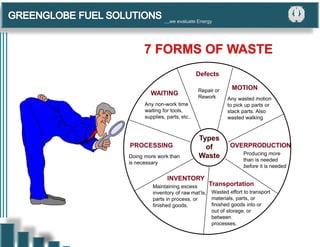
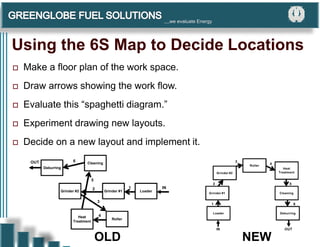
The document discusses the 6S methodology for workplace organization and continuous improvement. It describes the six elements of 6S - Sort, Set In Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain. Implementing 6S brings benefits like a safer work environment, lower costs, and higher customer satisfaction. Typical resistances to 6S include beliefs that it only applies to factories or that current systems are sufficient. The document provides guidance on implementing each element of 6S, including techniques for sorting items, visually organizing the workspace, cleaning processes, standardizing improvements, and sustaining new systems through habits and discipline.