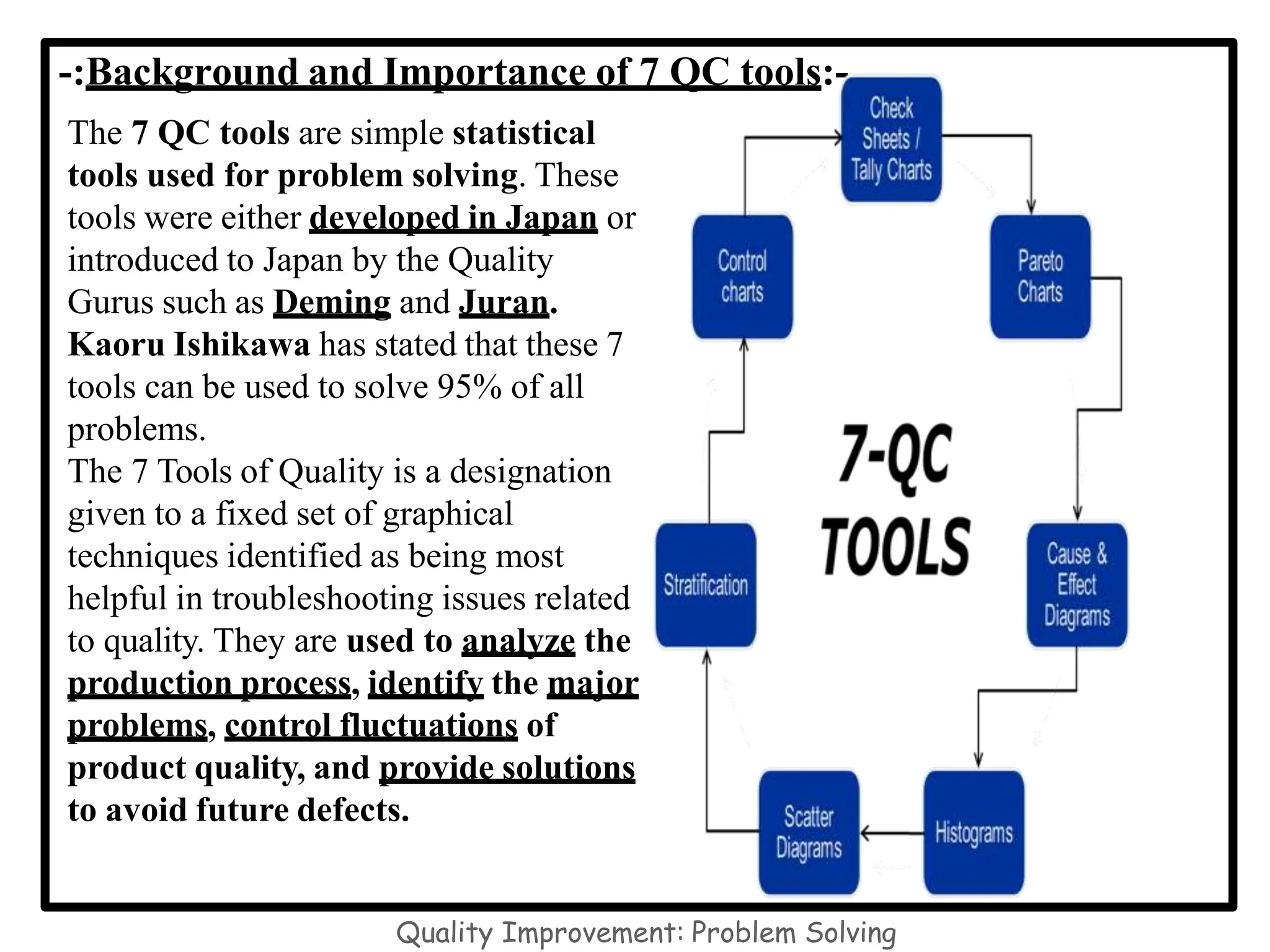
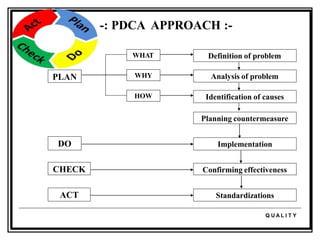
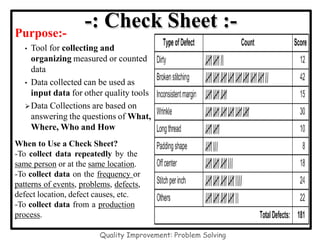
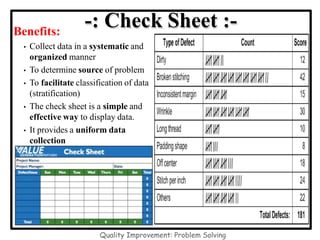
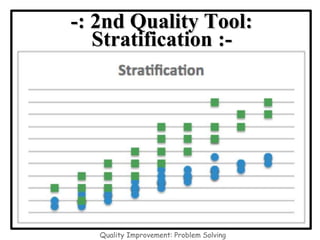
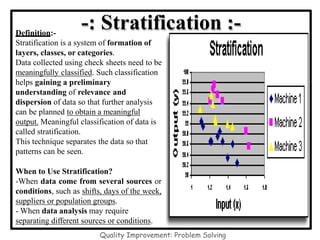
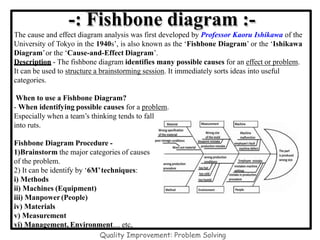
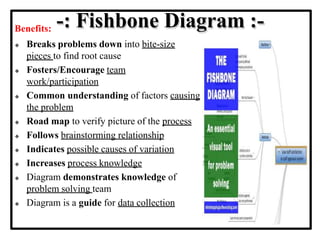
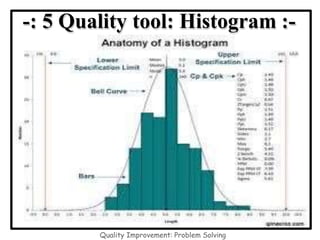
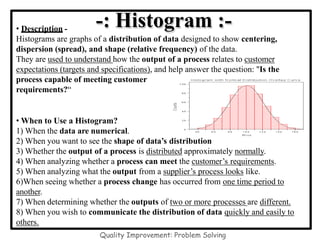
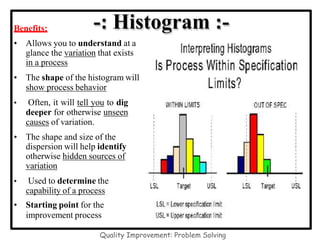
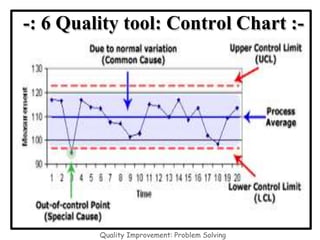
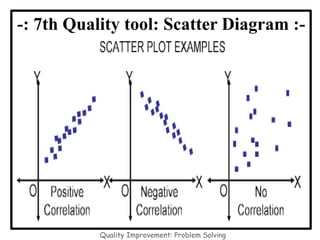
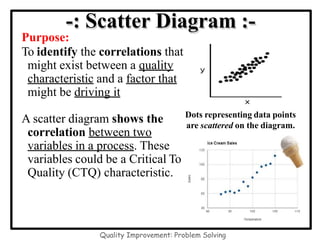
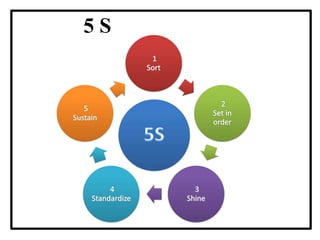
The document discusses the 7 quality control tools which are statistical methods used for problem solving. The 7 tools include check sheets, stratification, Pareto charts, cause-and-effect diagrams, histograms, control charts, and scatter diagrams. Each tool is described in terms of its purpose, benefits, and when it should be used. For example, check sheets are used to systematically collect data, Pareto charts identify the most important problems to focus on, and histograms show the shape of a data distribution to understand process capability. The 7 tools provide different graphical methods to analyze production processes, identify quality issues and their causes, and find solutions to prevent future defects.