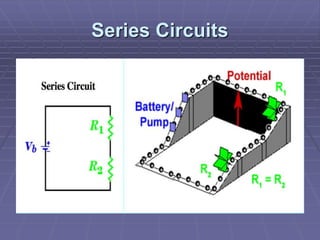
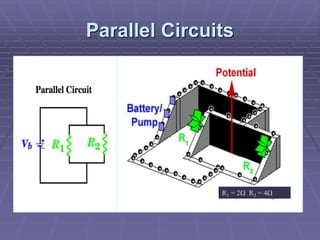
This document discusses series and parallel circuits. In a series circuit, all components are connected one after the other so there is only one path for electron flow. The total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances and the current is the same throughout. In a parallel circuit, each branch provides its own path so the voltage is the same across all branches but currents can differ depending on the branch resistances. The total current is the sum of the branch currents and the total resistance is lower than any single branch resistance.