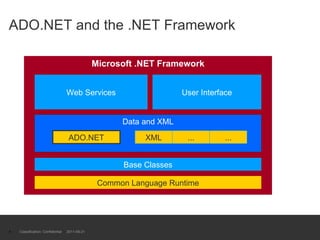
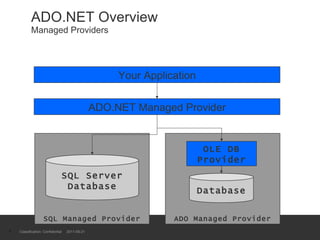
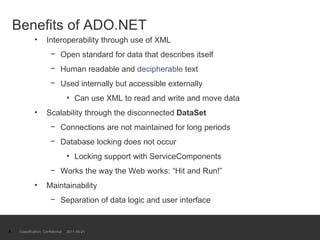
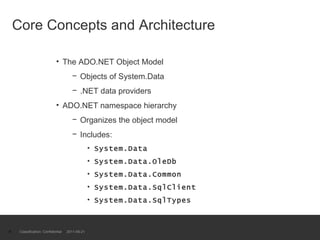
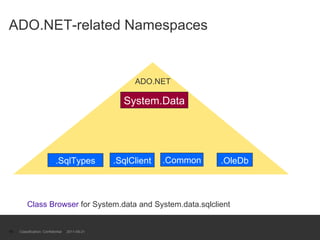
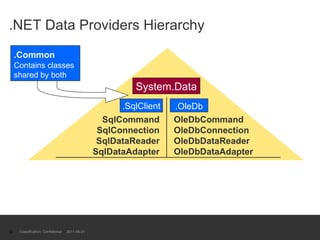
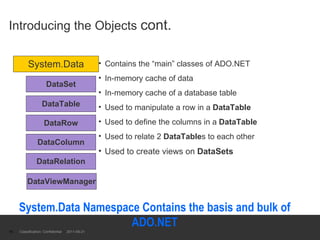
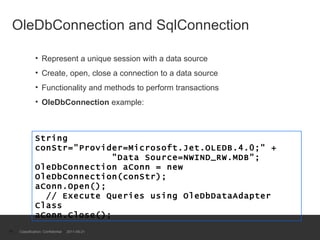
The document provides an introduction to ADO.NET architecture, including its benefits and core concepts. It discusses key ADO.NET objects like Connection, Command, DataReader, DataSet and DataAdapter. It explains how these objects are used to connect to databases, execute queries, retrieve and manage data in memory, and update data sources.