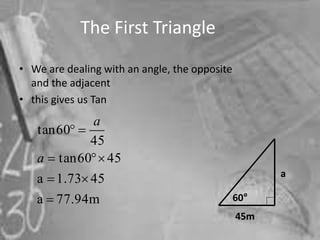
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with relationships between angles and sides of right triangles. It originated in ancient Greece. There are three basic trigonometric ratios - sine, cosine, and tangent - that relate the measures of angles to the lengths of sides in a right triangle. To solve problems using trigonometric ratios, one identifies the appropriate ratio based on the given and unknown sides, then substitutes the known values into the ratio formula and solves for the unknown.