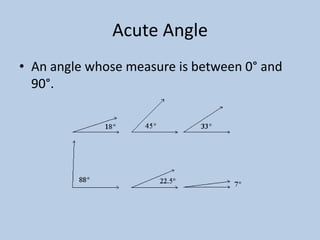
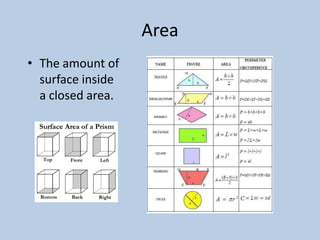
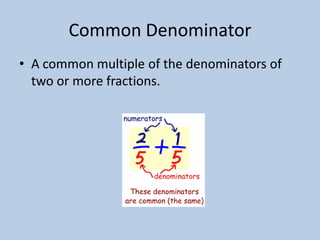
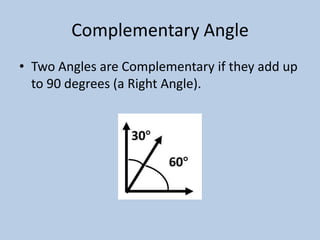
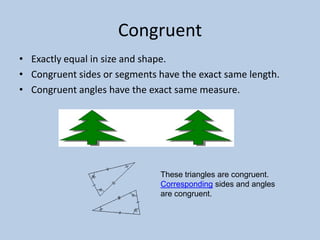
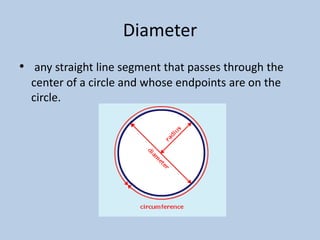
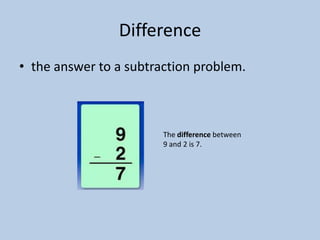
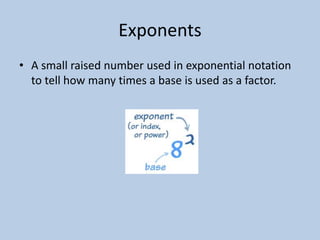
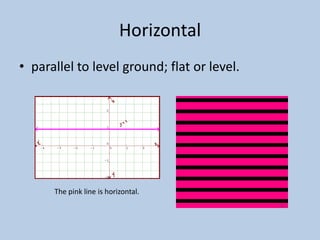
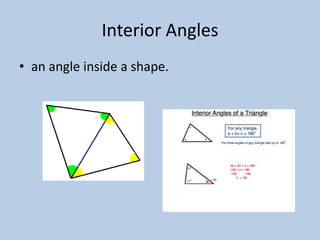
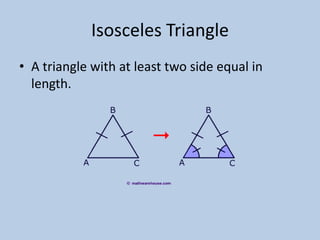
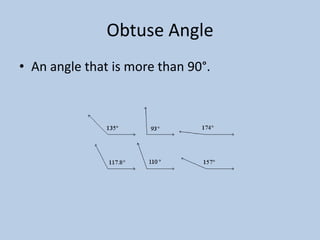
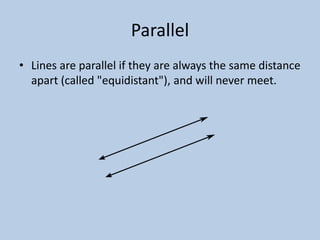
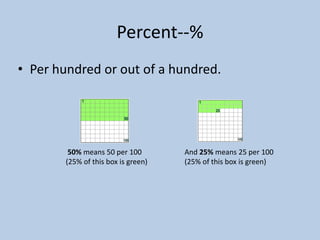
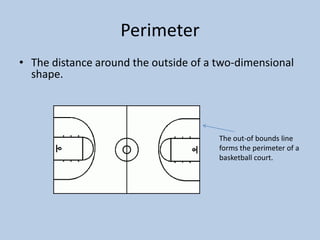
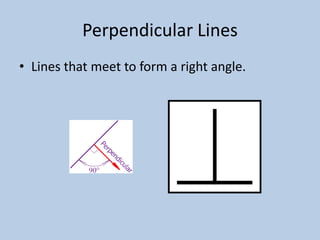
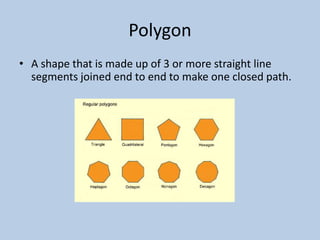
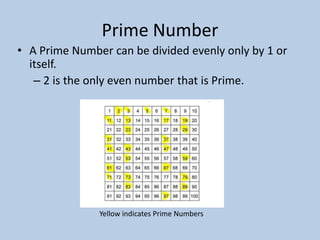
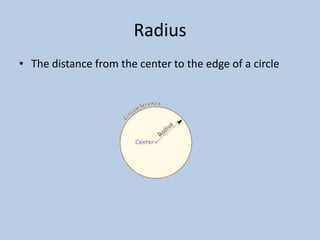
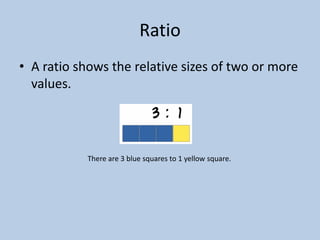
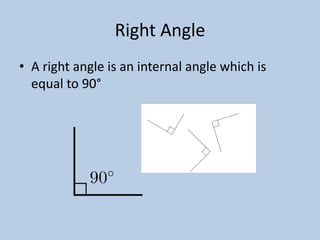
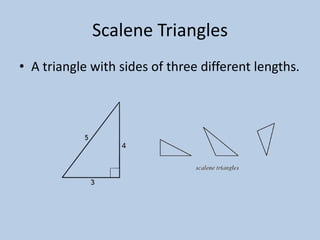
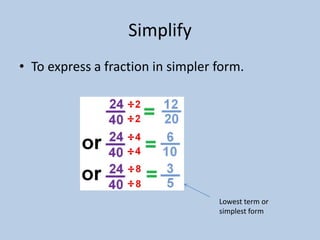
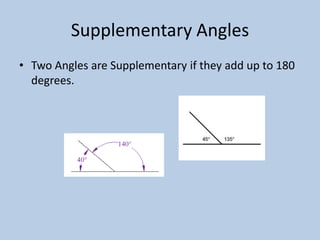
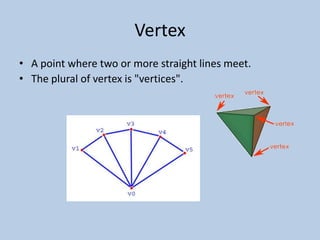
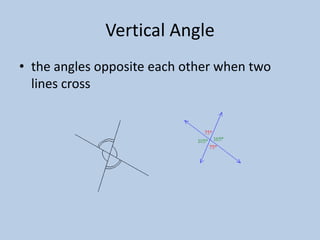
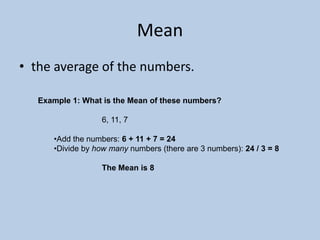This document defines various 6th grade math vocabulary terms in 3 sentences or less per term. There are over 50 terms defined ranging from acute angle, area, capacity, to vertical, vertex, and more. The definitions provide clear and concise explanations of common math terms students need to understand at the 6th grade level.