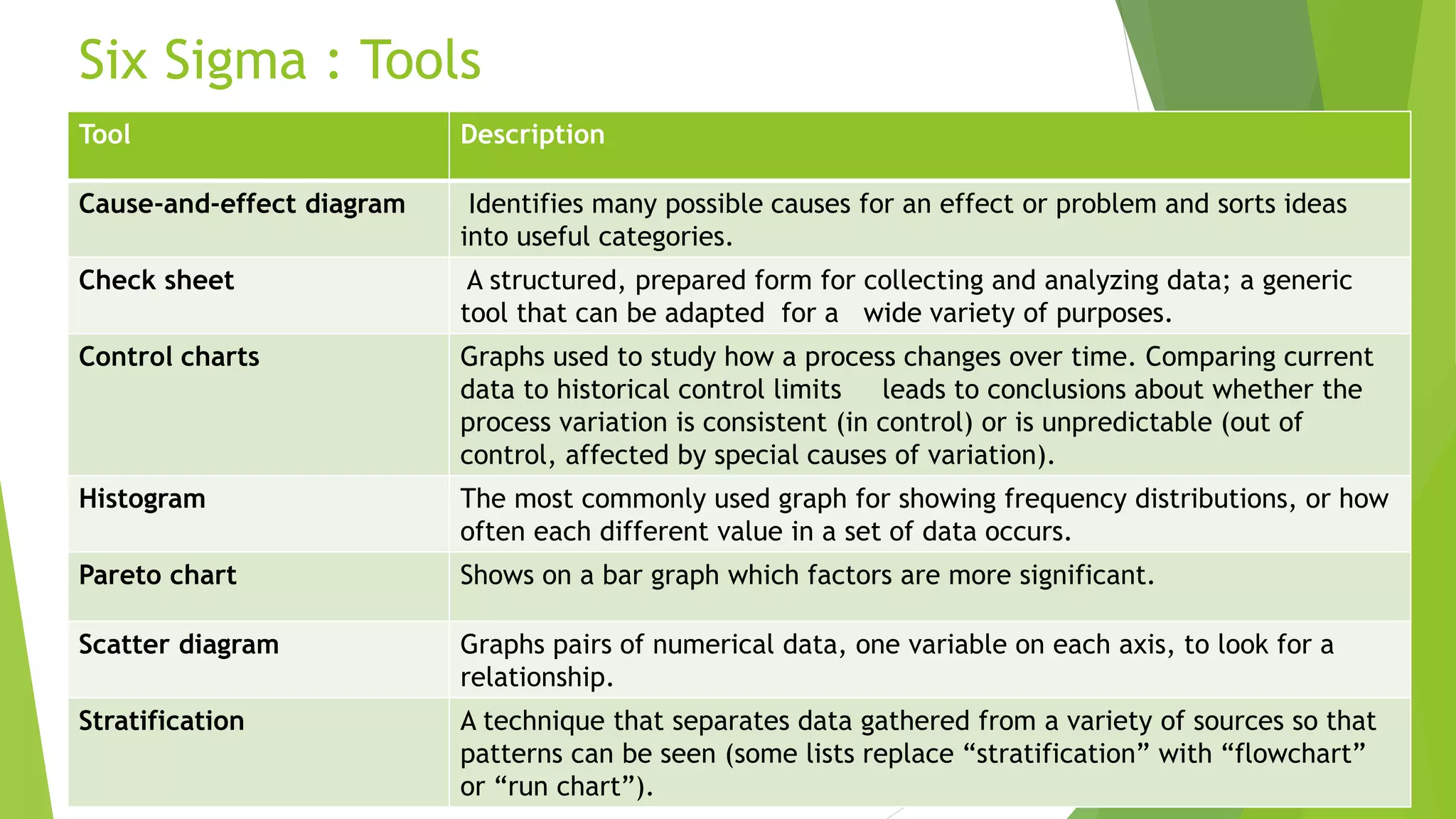
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology for improving processes by reducing variability and defects. It was developed by Motorola in the 1980s and aims for near-perfect process outputs. The objectives of Six Sigma are to understand and reduce variation in processes. It uses various quality tools like cause-and-effect diagrams, control charts, and value stream mapping. A key benefit is increased business performance through stable and consistent processes. Establishing a no-blame culture is important for Six Sigma, with a focus on accountability, teamwork, and continuous improvement.