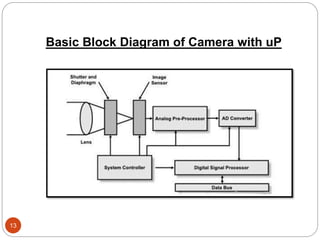
The document discusses the architecture of the Intel 8085 microprocessor. It describes the 8085 as an 8-bit microprocessor introduced in 1976 that uses a single +5 volt power supply. The internal architecture includes a control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), registers including the accumulator, program counter, stack pointer, instruction register/decoder, and timing and control unit. The document also briefly discusses interrupts, serial I/O, and some applications of microprocessors like mobile phones, watches, and appliances.