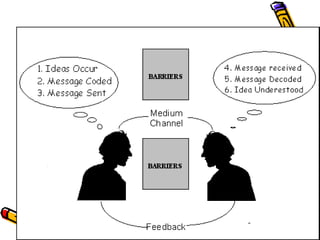
Communication barriers can be social, psychological, cultural, physiological, related to the system design, physical, or related to the receiver. Social barriers include factors like gender, age, race, socioeconomic class, and education level. Psychological barriers involve attitudes, perceptions, emotions, motivations, and ego. Cultural barriers stem from differences in language, norms, values, beliefs, and traditions. Physiological barriers encompass health issues, disabilities, and skills. System design barriers relate to organizational structure and information systems. Physical barriers consist of environmental factors, distractions, and settings. Barriers related to receivers include absenteeism, domination of discussion, silence, and negative attitudes. Overcoming communication barriers requires understanding their various sources and adapting communication