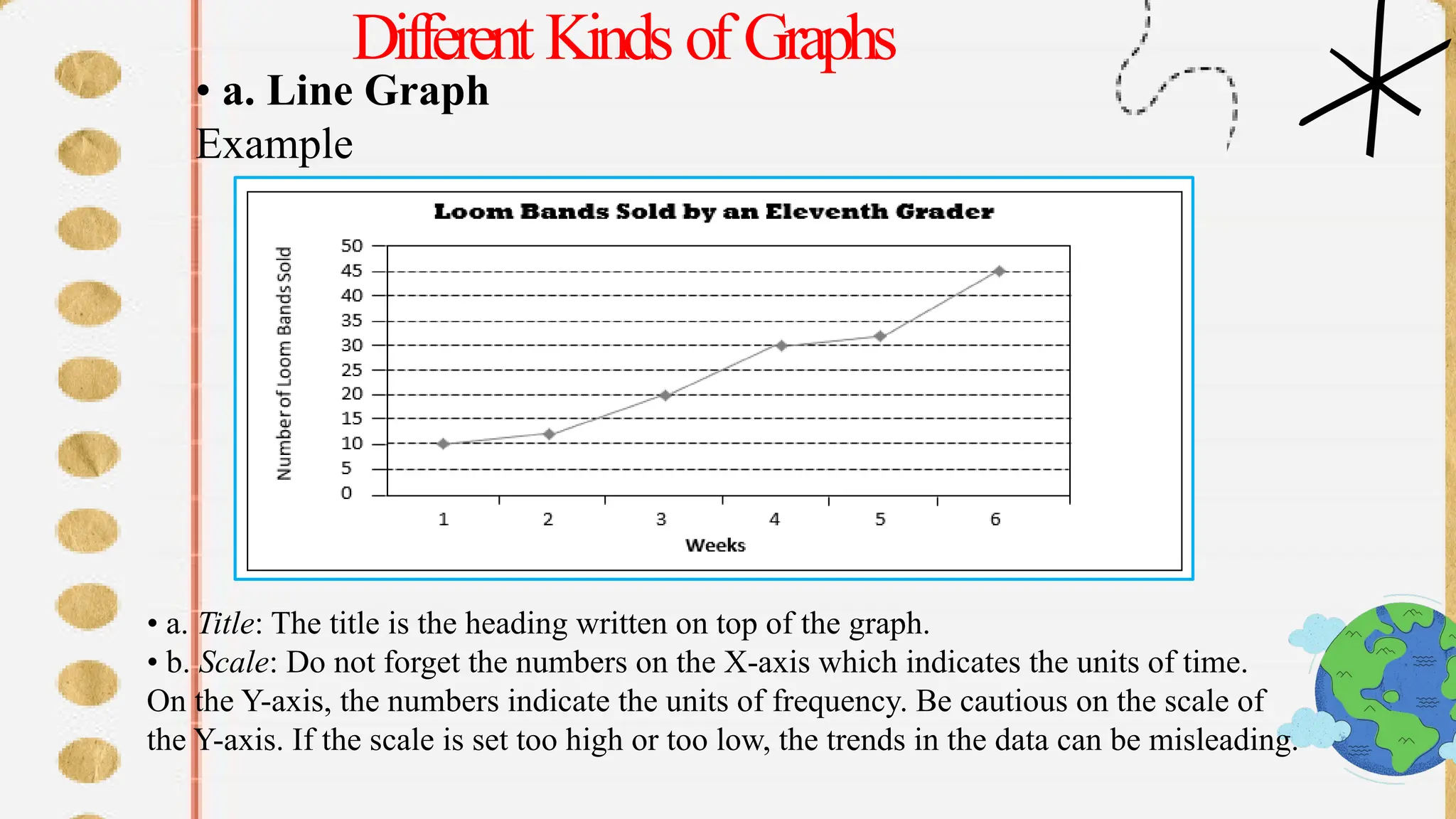
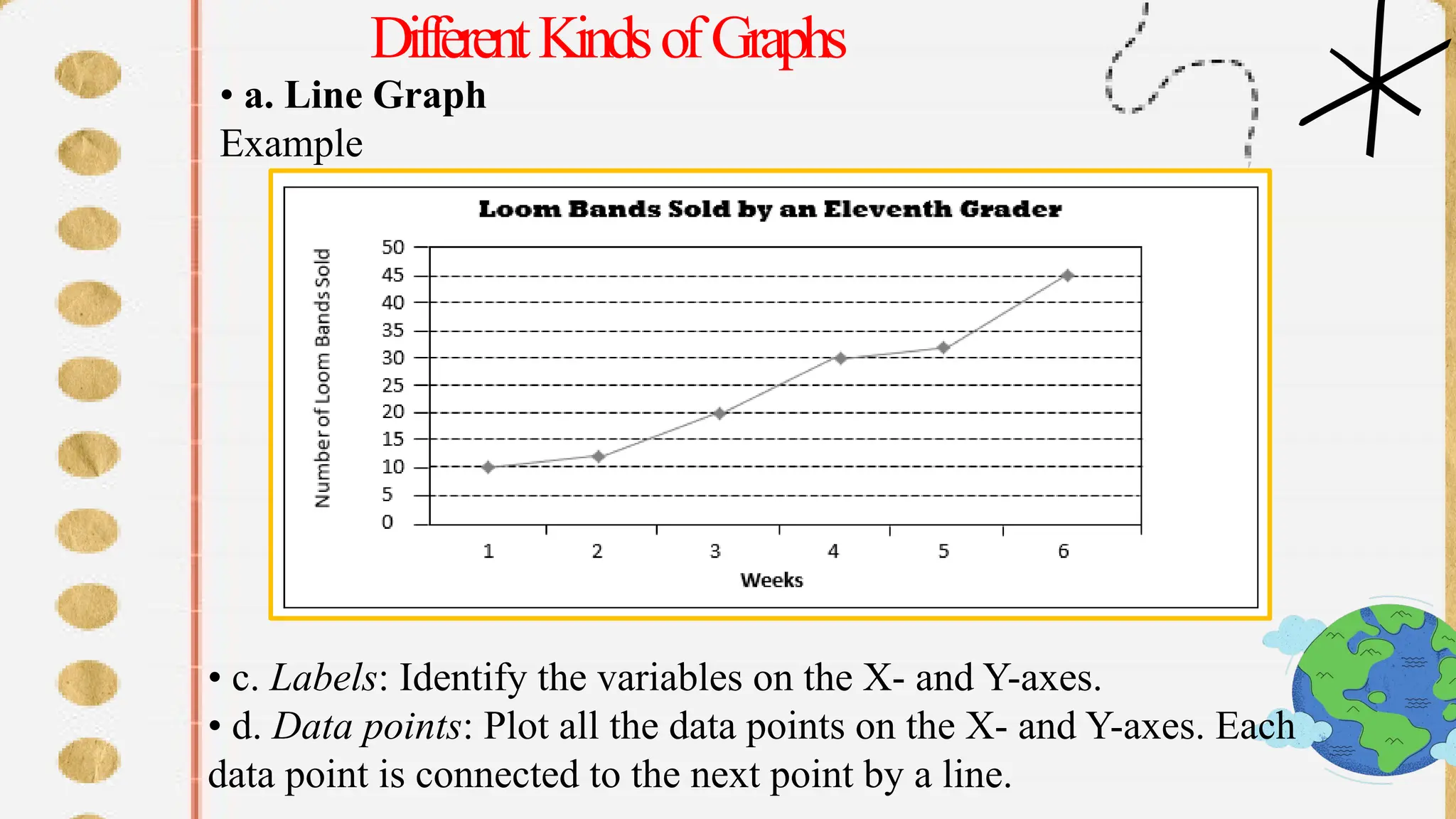
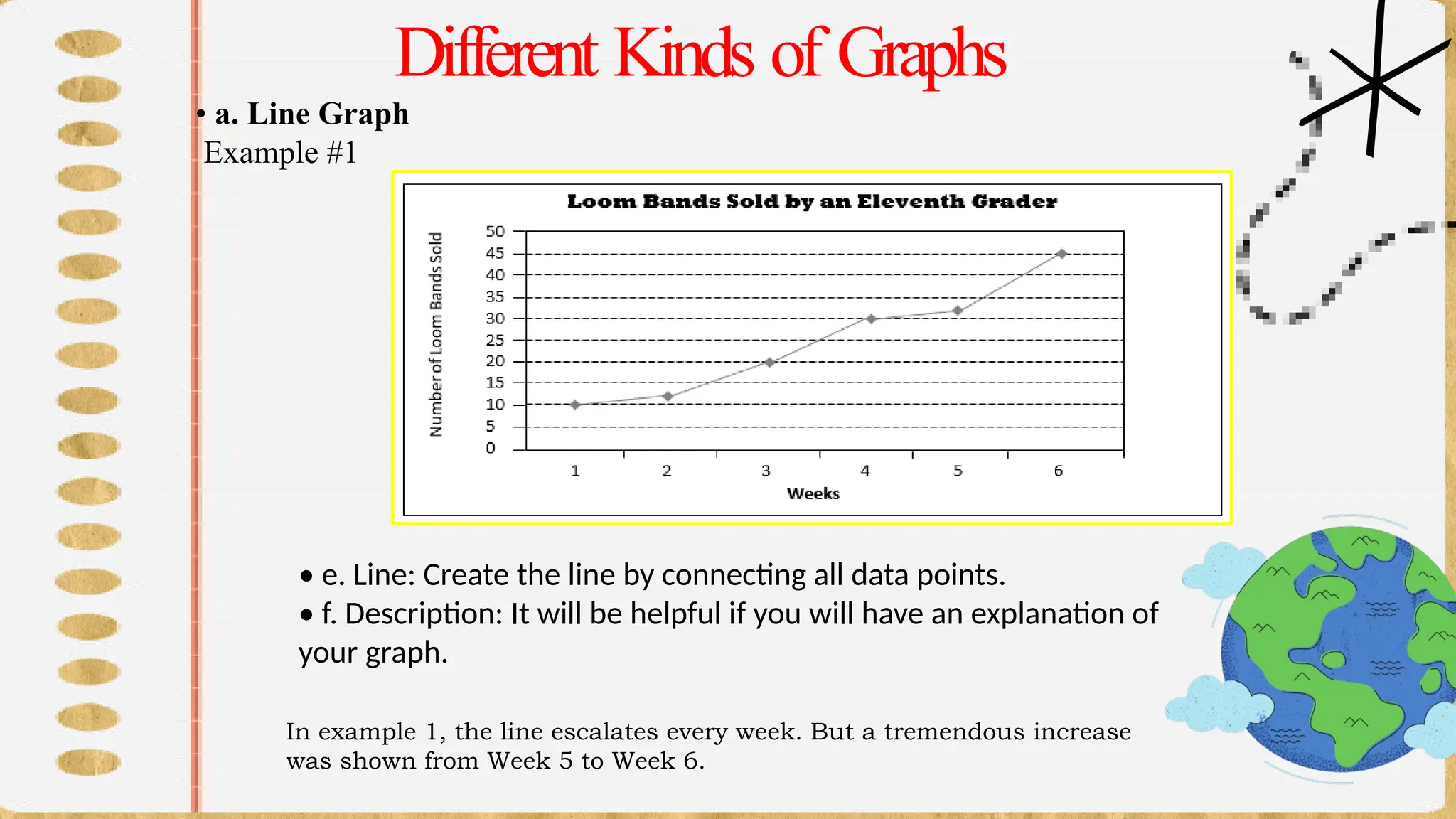
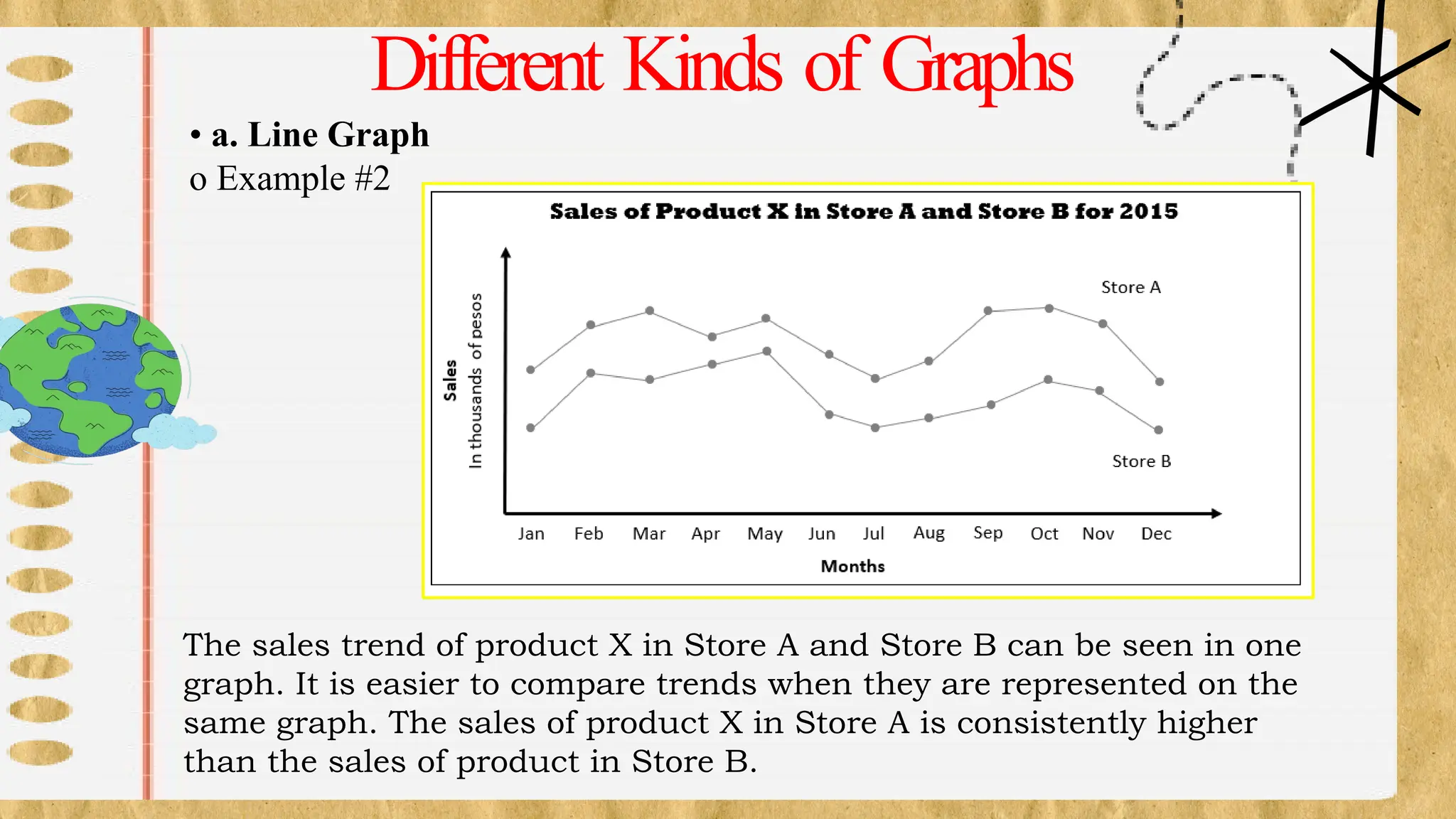
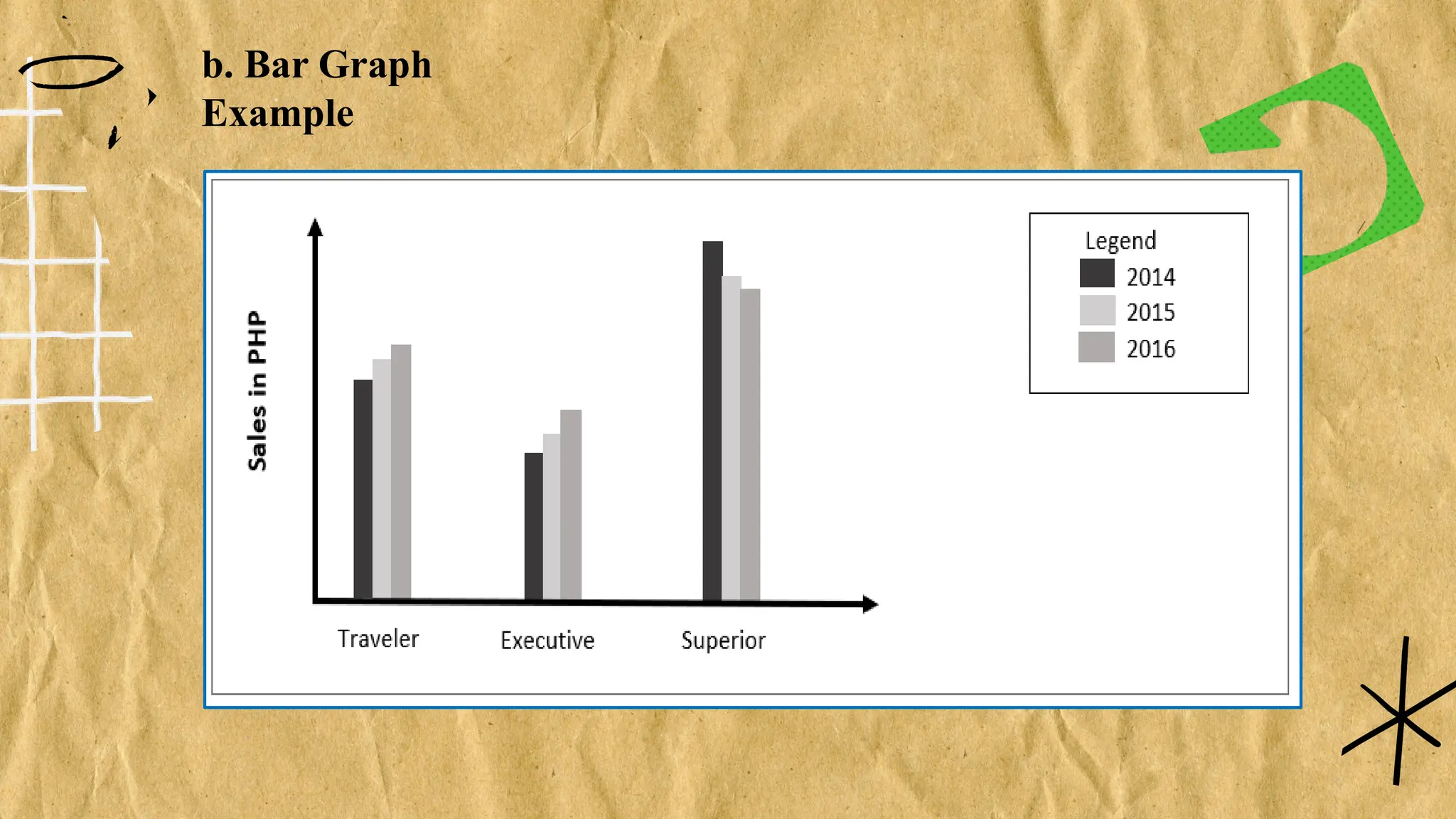
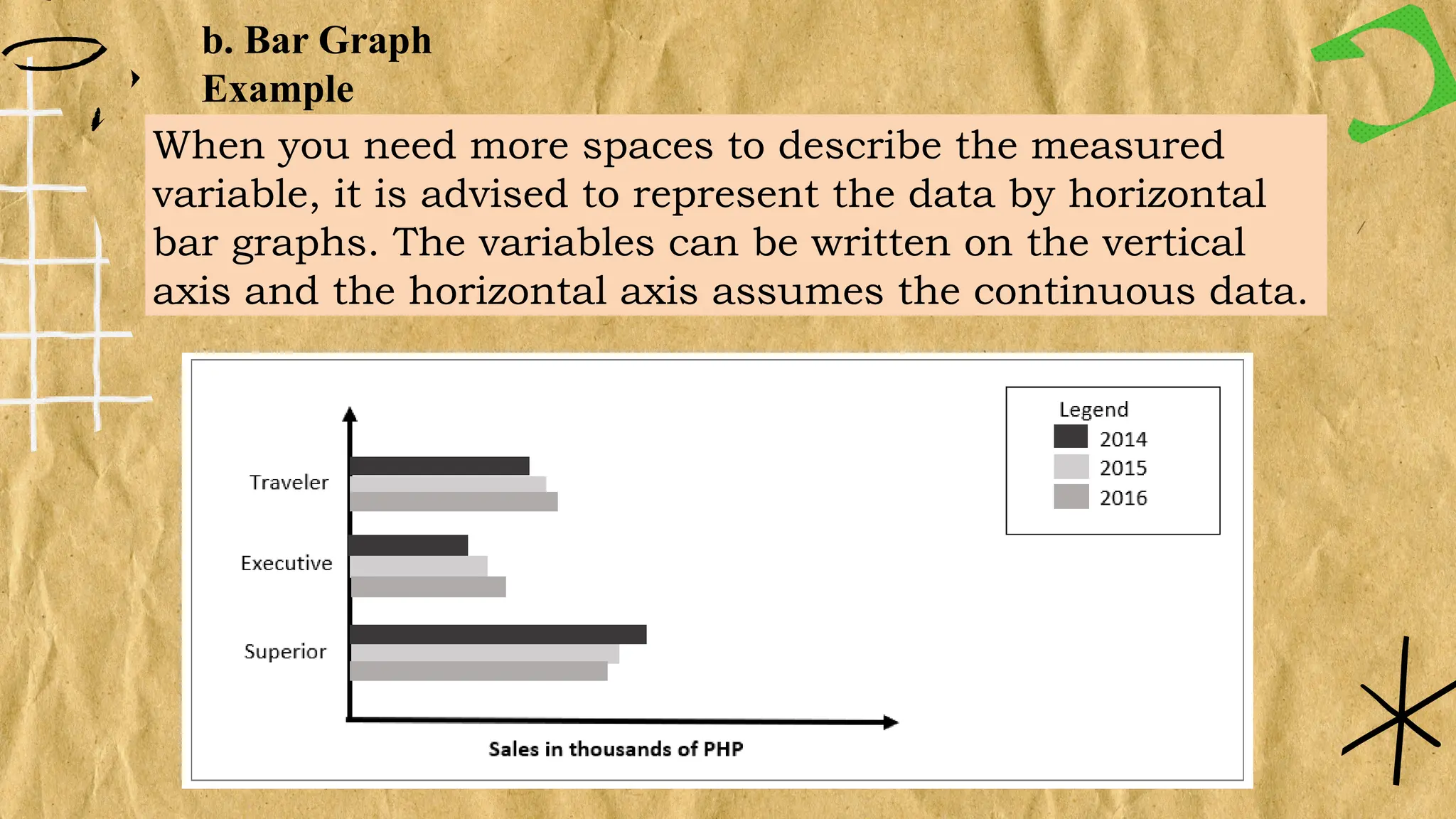
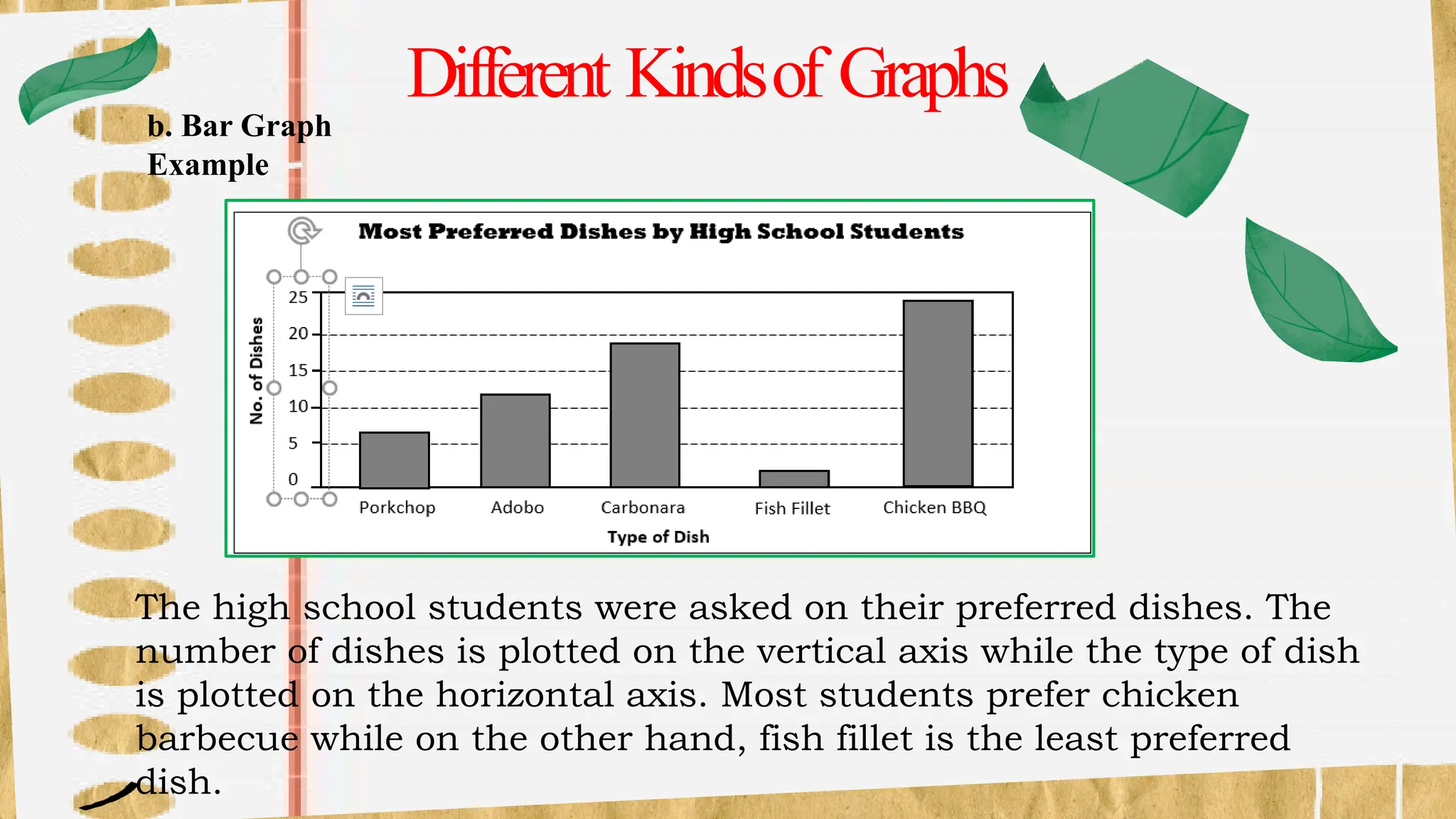
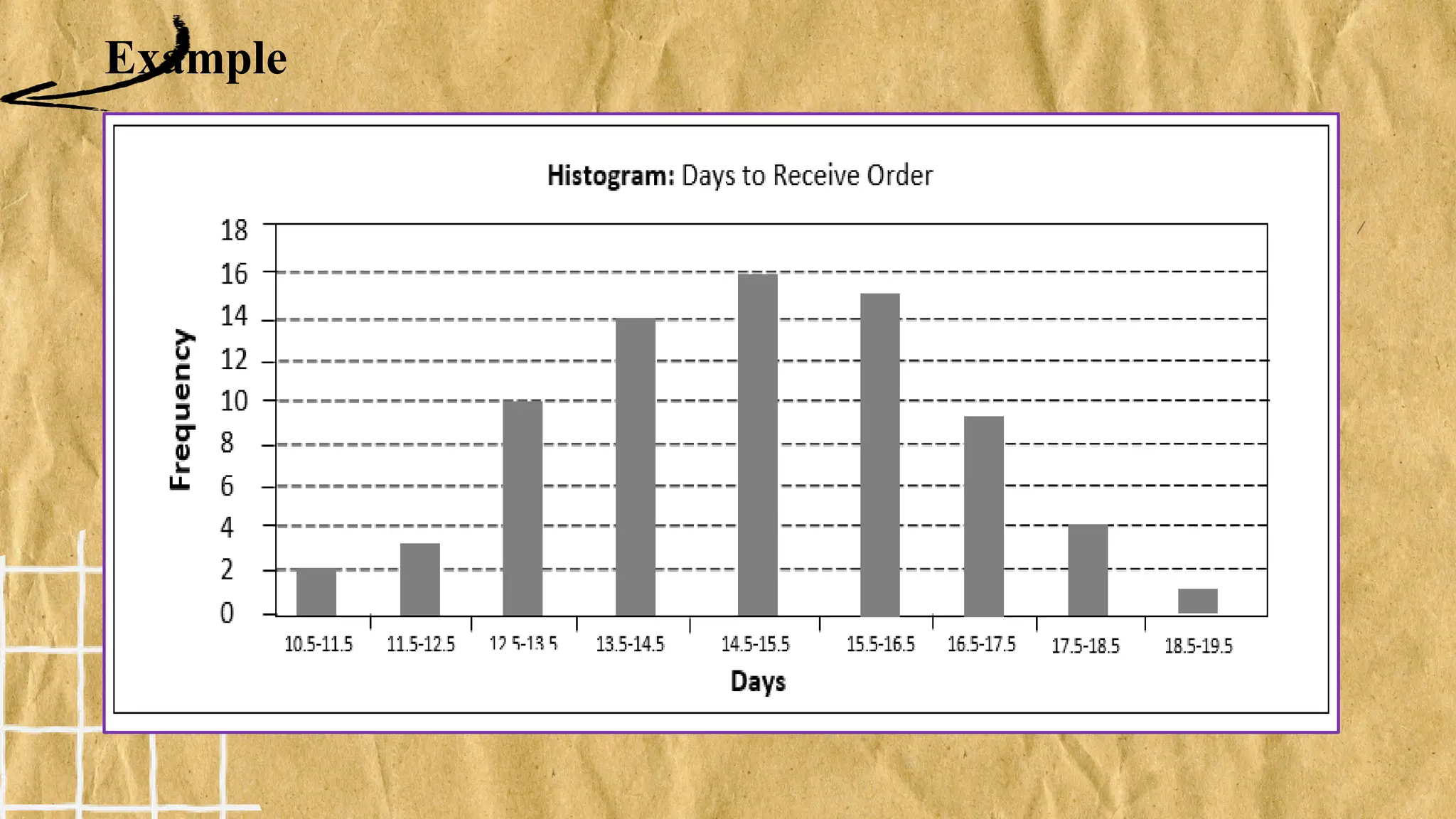
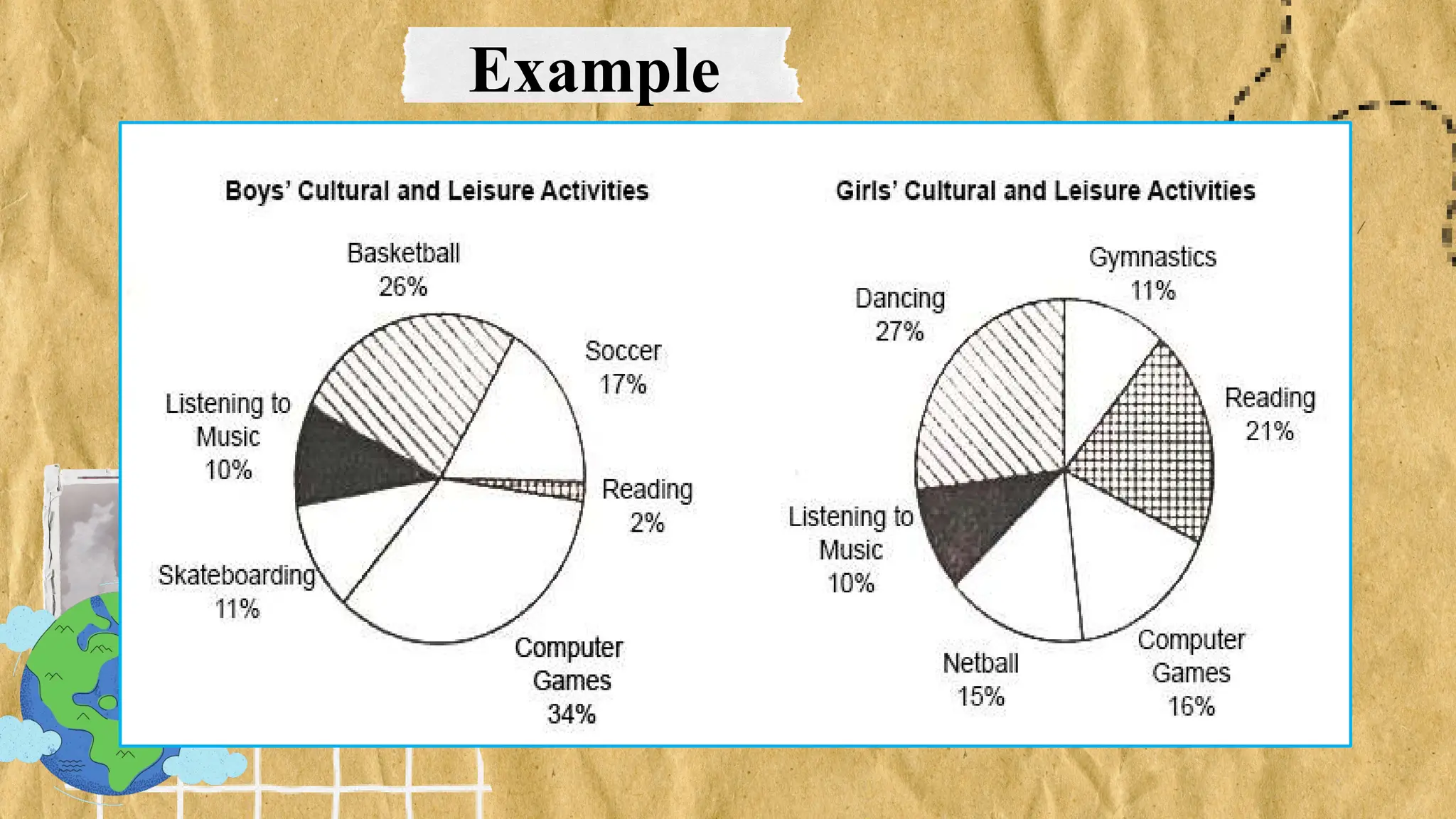
The document discusses various types of graphs for data presentation, emphasizing the importance of selecting the appropriate graph for different data sets. It covers line graphs, bar graphs, histograms, and pie charts, explaining their uses and how to interpret them effectively. Each graph type is illustrated with examples to demonstrate their application in conveying information effectively.