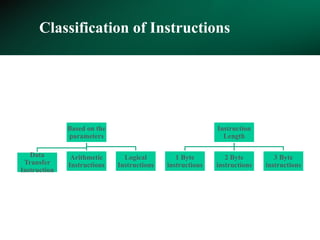
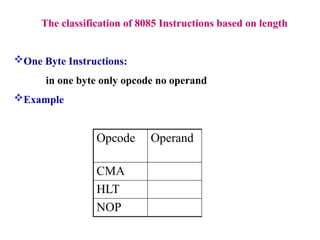
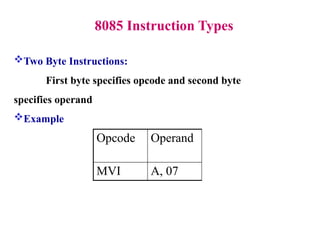
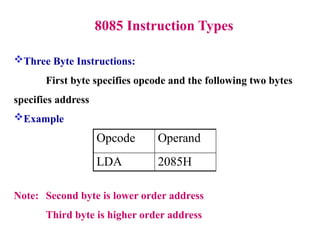
The **8085 microprocessor** is a fundamental component of early computing systems and embedded applications, known for its simplicity and efficiency. This presentation provides a **detailed study of the 8085 instruction set**, focusing on its classification, execution process, and impact on processor flags. The **8085 instructions** are categorized based on their **length and functionality**, helping users understand how different operations are executed at the machine level. The instruction set is broadly classified into **one-byte, two-byte, and three-byte instructions**. One-byte instructions contain only the opcode, while two-byte instructions include an additional operand, and three-byte instructions use two extra bytes to specify memory addresses.
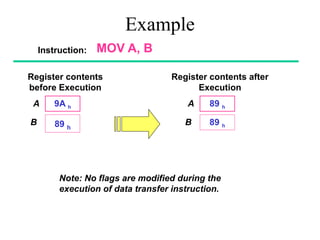
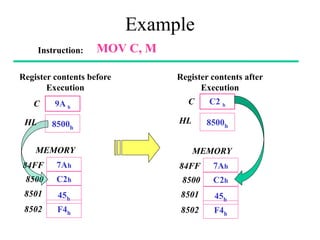
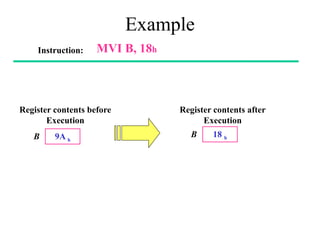
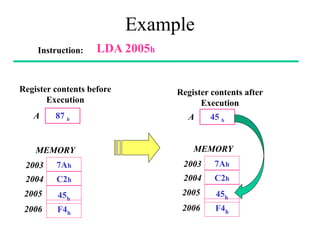
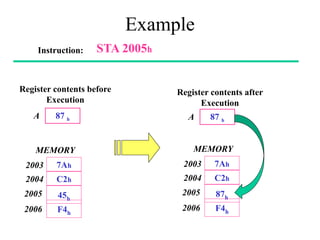
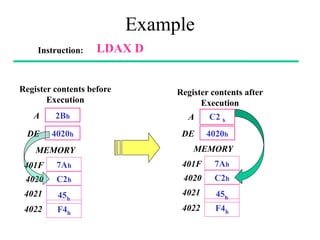
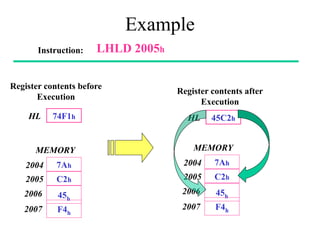
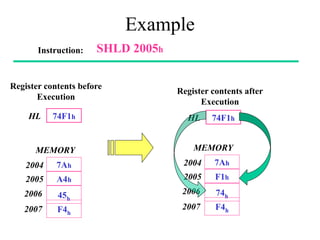
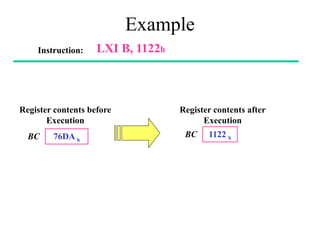
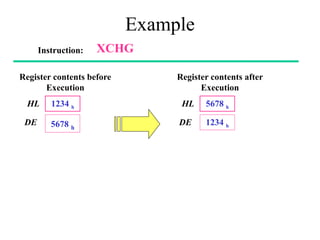
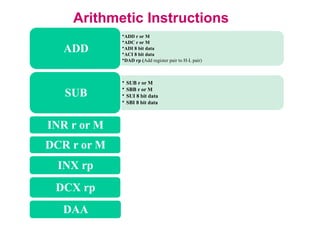
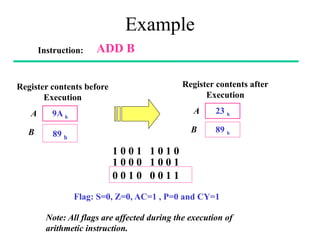
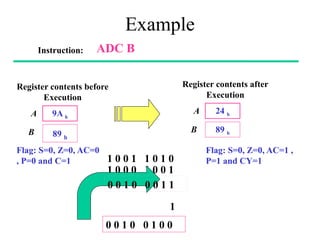
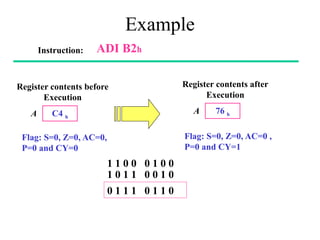
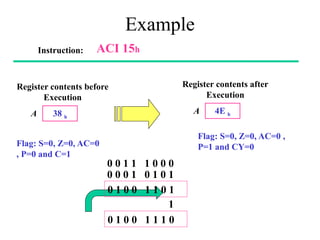
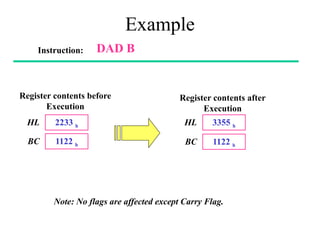
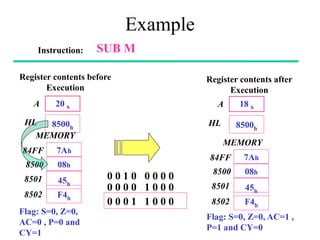
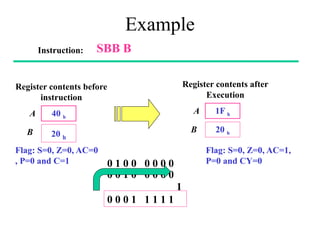
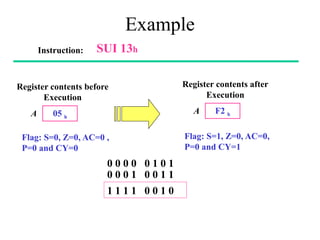
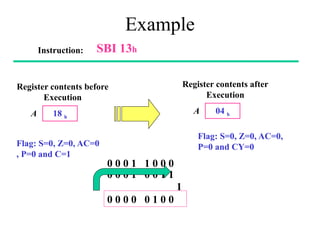
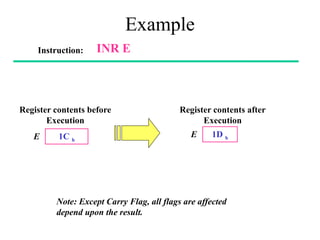
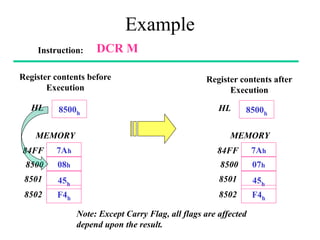
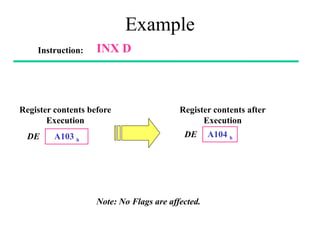
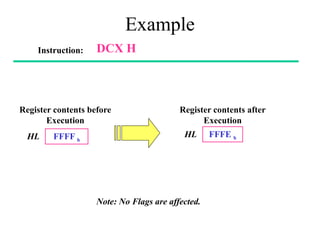
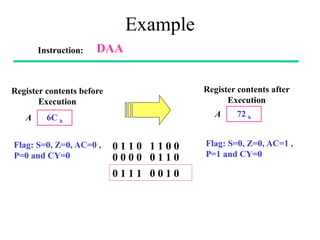
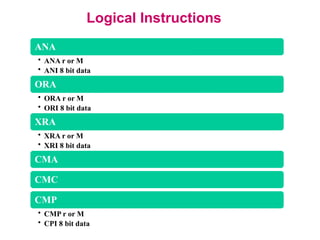
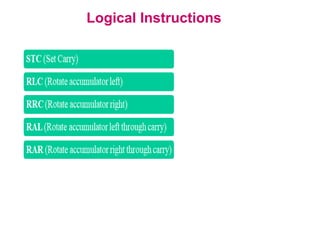
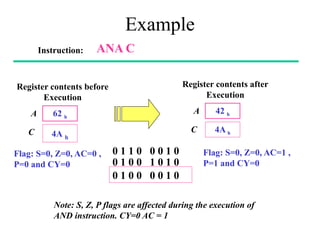
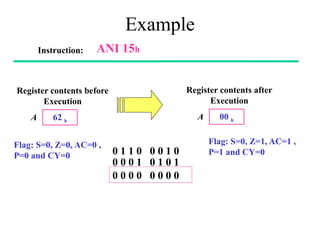
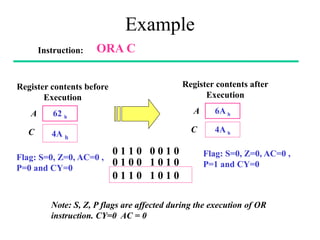
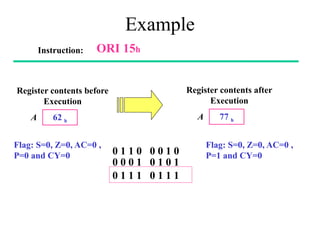
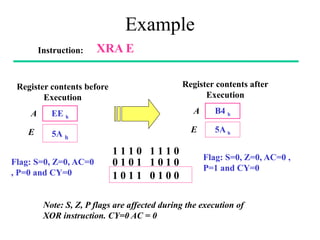
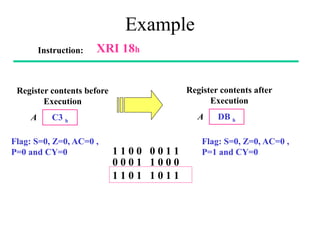
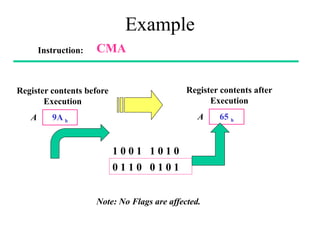
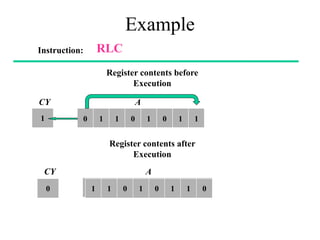
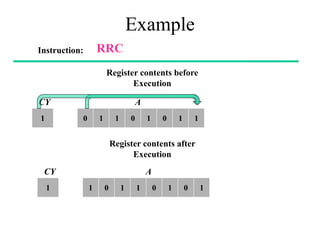
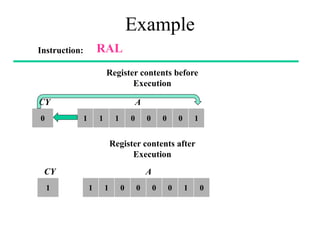
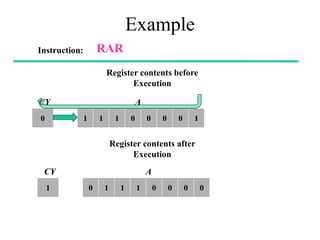
The **data transfer instructions** enable the movement of data between registers, memory, and I/O devices without affecting the processor flags. Examples include **MOV, MVI, LDA, STA, and LXI**. In contrast, the **arithmetic instructions** perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, increment, and decrement, directly modifying flags such as Zero (Z), Carry (CY), Sign (S), and Parity (P). Instructions like **ADD, ADC, SUB, SBB, and DAD** fall under this category. Additionally, the **logical instructions** such as **ANA, ORA, XRA, and CMA** execute bitwise operations, affecting specific flags while preserving others.
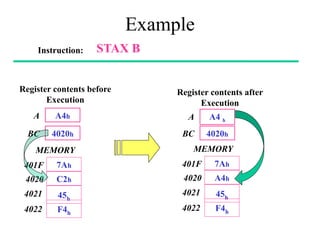
This presentation also explores the **branching and control instructions**, which are essential for decision-making and program flow control in assembly language programming. Unconditional branching instructions like **JMP and CALL** allow direct jumps, while conditional branching instructions like **JZ, JNZ, JC, and JNC** execute based on flag conditions. **Stack and machine control instructions** such as **PUSH, POP, HLT, and NOP** play a vital role in processor operation and subroutine execution.
By analyzing these instructions, this presentation provides a **clear understanding of how the 8085 microprocessor executes commands at the hardware level**. Whether you are a student, researcher, or professional in microprocessor-based system design, this guide will enhance your knowledge of **8085 assembly programming and system architecture**.