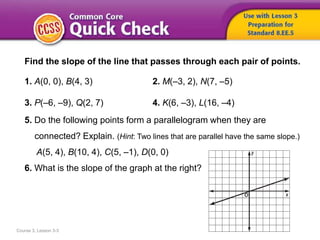
1. The document provides examples of finding slopes of lines from given points and determining if points form a parallelogram. It also discusses direct variation relationships and using equations, tables, and graphs to represent and compare them.
2. A constant of variation in a direct variation relationship is the constant that relates the ratio of the output quantity to the input quantity. It represents the unit rate or slope in the direct variation equation and graph.
3. Graphs are helpful for comparing different proportional relationships represented in different ways and finding the unit rate between quantities in a relationship from its graphical representation.