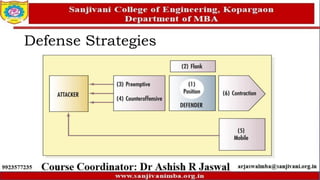
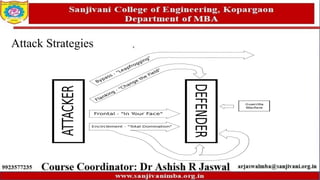
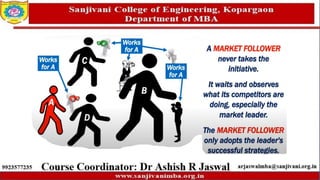
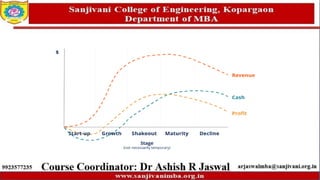
The document discusses various marketing strategies, focusing on offensive and defensive competitive strategies for different market roles such as market leaders, challengers, followers, and nichers. It outlines the characteristics and challenges of mature and declining markets, along with strategic options for revitalization and survival in hostile market conditions. Key strategies include differentiation, cost reduction, target marketing, and adapting to market dynamics to improve profitability.