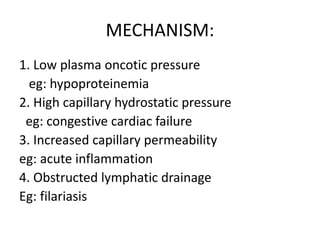
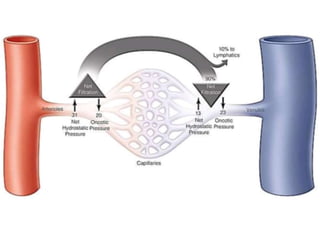
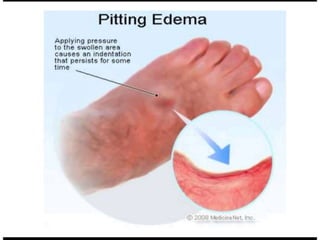
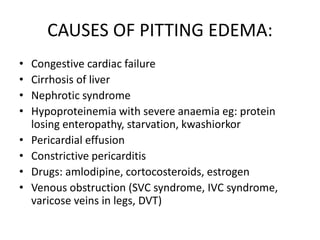
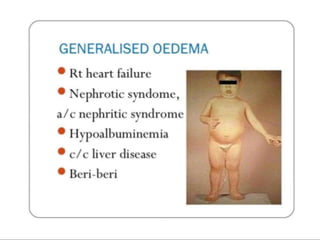
Oedema is the accumulation of excessive tissue fluid in the subcutaneous tissue, causing swelling. It can be caused by low plasma oncotic pressure, high capillary hydrostatic pressure, increased capillary permeability, or obstructed lymphatic drainage. Symptoms include localized or whole body swelling, facial puffiness, and pain or tightness in affected areas. Examination involves applying pressure to check for pitting edema, which indicates increased interstitial fluid, versus non-pitting edema with protein deposition. Common causes of pitting edema are congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, and hypoproteinemia.