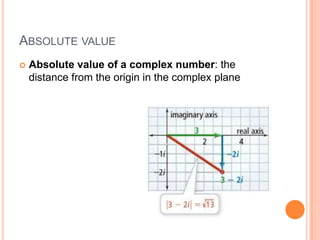
The document discusses complex numbers, including:
- Complex numbers are based on the imaginary unit i, where i^2 = -1.
- Complex numbers can be expressed as a + bi and graphed in the complex plane.
- Operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division can be performed on complex numbers by combining real and imaginary parts.
- Quadratic equations can have complex number solutions. Finding these solutions involves factoring or using the quadratic formula.