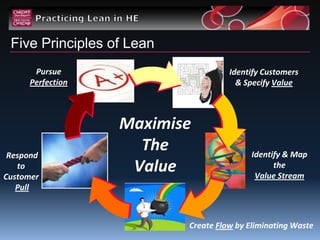
The document discusses adopting Lean principles to improve leadership skills. It outlines the five principles of Lean: identify customers and specify value, identify and map the value stream, create flow by eliminating waste, respond to customer pull, and pursue perfection. Adopting Lean will help continuously improve work and ensure everything adds value. Delegates will learn about the principles, identify wasteful activities, and understand how Lean enhances leadership. Examples show how Lean reduced time, failure demand, and increased capacity and satisfaction at Cardiff University. Personal reflection encourages starting small and thinking big to implement sustained change.