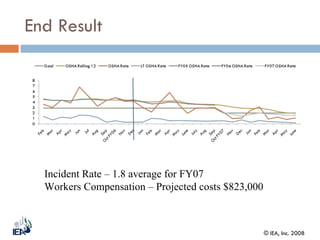
The document outlines a Six Sigma approach aimed at improving safety processes, focusing on reducing workplace injuries and associated costs through management commitment and employee participation. Key analysis tools include Pareto charts and cause-and-effect diagrams to identify major contributors to incidents and implement standardized safety practices. As a result, the average incident rate significantly decreased from 40 injuries annually to less than 5, demonstrating the effectiveness of the implemented corrective actions.





























![Contact Info Email: [email_address] Phone: 507-281-6661 Cell: 507-884-6691 LinkedIn http://www.linkedin.com/in/timpuyleart](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sixsigmaasse-124447647279-phpapp02/85/Six-Sigma-Asse-32-320.jpg)