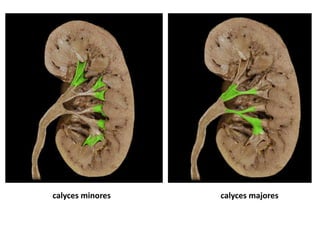
The document provides an overview of kidney, ureter, and bladder anatomy. It describes the location and structure of the kidneys, including their coverings, vasculature, and internal organization into cortex, medulla, pyramids, and papillae that drain into minor and major calyces. The ureters are described as retroperitoneal tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder is an infraperitoneal organ divided into regions that collects urine via ureteric openings in the trigone and empties via the urethra.