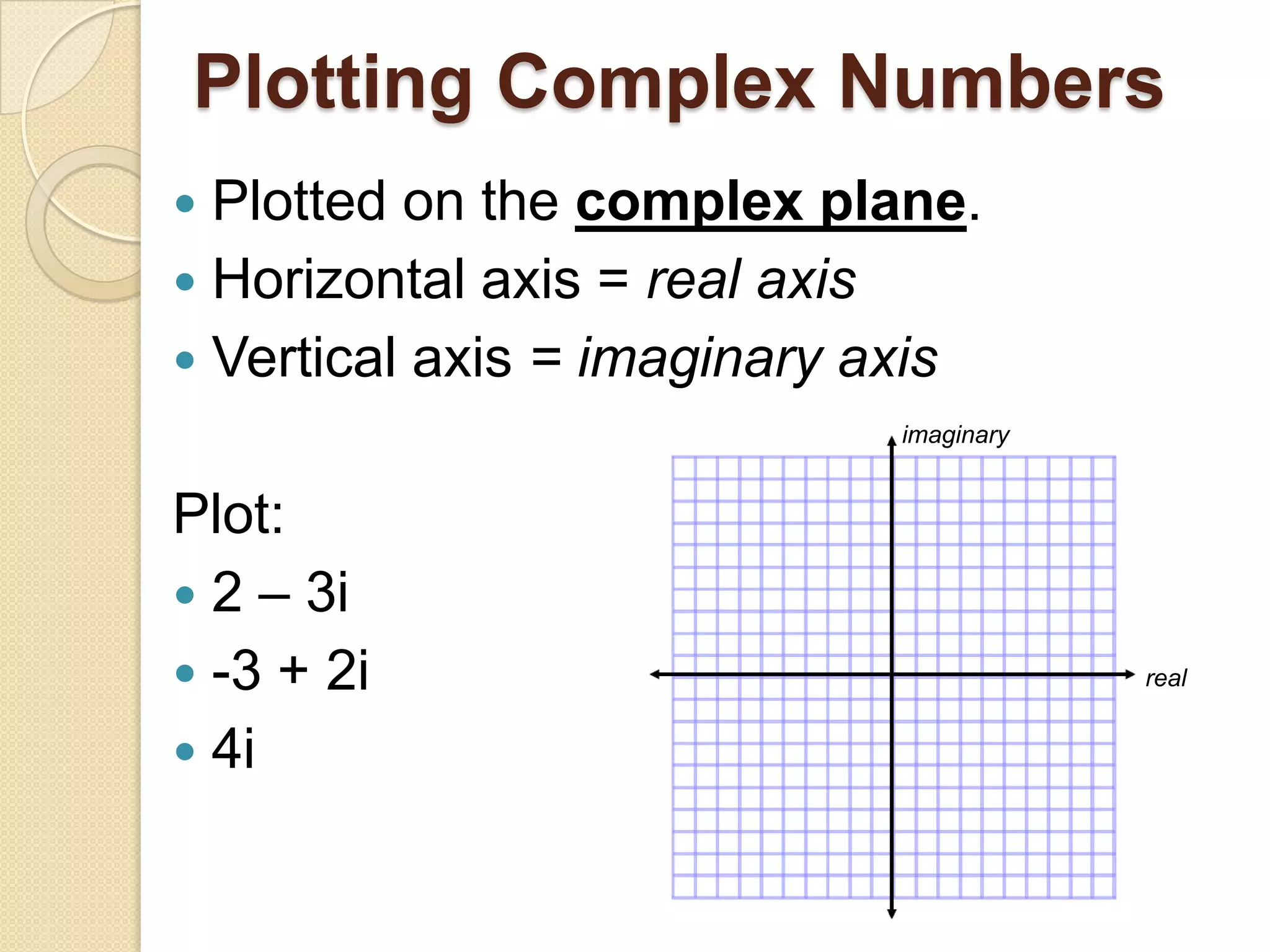
This document introduces complex numbers. It defines the imaginary unit i as the square root of -1, which allows quadratic equations with no real solutions, like x^2=-1, to be solved. Complex numbers have both a real part and an imaginary part in the form a + bi. They can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided by distributing terms and using properties of i such as i^2 = -1. Complex numbers are plotted on a plane with real numbers on the x-axis and imaginary numbers on the y-axis.