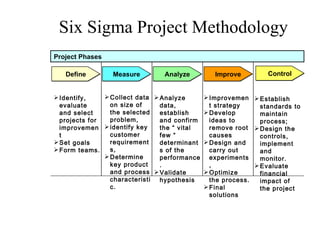
Six Sigma is a quality improvement methodology that aims to reduce defects to 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It was developed by Bill Smith at Motorola in the 1980s and has since been adopted by many major organizations. Six Sigma uses statistical tools and process improvement strategies to enhance customer satisfaction and increase profits by eliminating defects in business processes.