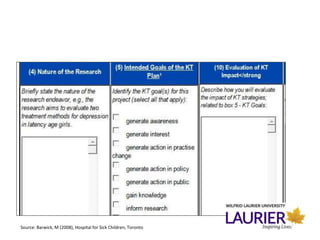
This document provides guidance on developing a knowledge mobilization plan. It defines knowledge mobilization and different related terms used across funding agencies. An effective plan must identify the research outcomes, target audiences and how they will be reached. It should also explain how impact will be evaluated over time. The plan requires determining appropriate knowledge products and resources like budgets, timelines, and ensuring open access of research outputs. Support services are available to help with workshops on clear writing, digital identity, and engaging events on social media. Developing a strong knowledge mobilization plan is important for sharing research broadly and creating real-world impact.