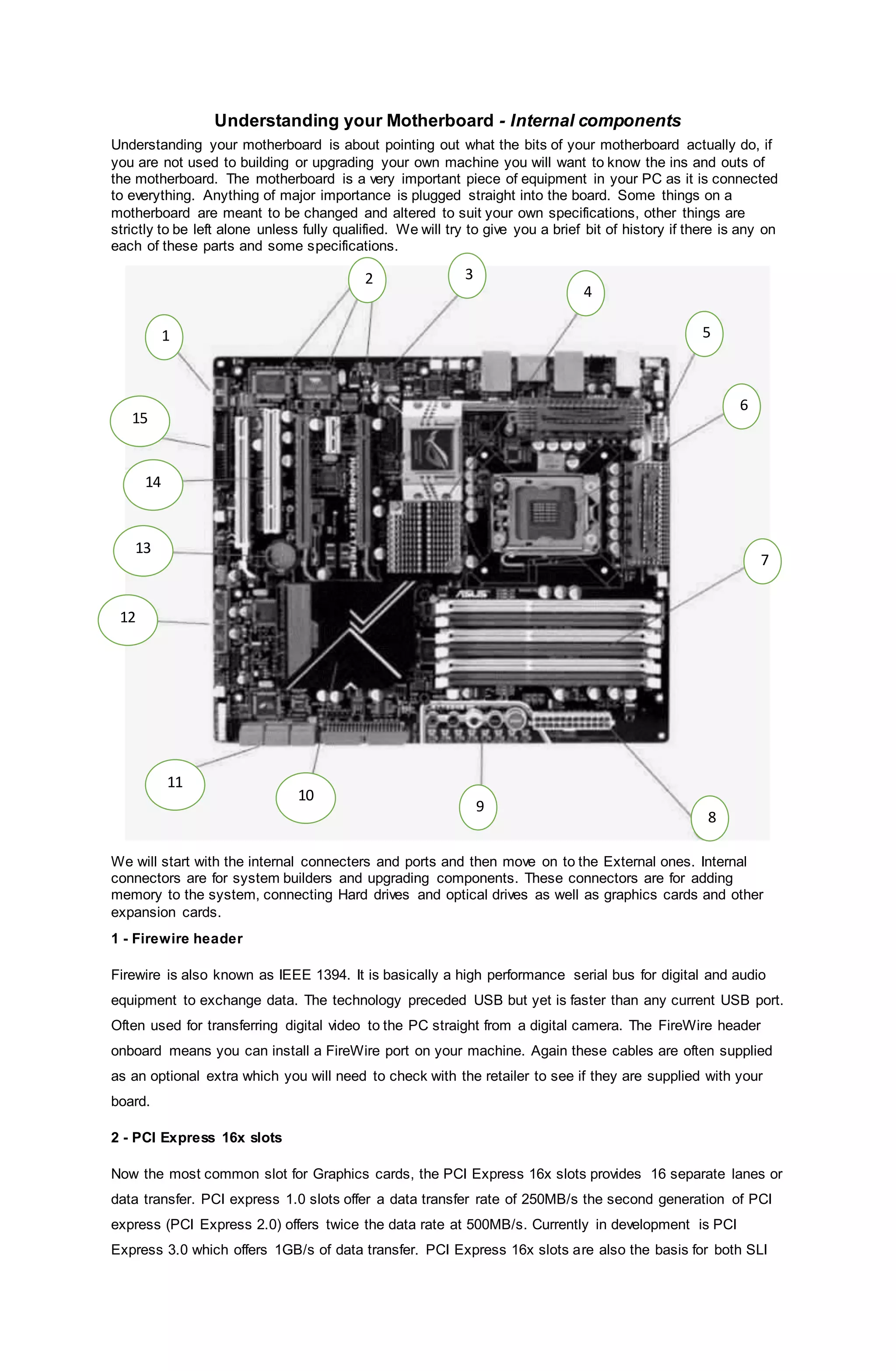
The motherboard is the central component of a PC that connects all other major components. It contains various internal connectors for components like the CPU, memory, storage drives, graphics cards, and expansion slots. Understanding what each connector is used for helps with building and upgrading a PC. The document discusses different internal connectors on motherboards like the CPU socket, memory slots, power connectors, and various ports.