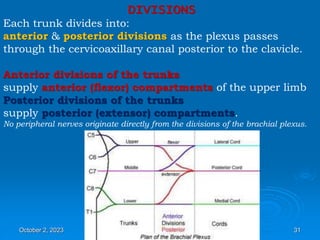
The axilla is a pyramid-shaped space between the upper arm and chest. It contains nerves, blood vessels, lymph nodes, and fat. The boundaries include the clavicle, ribs, and muscles. The brachial plexus forms in the neck and provides motor and sensory innervation to the upper limb. It gives off branches in the axilla including the nerves that form its three cords surrounding the axillary artery. These cords supply the different regions of the upper limb.