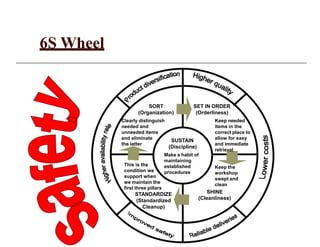
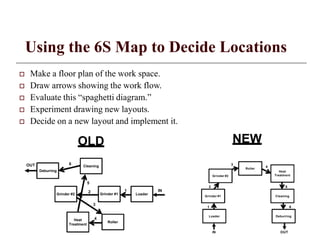
The document provides an overview of the 6S methodology for workplace organization and continuous improvement. It describes the six elements of 6S - Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain, and Safety. For each element, it outlines the goals, implementation steps, tools, and benefits. The 6S process aims to create an organized, clean, safe work environment as a foundation for further improvements. By implementing 6S, companies can achieve higher quality, lower costs, and greater customer satisfaction.