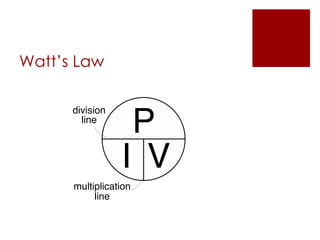
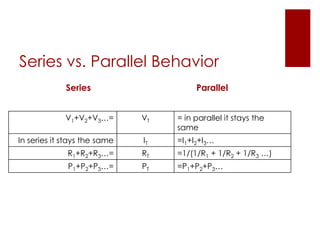
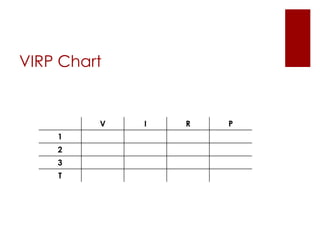
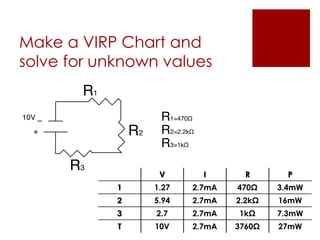
The document provides an overview of key calculations and concepts in electronics, focusing on series and parallel circuits. It includes definitions of fundamental electrical terms such as voltage, current, resistance, and power, along with Ohm's Law and Watt's Law. Additionally, it presents examples using a 'VIRP' chart to solve for unknown values in circuit calculations.