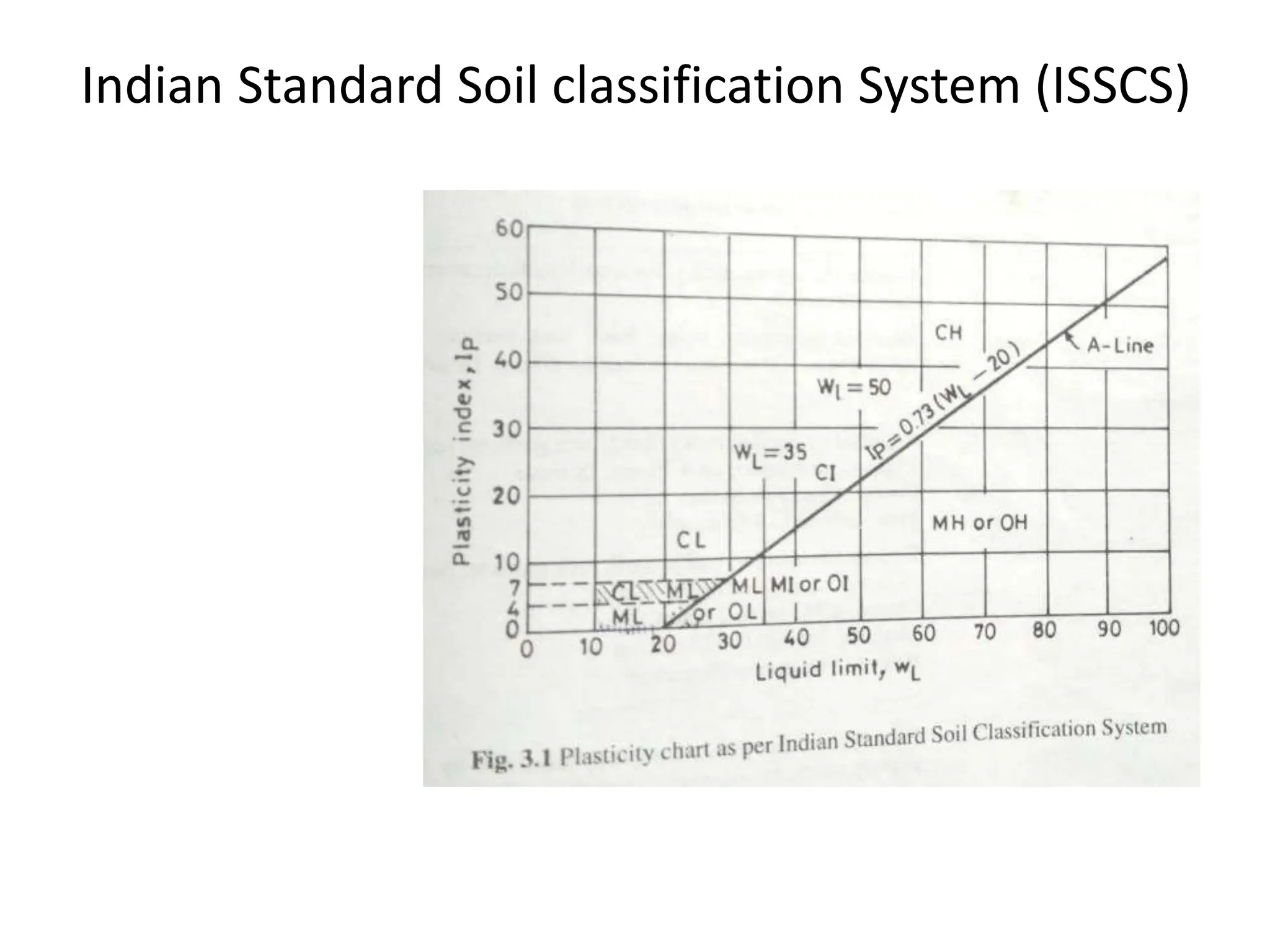
The document discusses various soil classification systems, particularly focusing on the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) and the Indian Standard Soil Classification System (ISSC). It categorizes soils into coarse-grained and fine-grained based on grain size distribution and plasticity characteristics, with further subdivisions for different types of soils. Key features such as group symbols and the plasticity chart are also highlighted to differentiate soil properties.