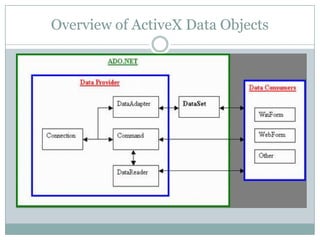
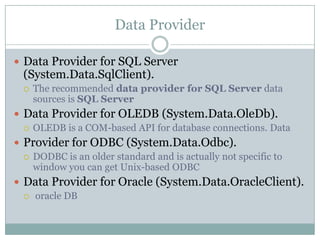
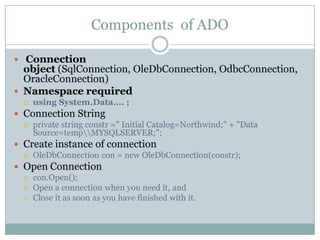
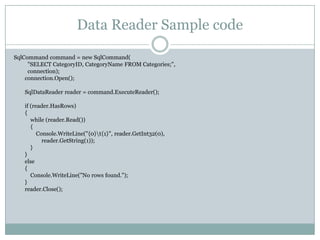
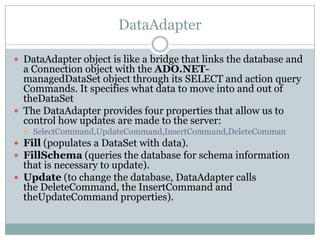
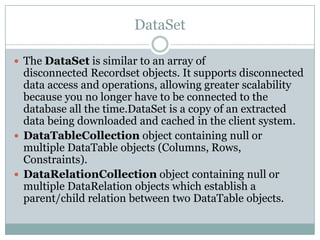
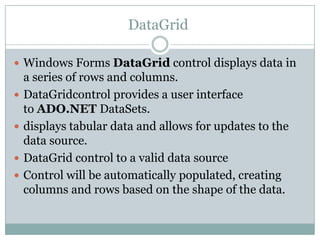
This document provides an overview of ADO.NET components for accessing and manipulating database data in .NET applications. It describes key ADO.NET classes like Connection, Command, DataReader, and DataAdapter that allow establishing connections and executing queries to retrieve and update data. It also covers DataSet which stores a local copy of data disconnected from the database, and DataGrid control for displaying tabular data.