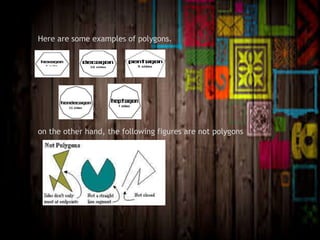
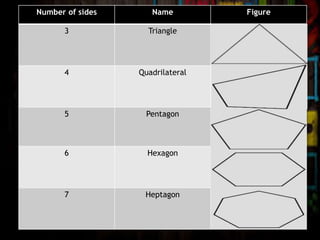
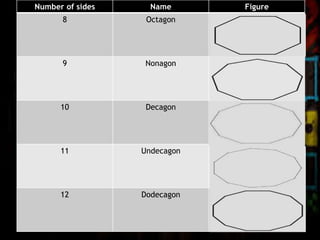
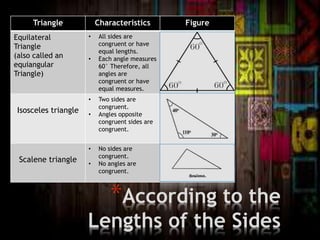
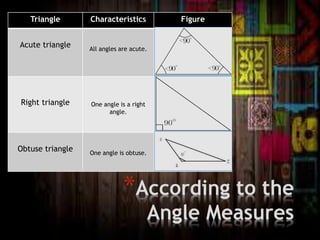
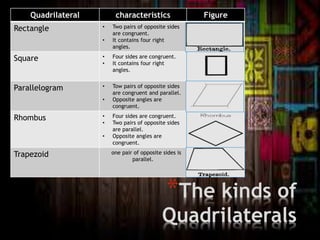
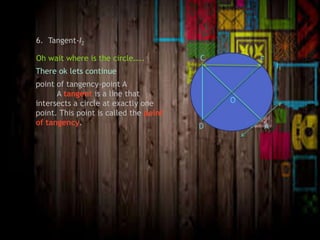
The document discusses the classification of polygons and circles, defining polygons as closed plane figures formed by line segments and highlighting circles as a distinct category due to their lack of such boundaries. It details various types of triangles and quadrilaterals, including their properties and classifications based on sides and angles. Additionally, the document explains the components of a circle, including the center, radius, diameter, chord, secant, and tangent.