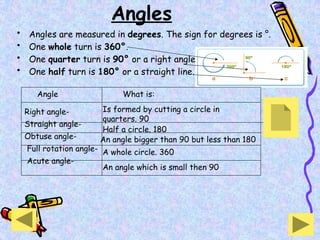
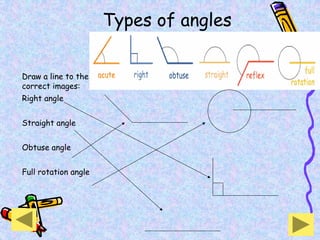
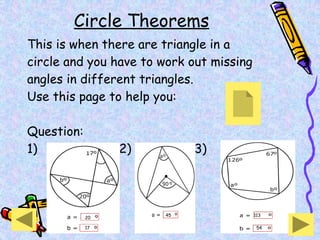
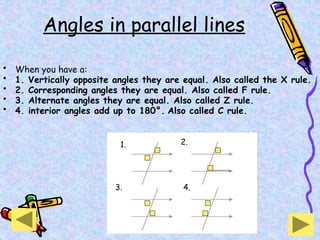
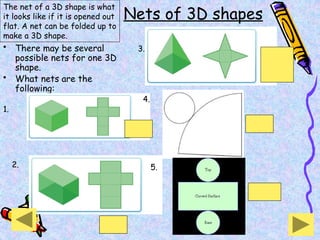
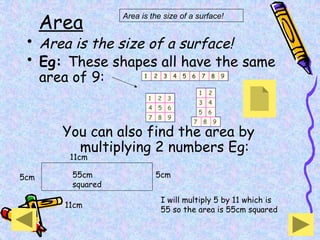
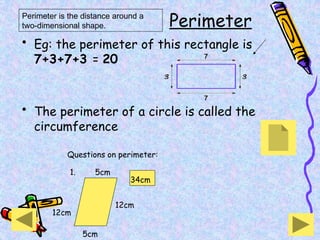
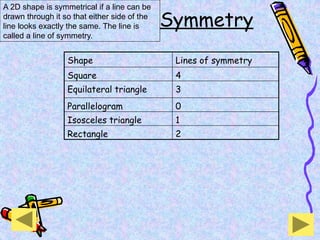
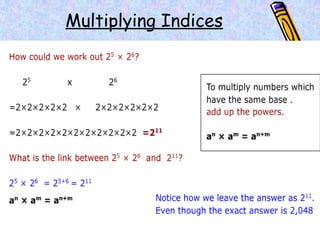
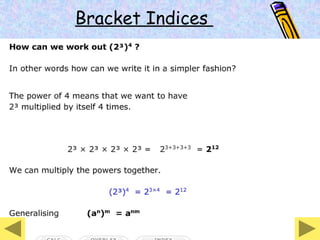
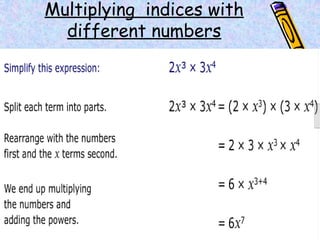
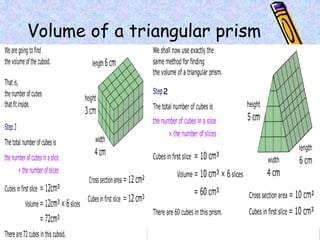
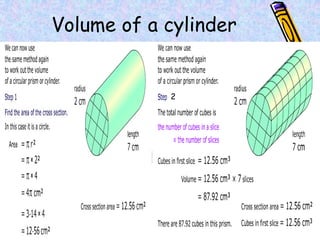
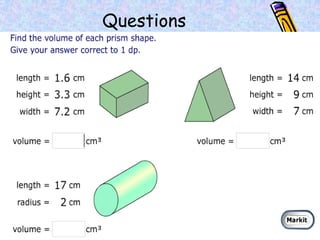
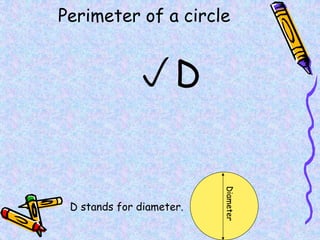
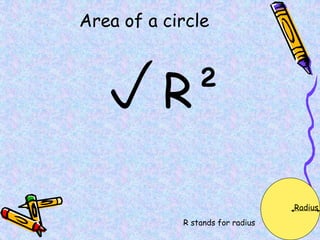
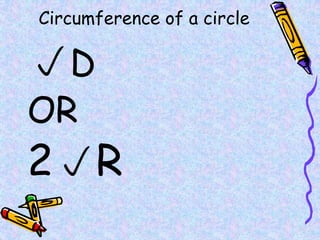
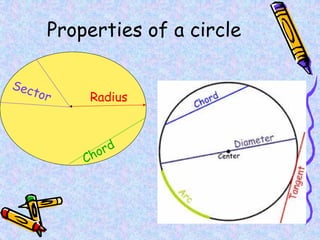
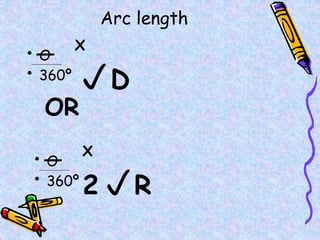
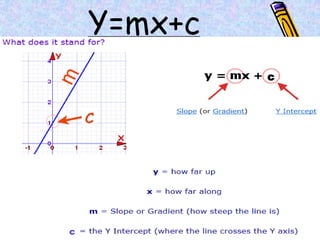
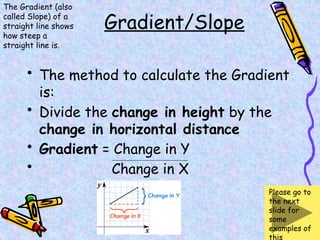
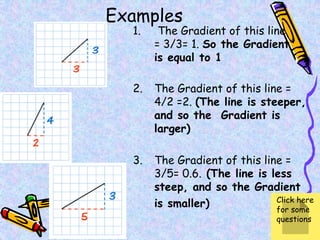
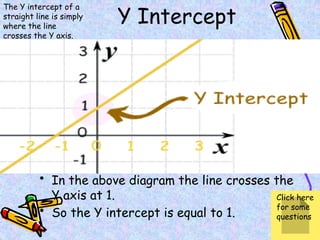
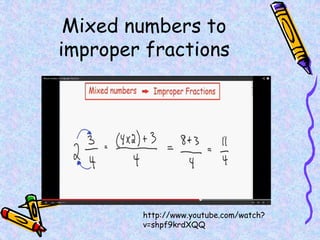
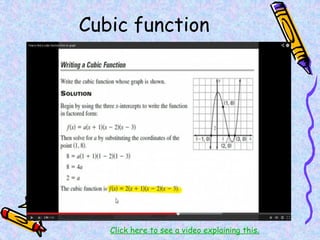
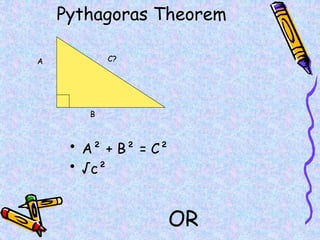
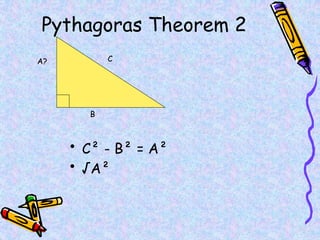
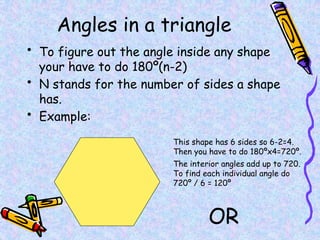
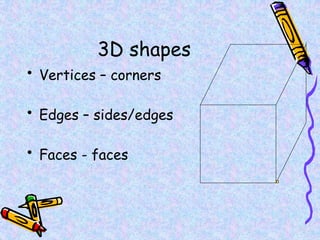
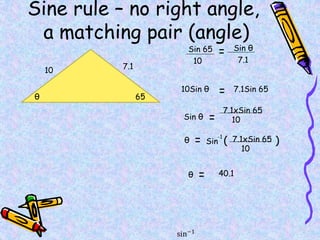
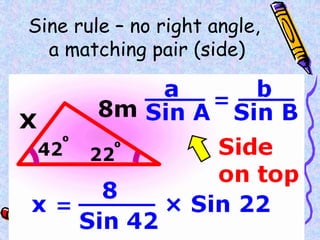
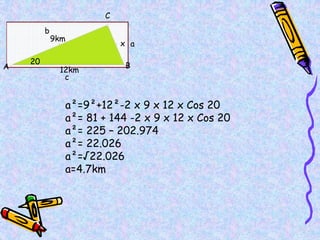
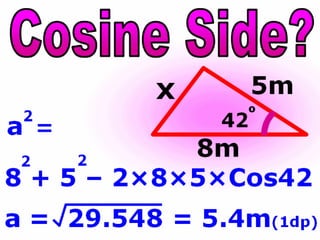
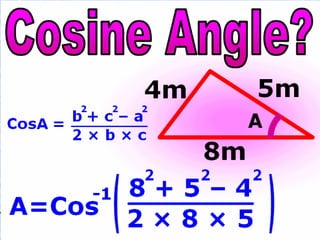
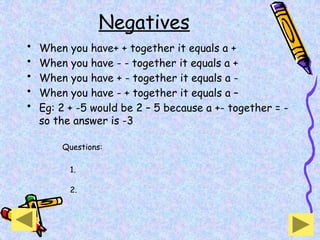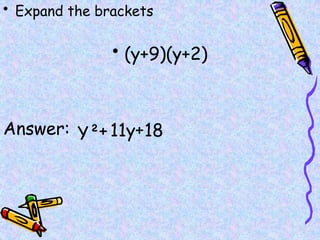The document covers various mathematical concepts including square numbers, factors, prime numbers, substitution in algebra, nth terms, mean, median, mode, angles, 3D shapes, area, volume, and probability. It provides definitions, examples, and questions to reinforce learning, making it a comprehensive revision guide. Additionally, it includes topics on the metric system, symmetry, and procedures for calculations involving fractions, decimals, and indices.