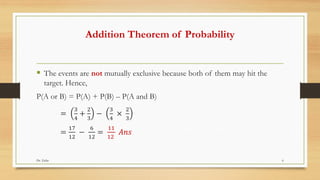
The addition theorem of probability states that if two events A and B are mutually exclusive, the probability of occurrence of either A or B is the sum of the individual probabilities of A and B, or P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B). The theorem can be extended to three or more mutually exclusive events. The document provides an example calculation for finding the probability that a randomly drawn ball will have a number that is a multiple of 5 or 9. It also provides an example where two people shooting at a target are not mutually exclusive events, so the formula is modified to P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B).