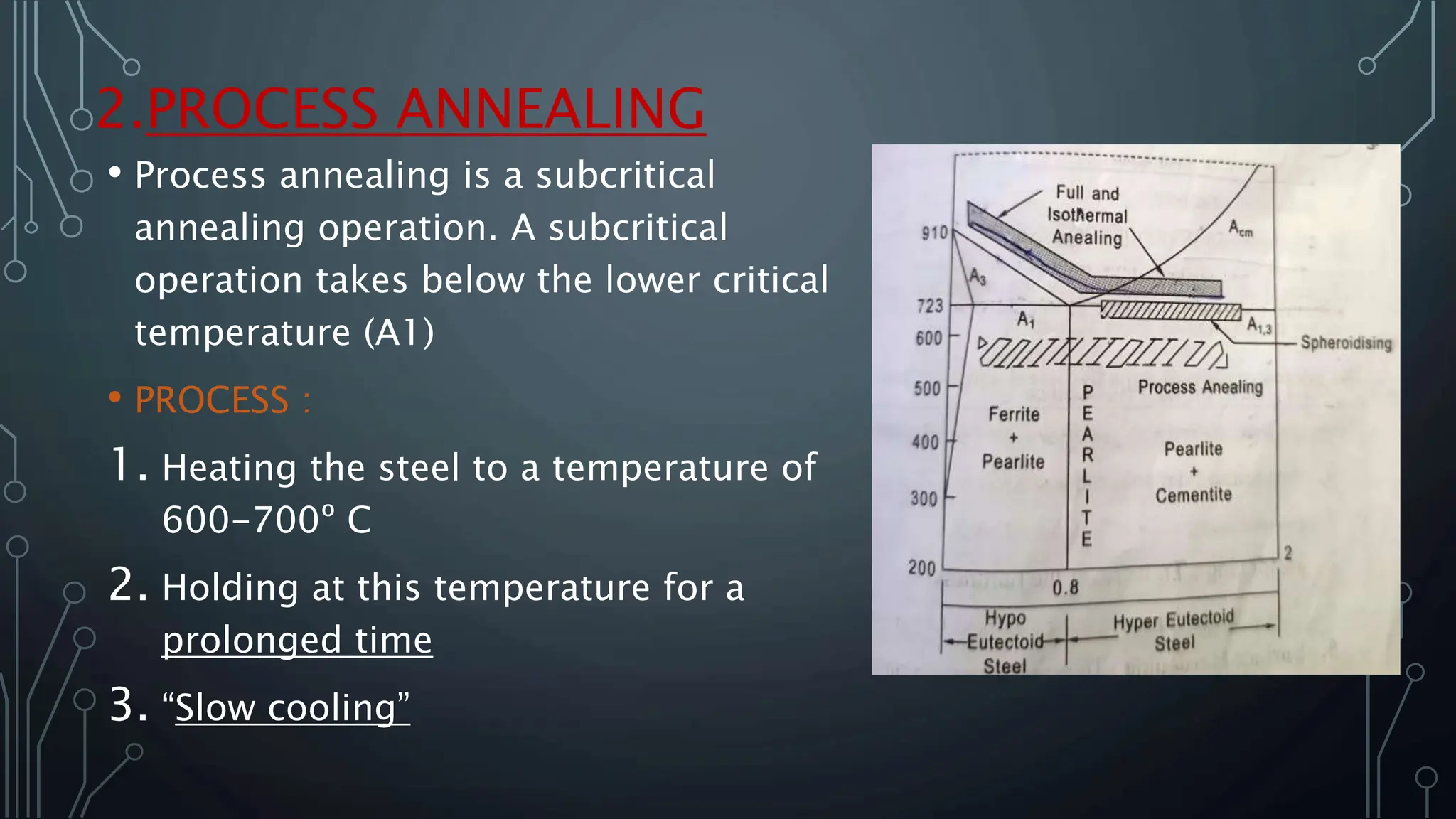
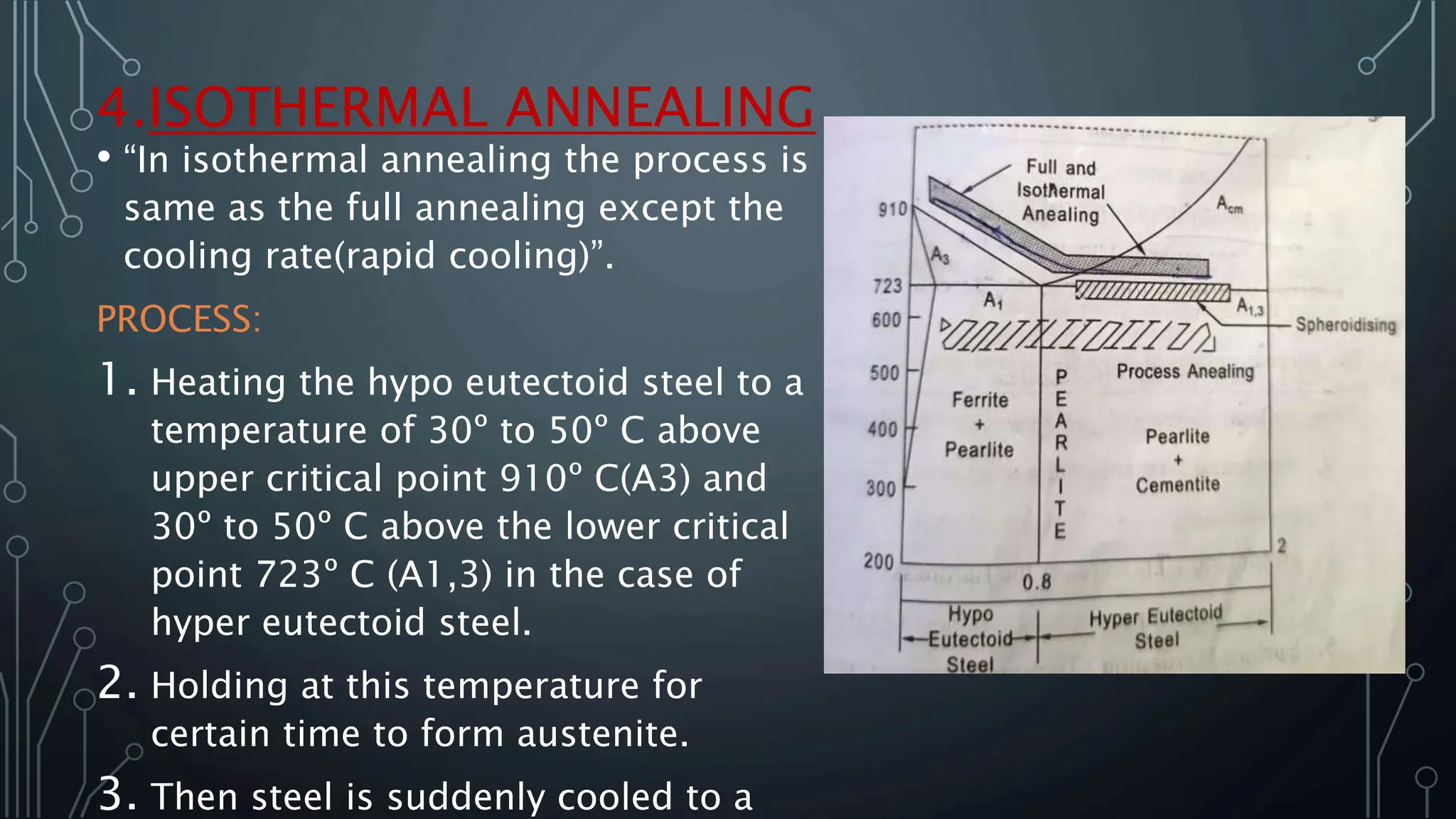
The document provides an overview of heat treatment processes for metals, which involve heating and cooling to alter mechanical properties for improved usability and safety. It describes various types of heat treatments, such as annealing, normalizing, hardening, tempering, and spheroidizing, with a focus on the annealing process, which softens steel and enhances its properties. Specific annealing methods are detailed, including full annealing, process annealing, spheroidizing annealing, and isothermal annealing, along with their purposes and processes.