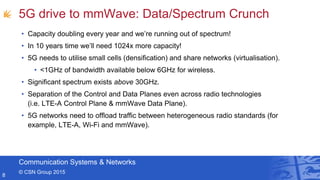
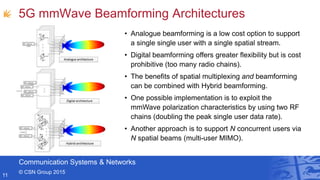
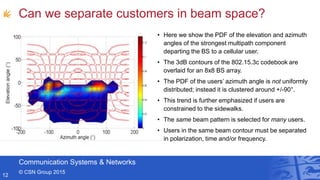
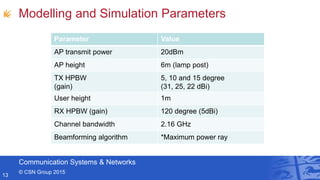
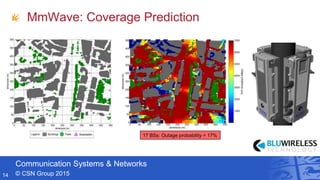
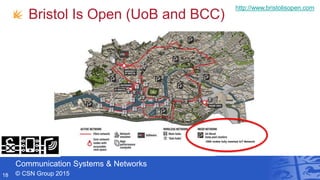
- Professor Andrew Nix gave a presentation on 5G and beyond communication from a Bristol perspective. He discussed the Communication Systems & Networks group at the University of Bristol, their work on mmWave simulations and beamforming for 5G, applications for automotive, and their leadership in European 5G research projects. He highlighted Bristol's testbeds and infrastructure for innovations in areas like the Internet of Things and smart cities.