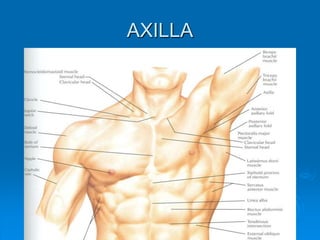
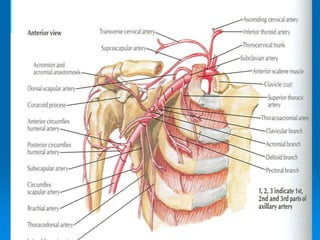
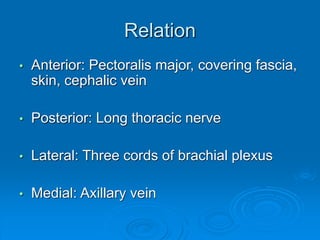
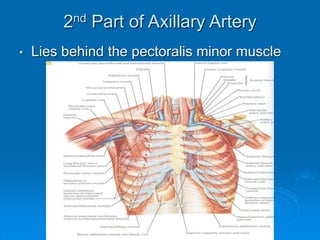
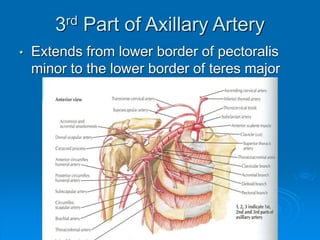
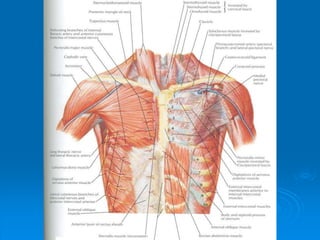
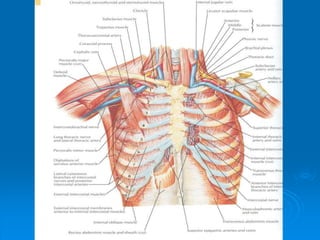
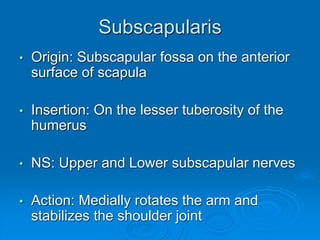
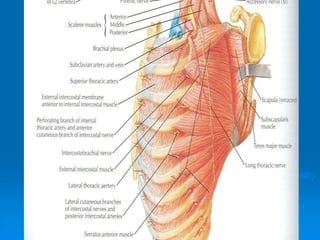
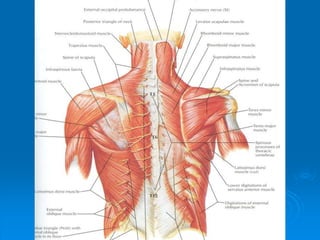
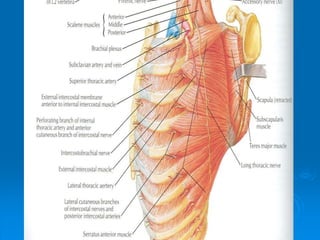
This document defines and describes the anatomy of the axilla region. It details the boundaries, contents, and structures found within the axilla, including nerves, blood vessels, muscles, and lymph nodes. Specifically, it outlines the apex and base boundaries, lists the anterior, posterior, medial and lateral walls, and notes the axillary artery and its branches that pass through.