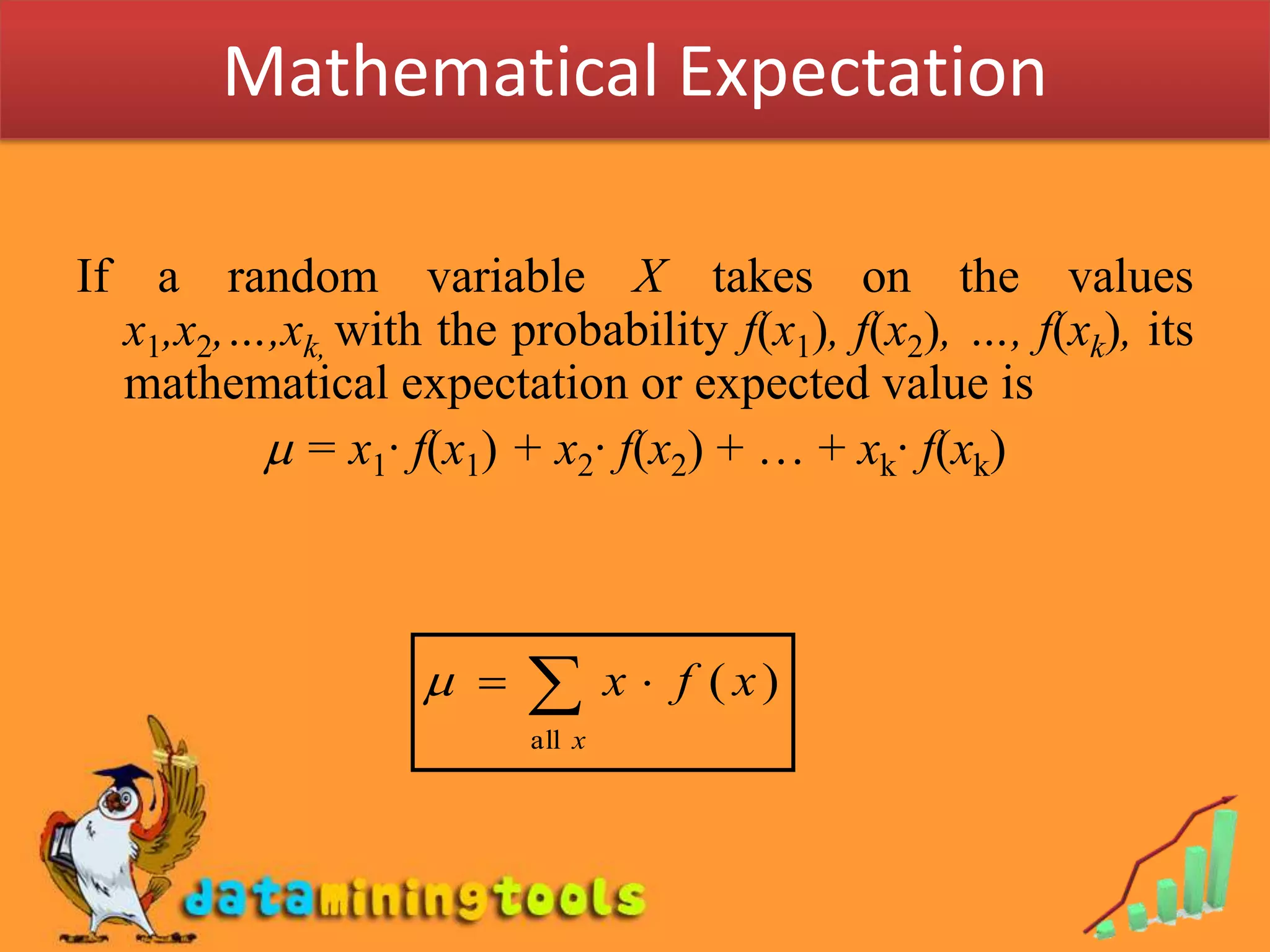
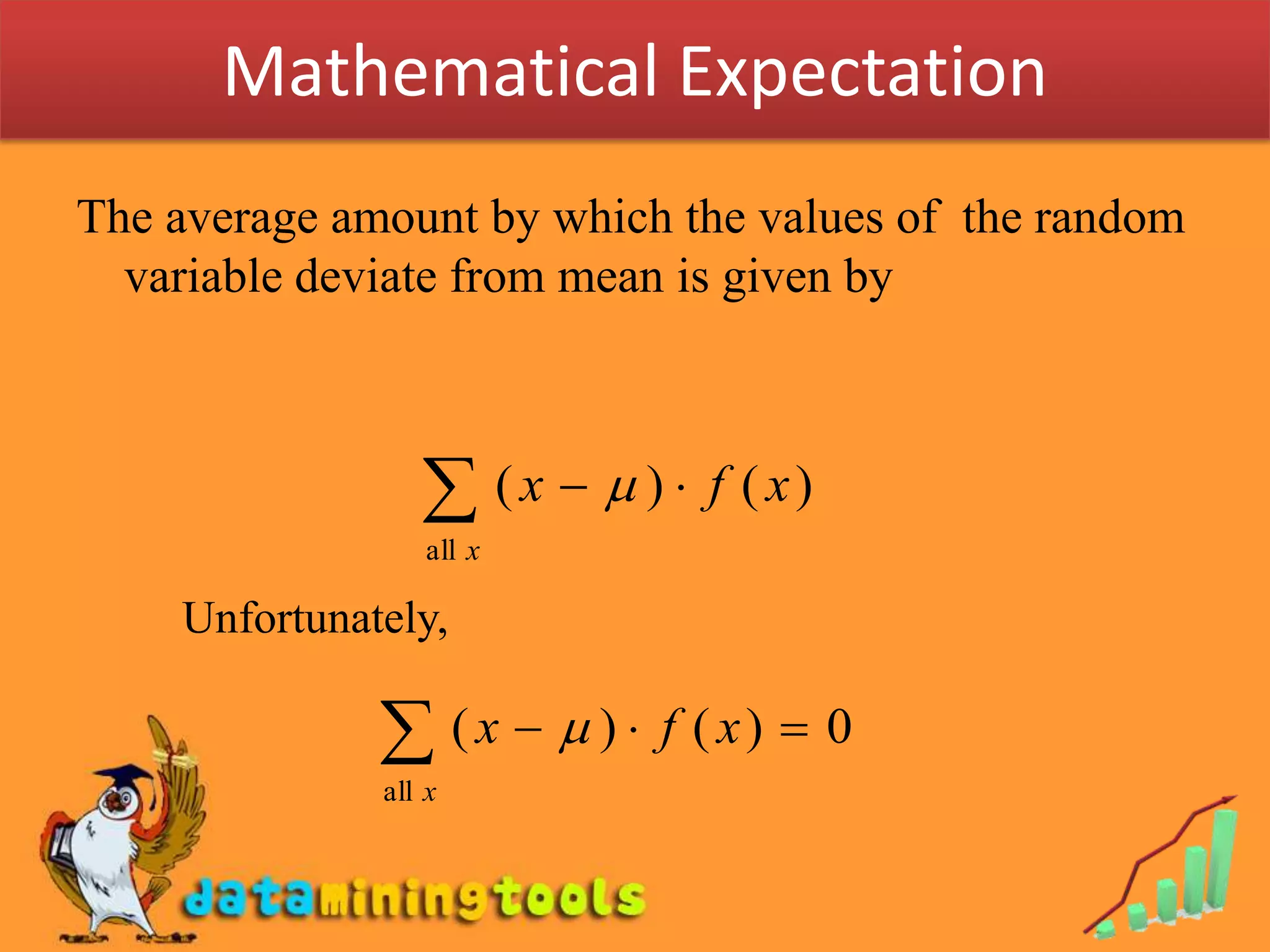
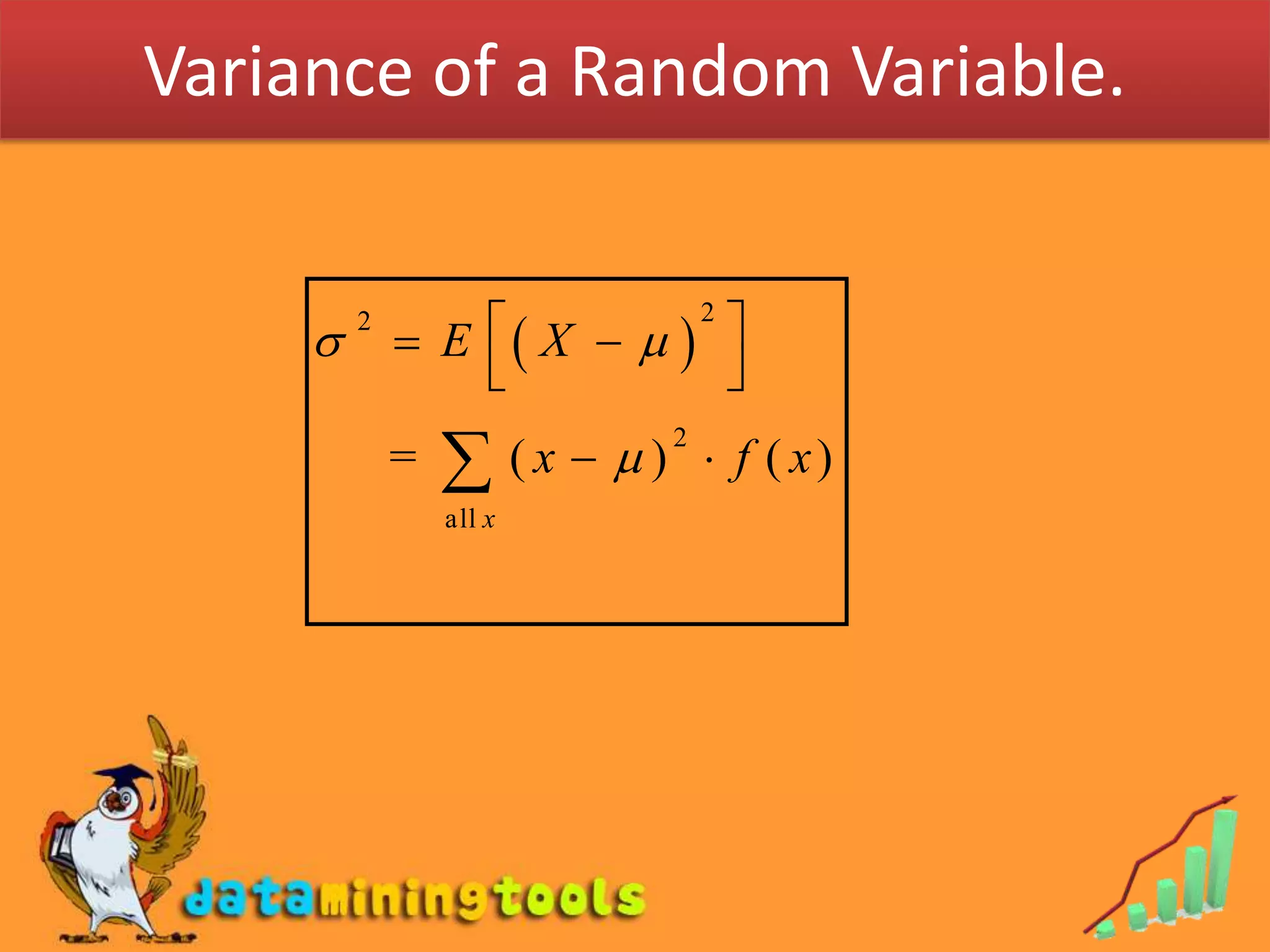
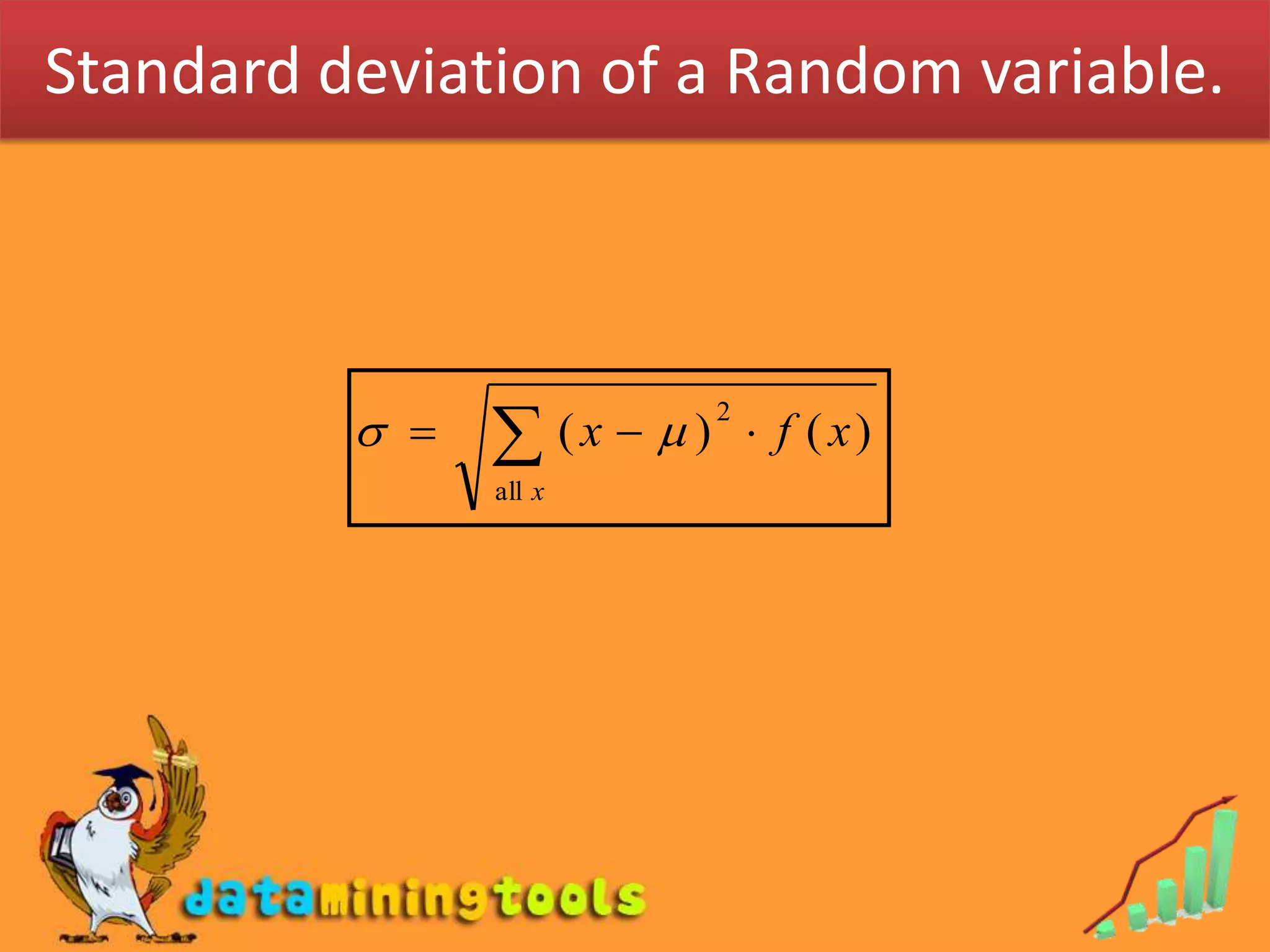
1. Mathematical expectation, or expected value, of a random variable is calculated by taking the sum of each possible outcome value multiplied by its probability of occurring.
2. For a game with multiple outcomes and their associated probabilities and payoffs, the expected value is the average amount a player can expect to win or lose over many plays. A positive expected value means the game favors the player, while a negative value means it is biased against the player.
3. Variance measures the average amount that values of a random variable deviate from the mean or expected value. Unfortunately, the document does not provide the formulas for variance or standard deviation of a random variable.