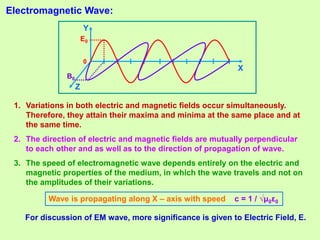
This document summarizes key concepts in wave optics, including:
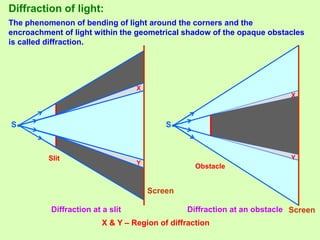
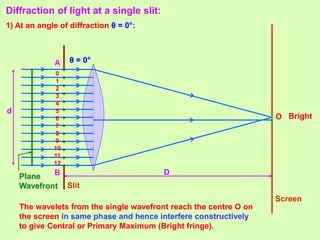
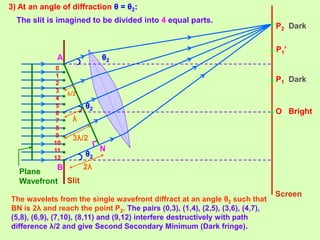
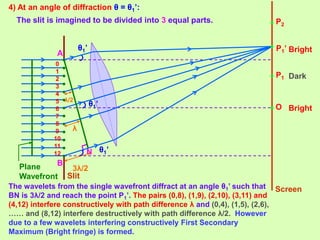
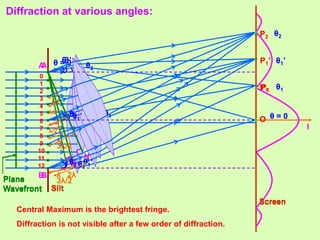
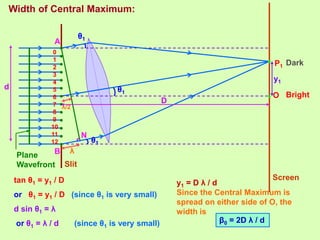
1. Diffraction occurs when light bends around obstacles and into regions of geometric shadows. Diffraction can be observed at a single slit, with a central bright fringe and alternating dark and bright fringes at increasing angles.
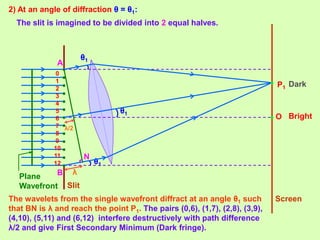
2. The theory of diffraction is based on interference between secondary wavelets. The angles of maxima and minima depend on the slit width and wavelength.
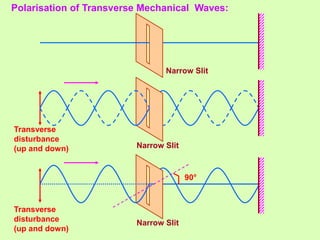
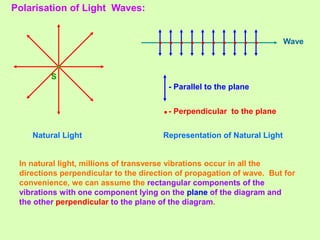
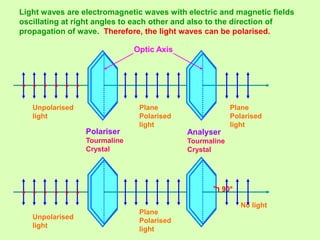
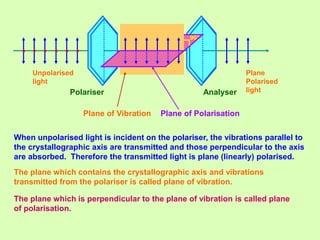
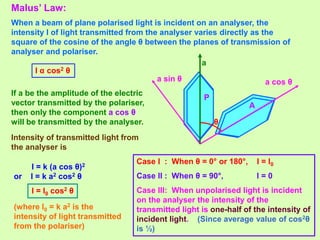
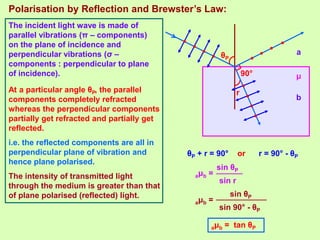
3. Polarization of light occurs as the electric field oscillates perpendicular to the propagation direction. Polarizers and analyzers can be used to produce and detect plane polarized light according to Malus' law.