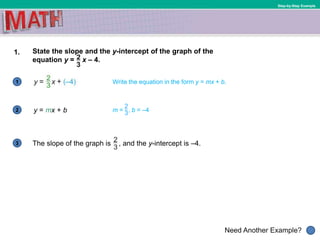
This document contains a mathematics lesson on graphing linear functions and interpreting slope and y-intercept. It includes examples of writing equations from graphs, finding slope and y-intercept, graphing linear equations, and interpreting slope and y-intercept in real world contexts. Key concepts covered are slope-intercept form, slope, y-intercept, rate of change, and using graphs to model proportional relationships.