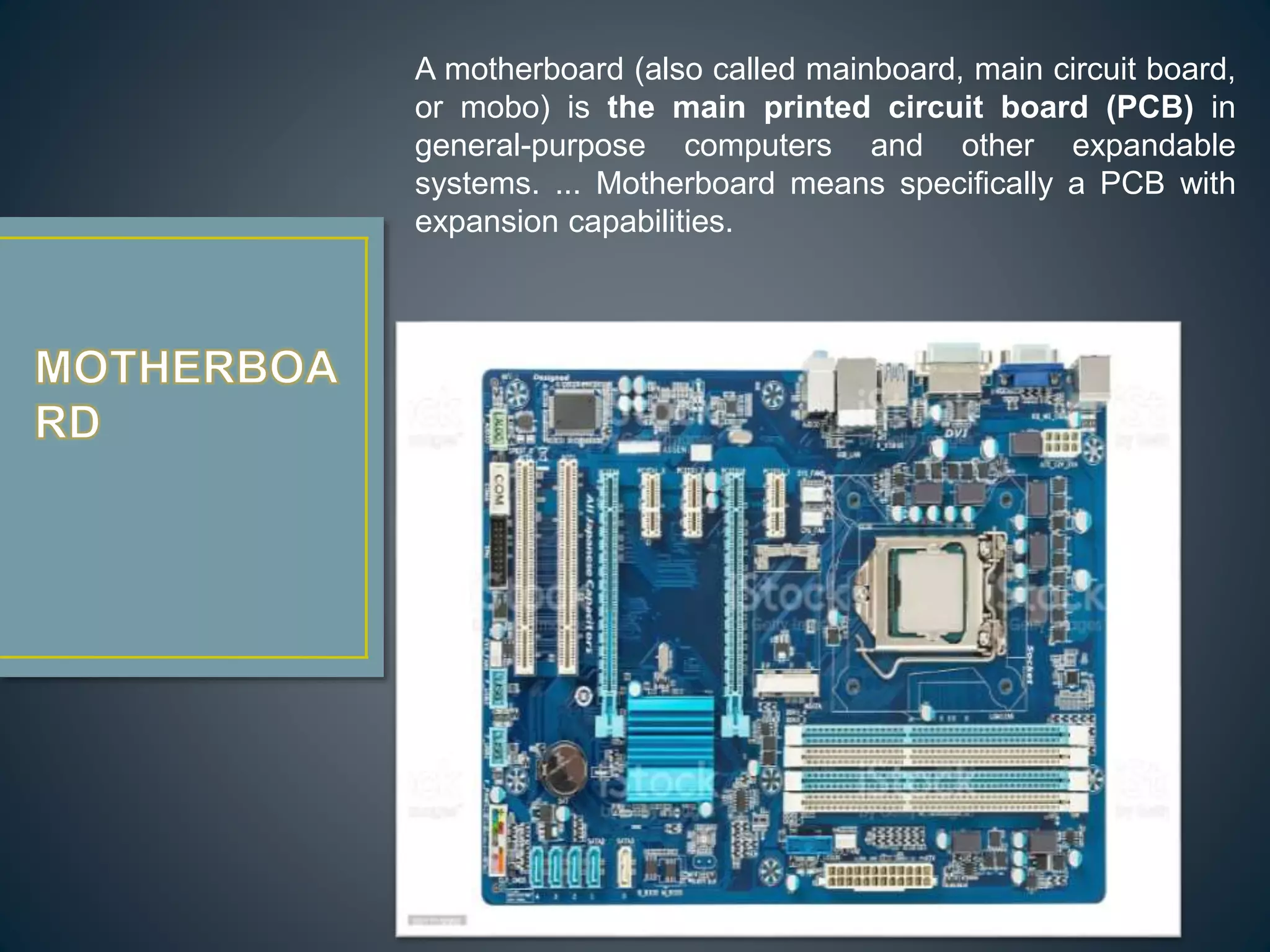
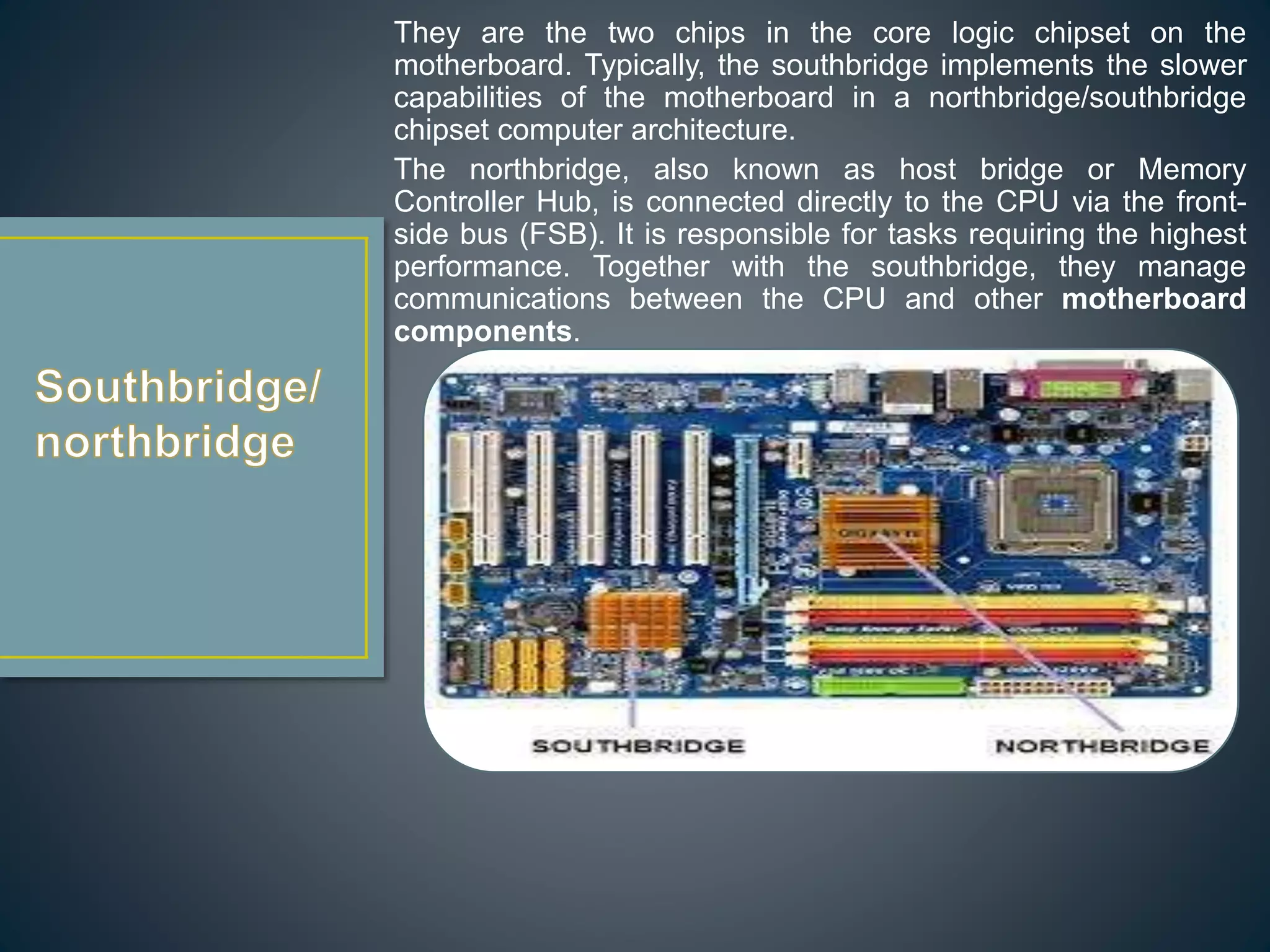
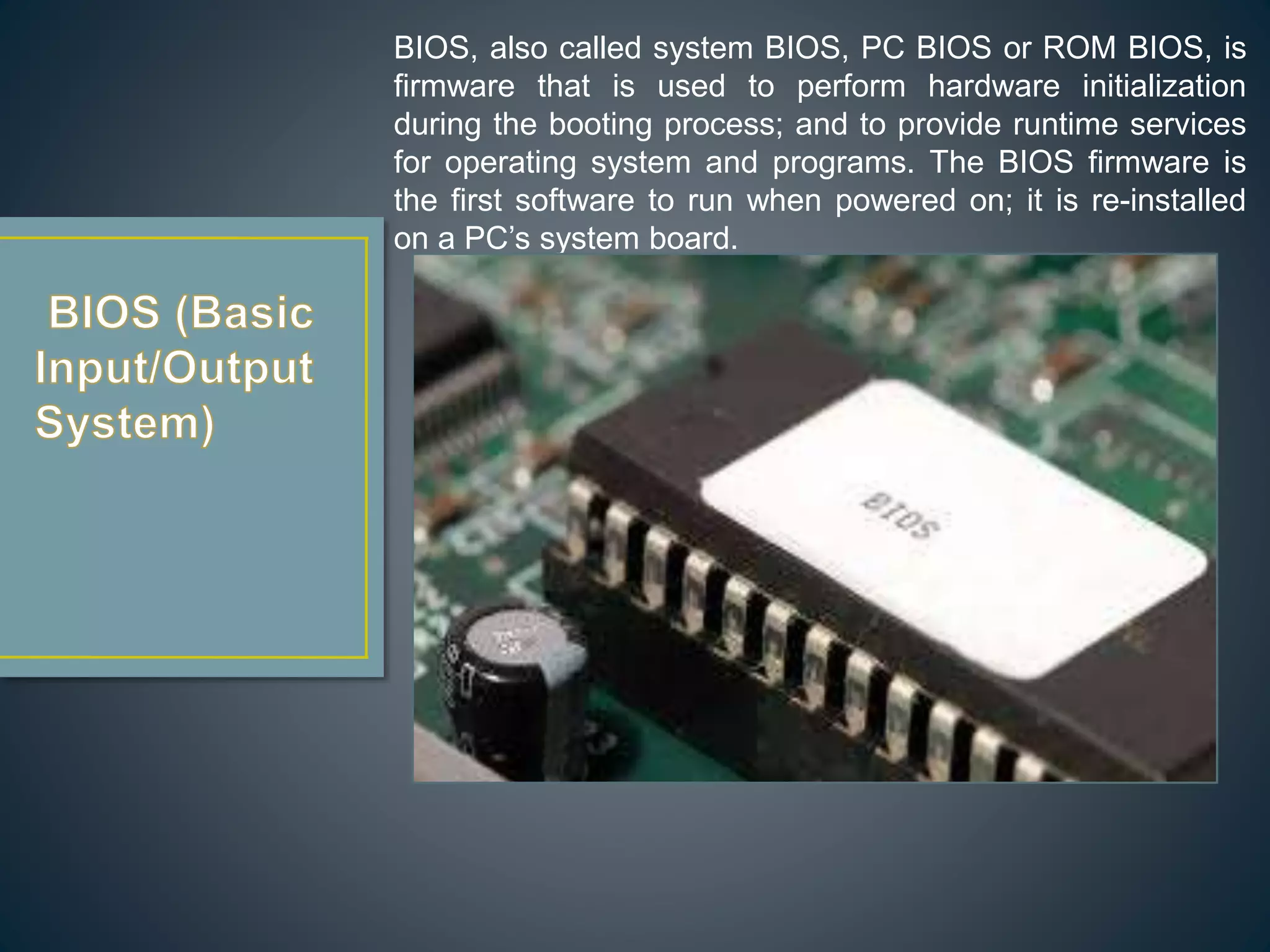
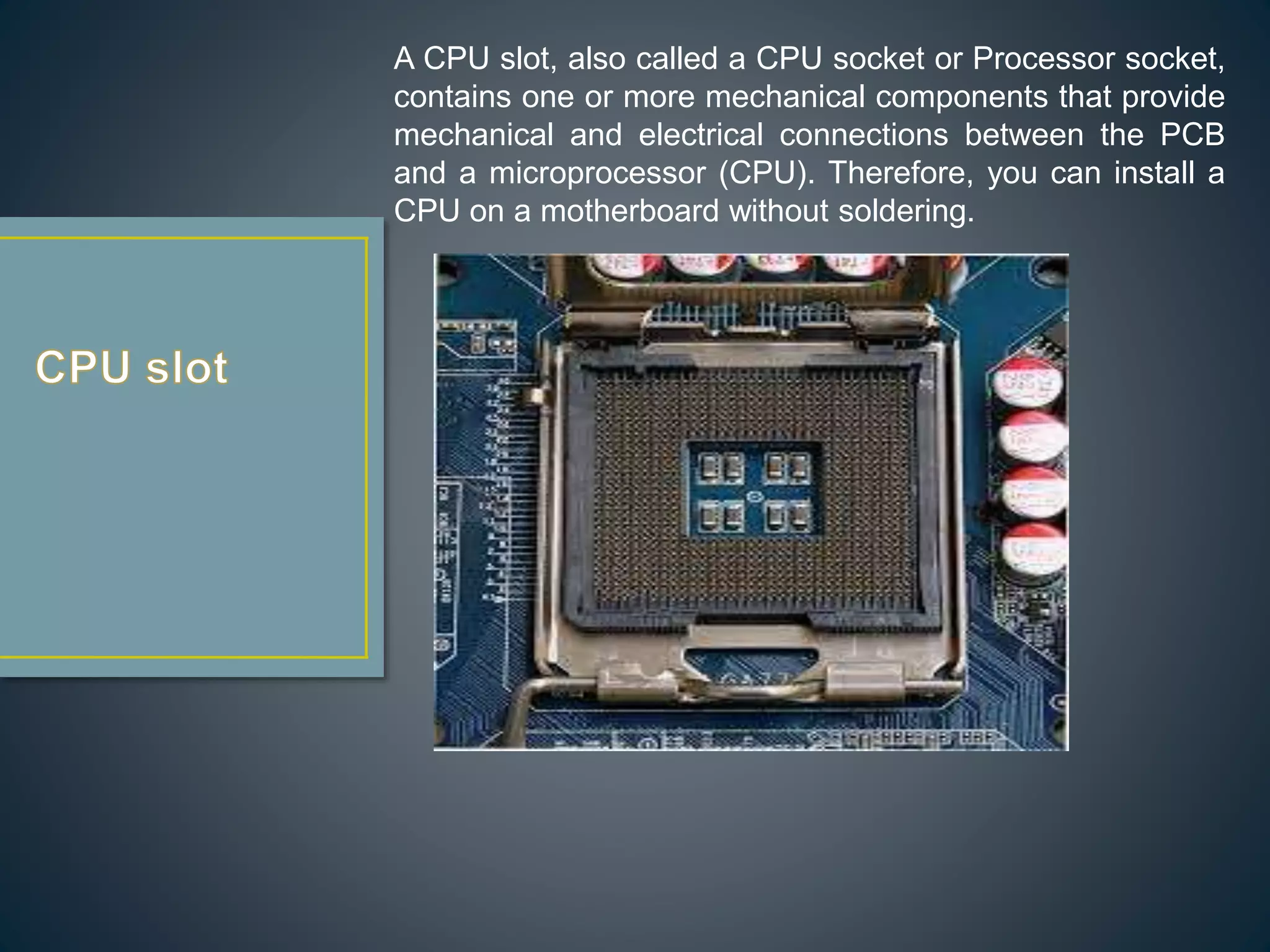
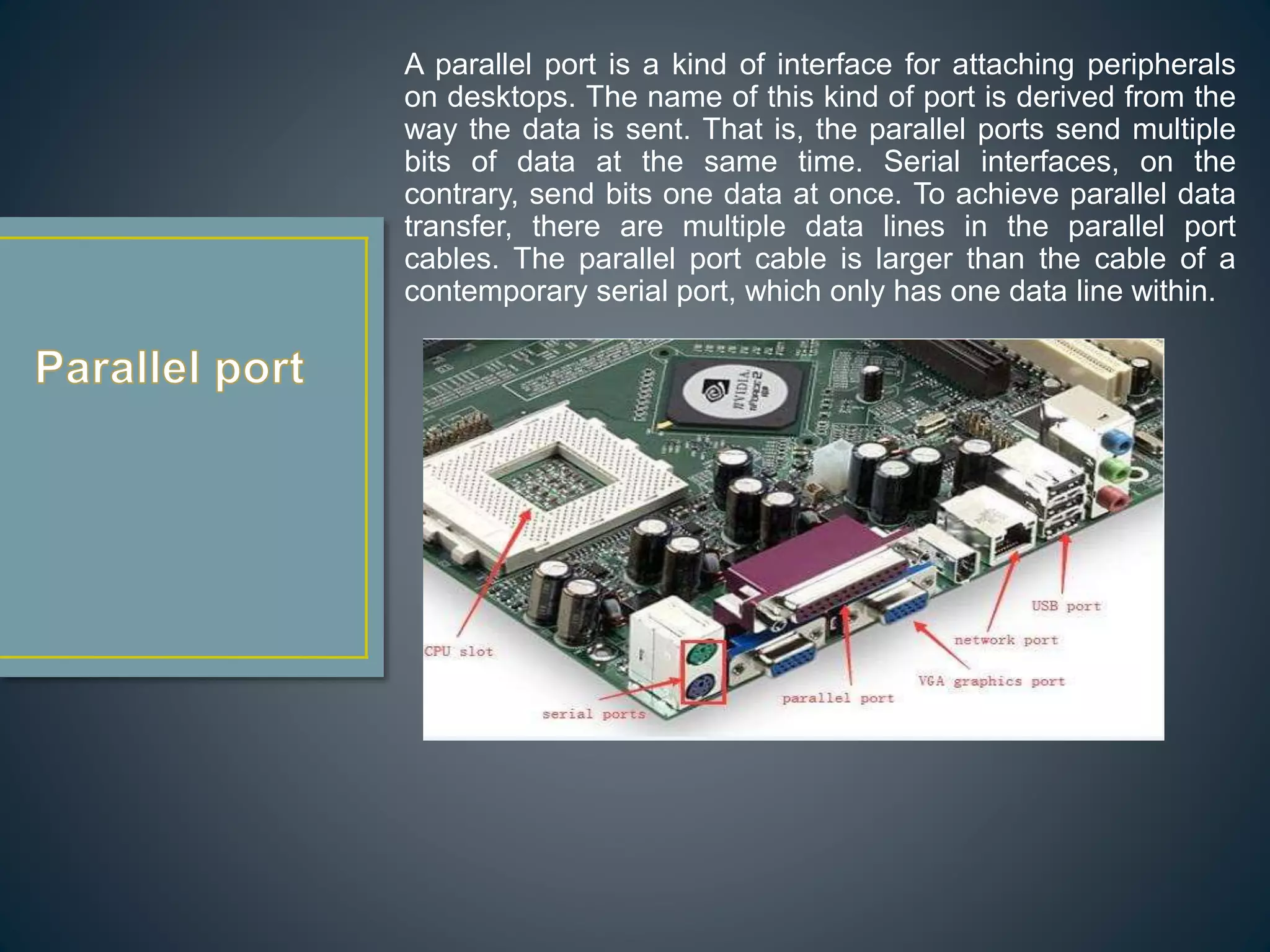
The CPU executes instructions to run programs and performs basic logic, arithmetic, and input/output operations. A motherboard is the main circuit board that contains the CPU and connections for components like RAM, graphics cards, hard drives, and ports. RAM is a type of memory that can be quickly written and read from, and is used to store active programs and data.