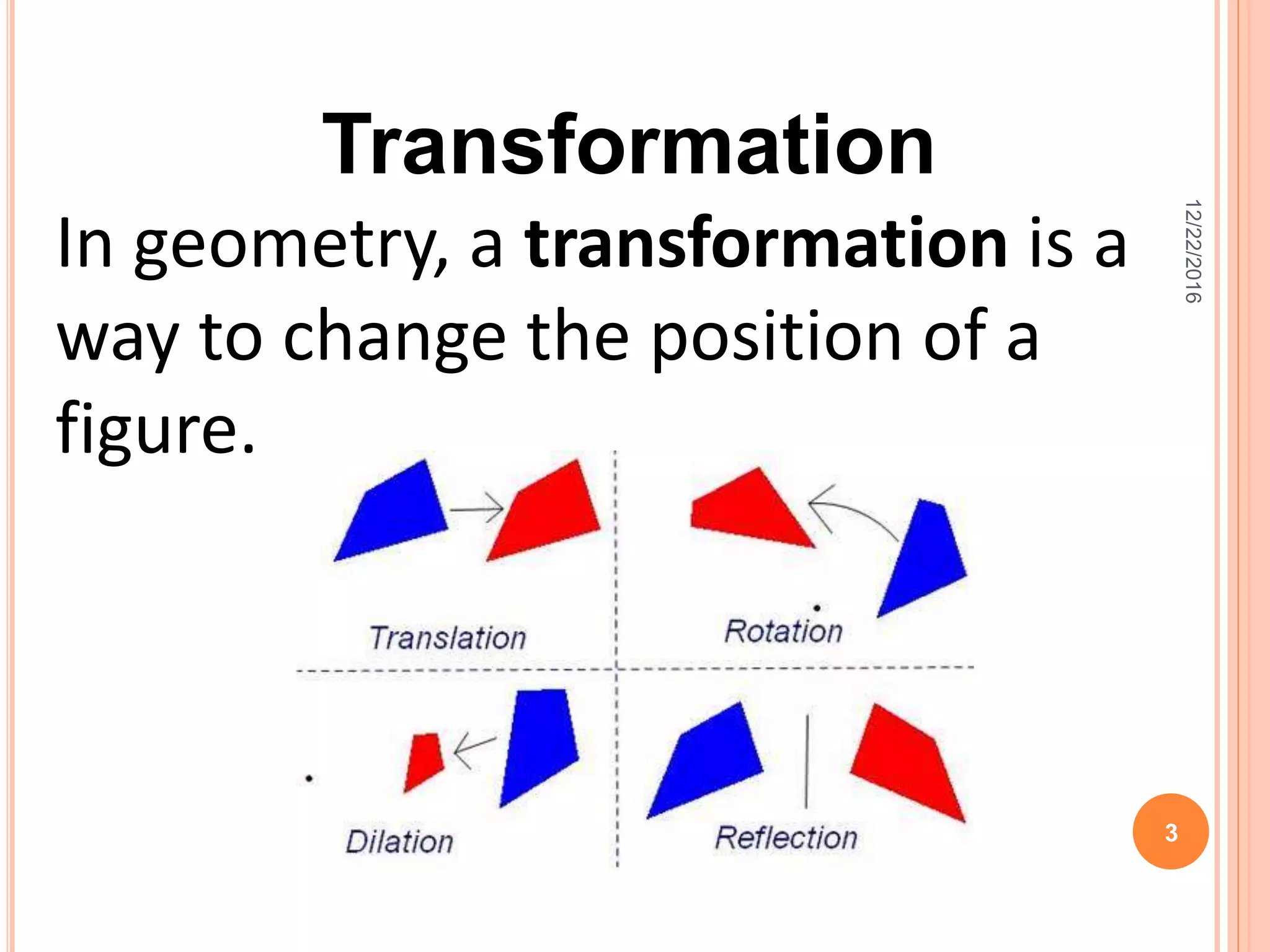
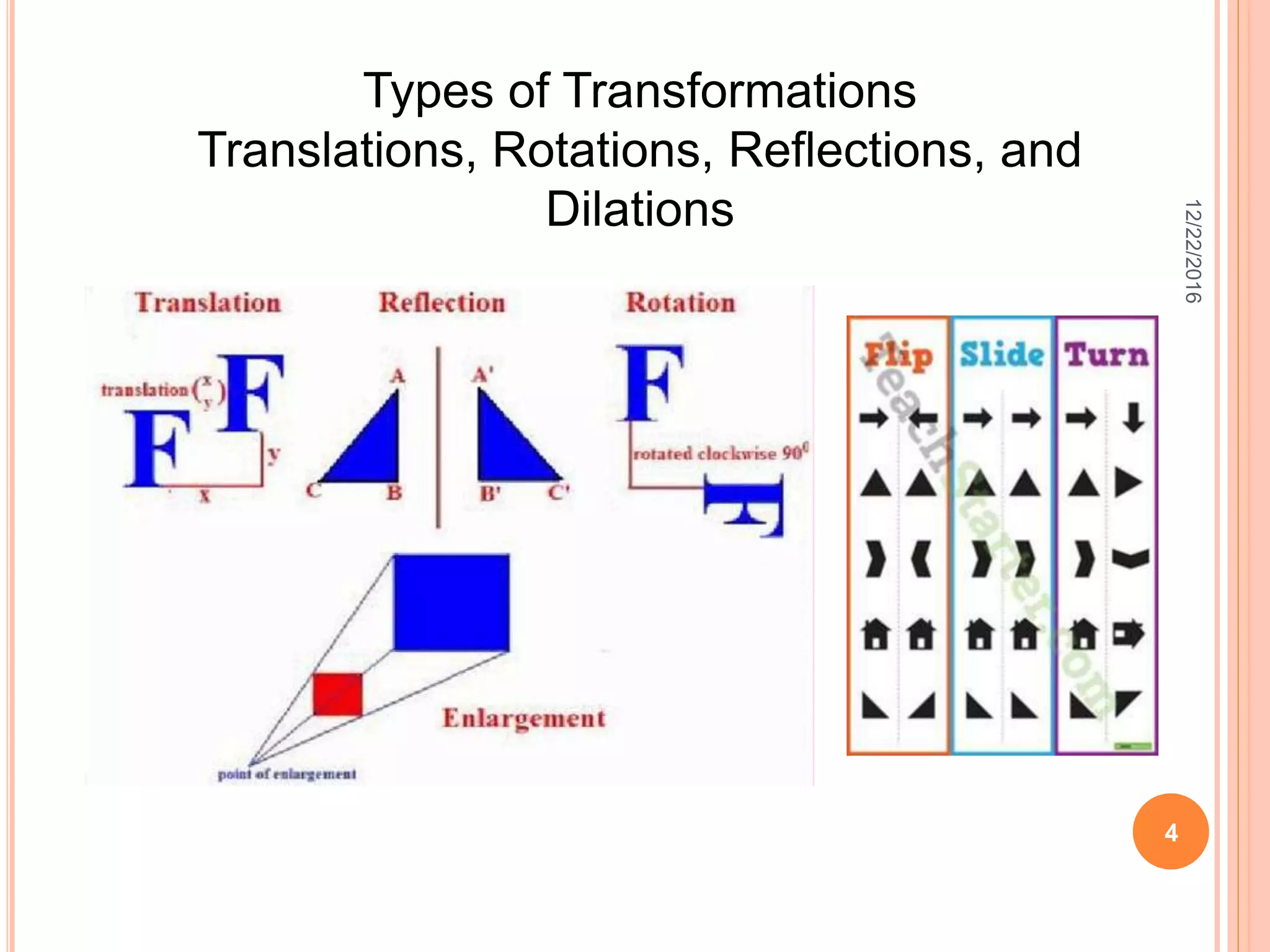
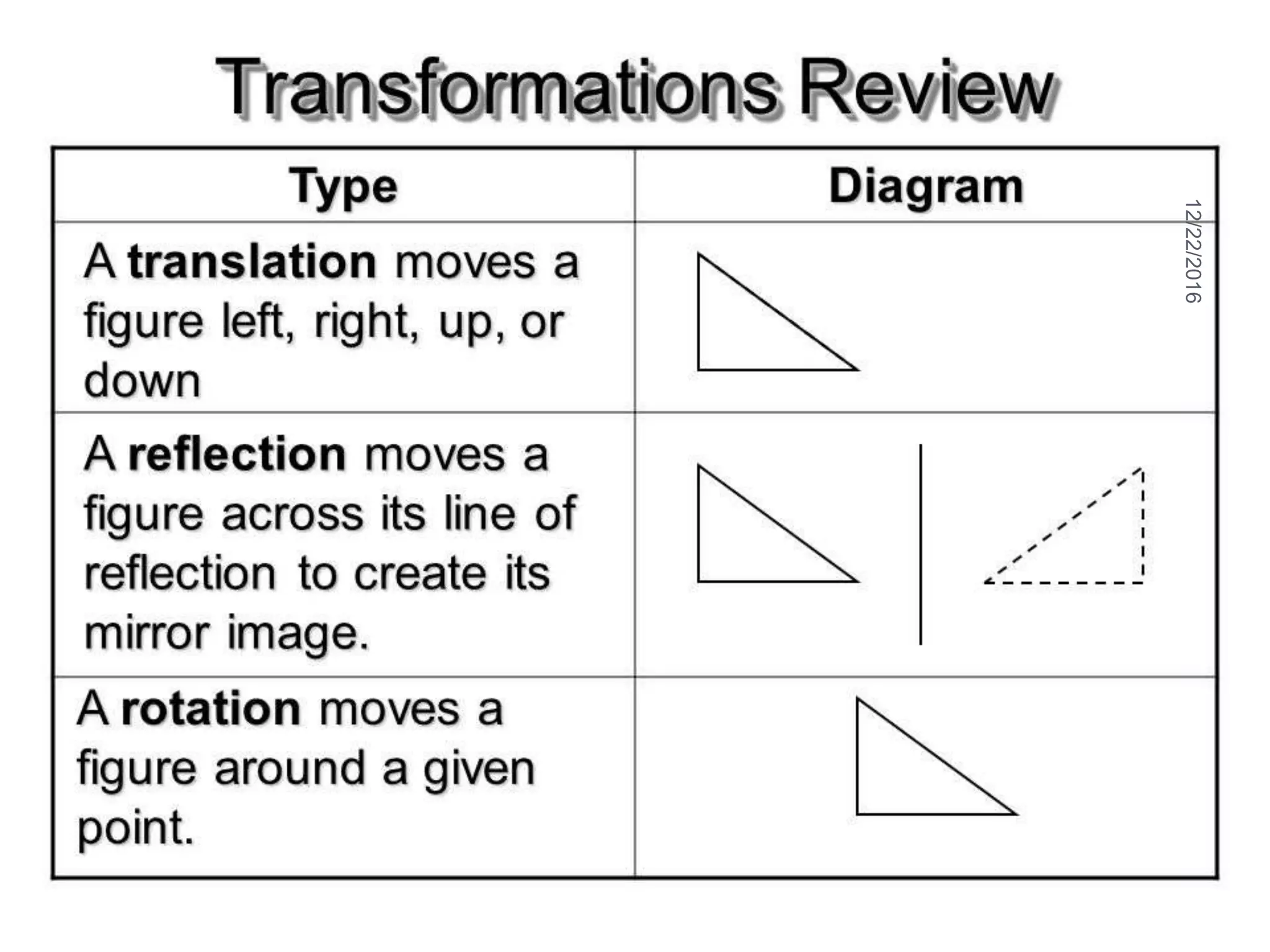
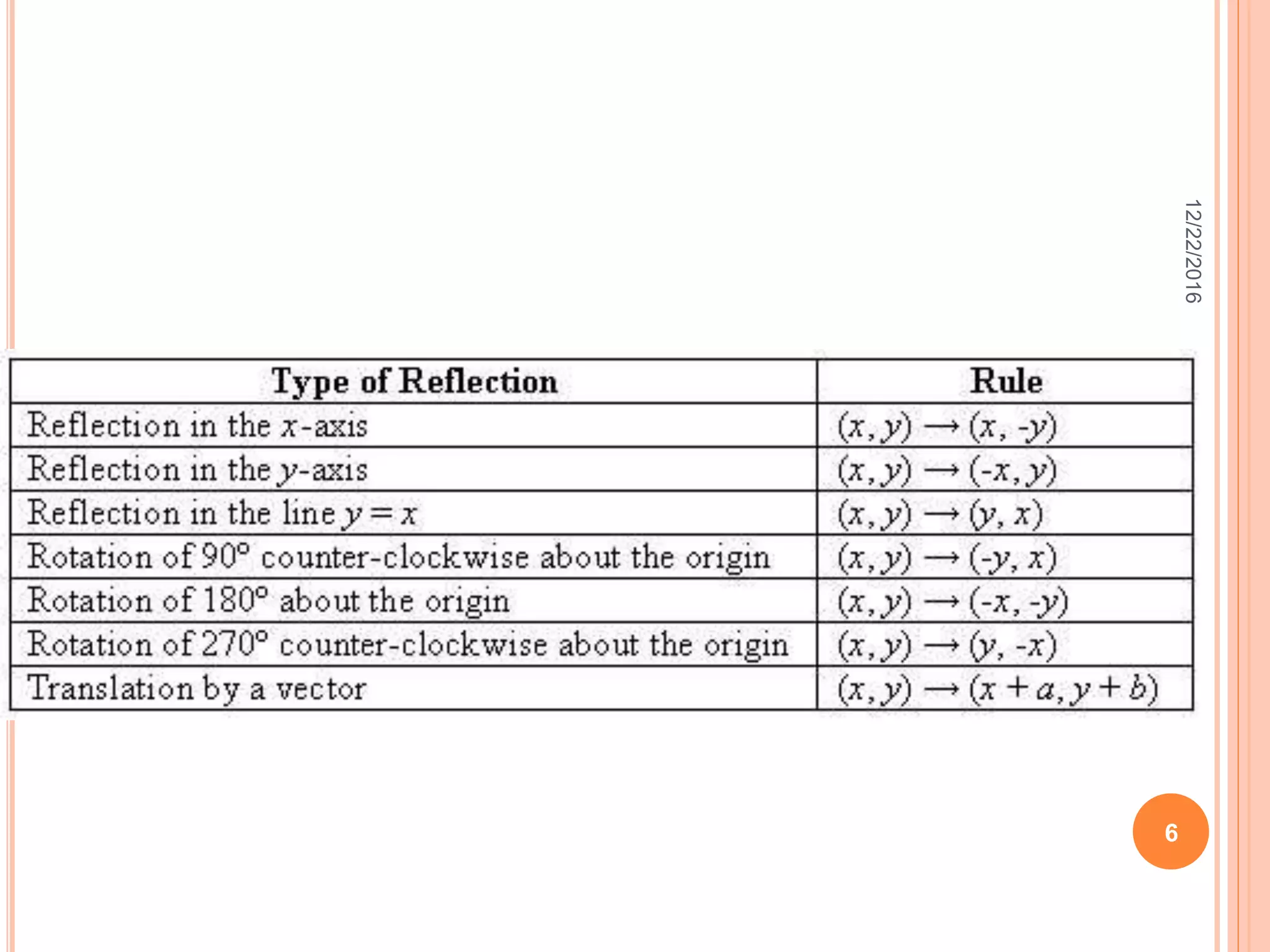
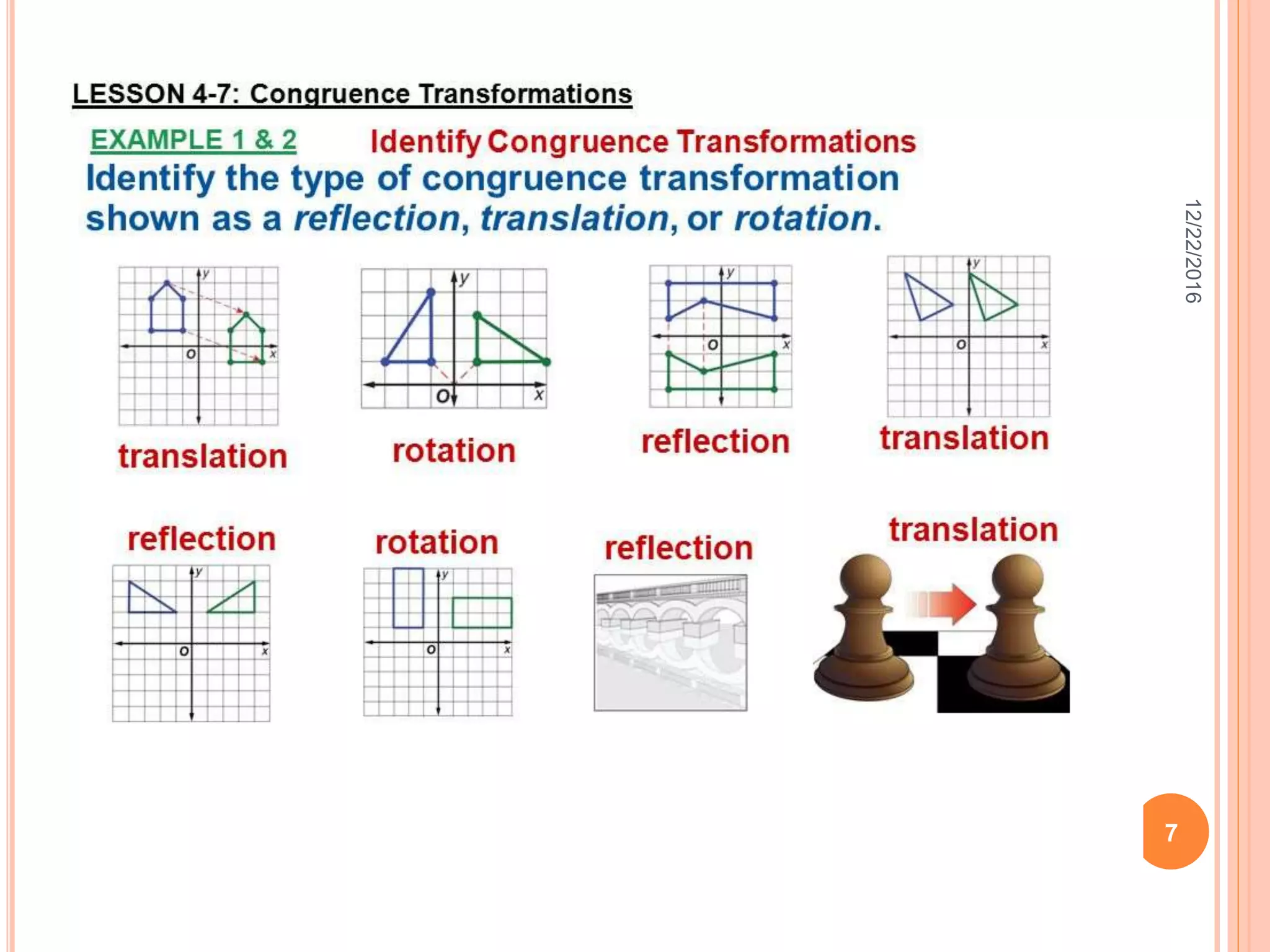
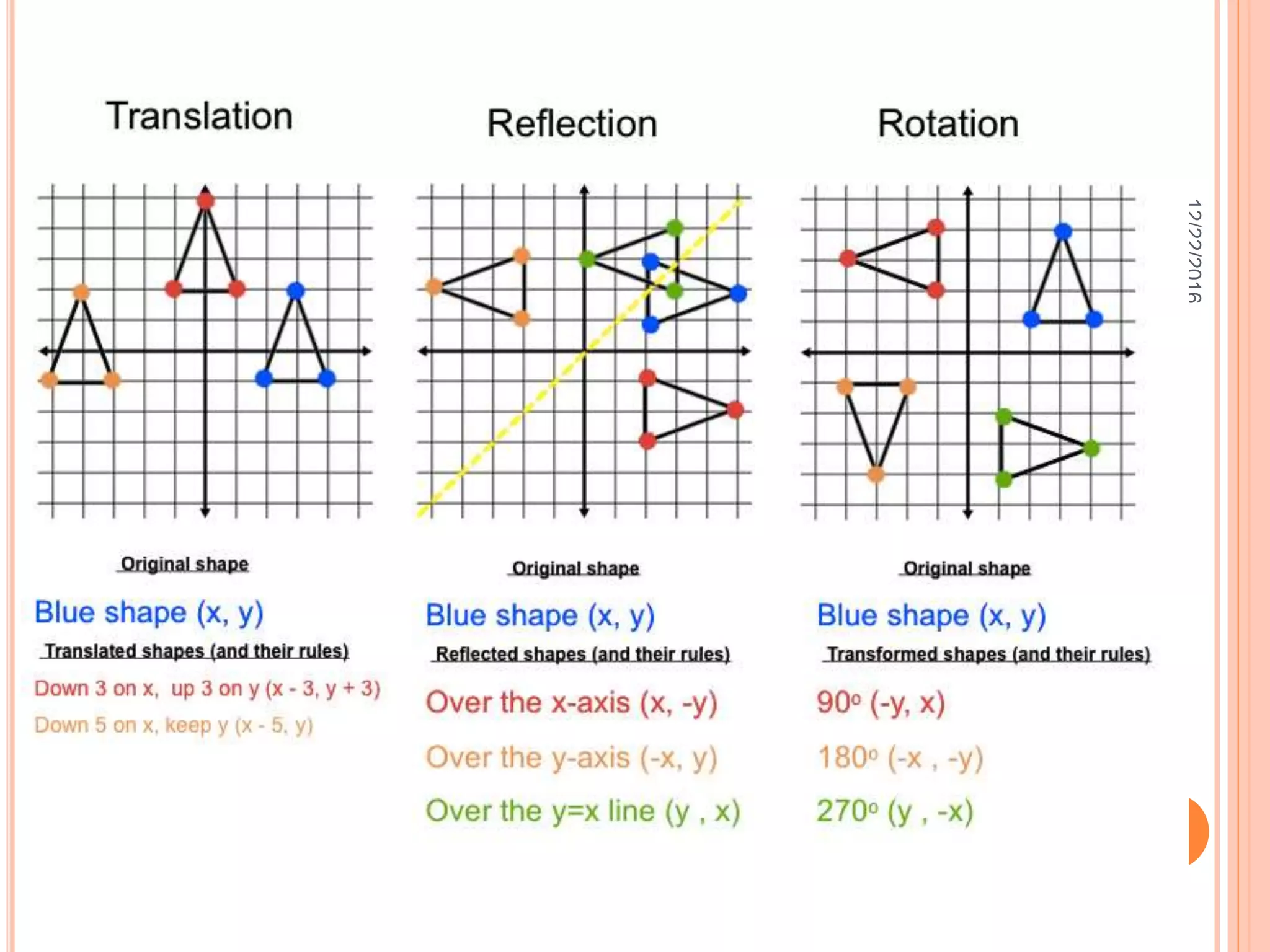
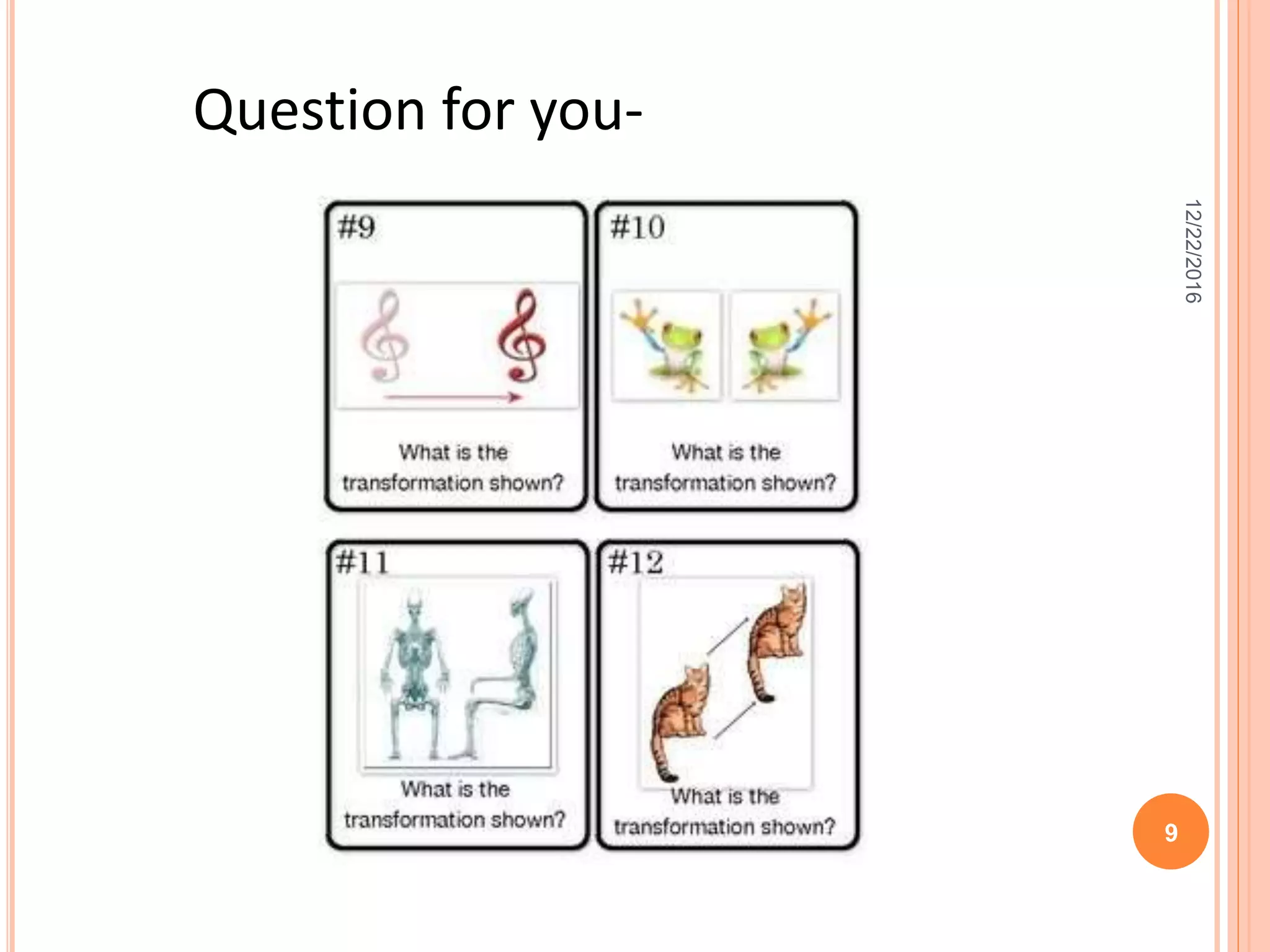
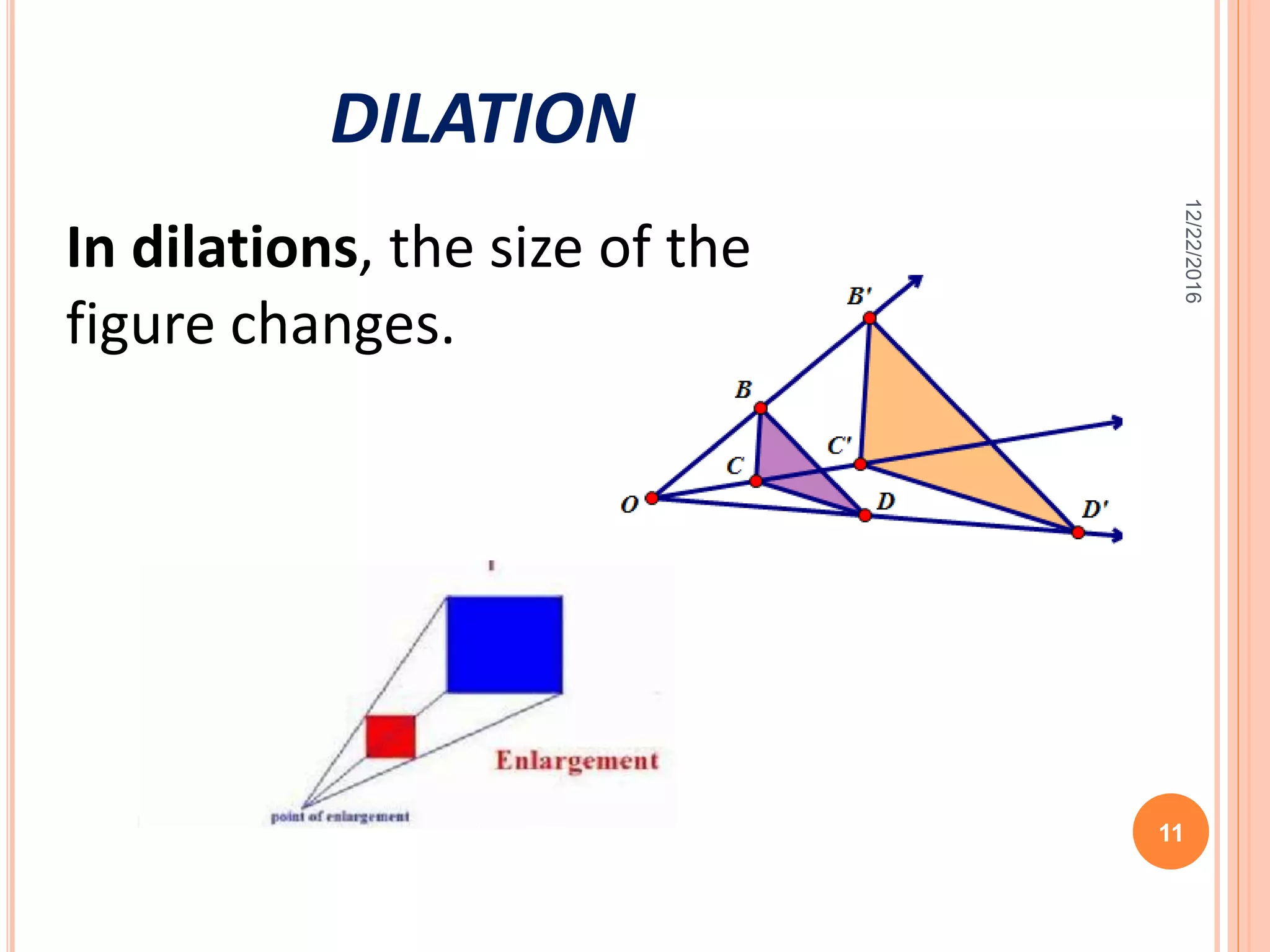
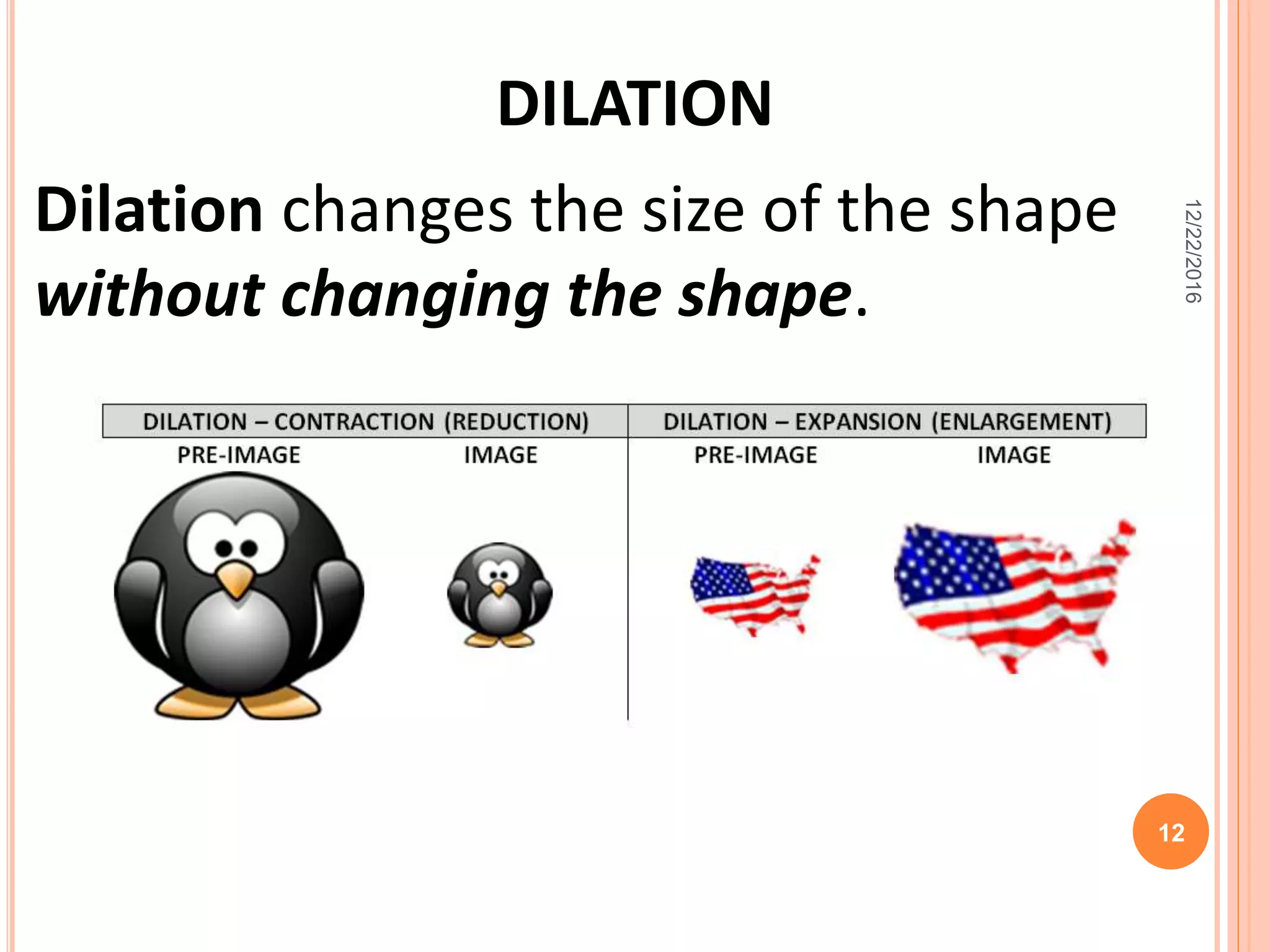
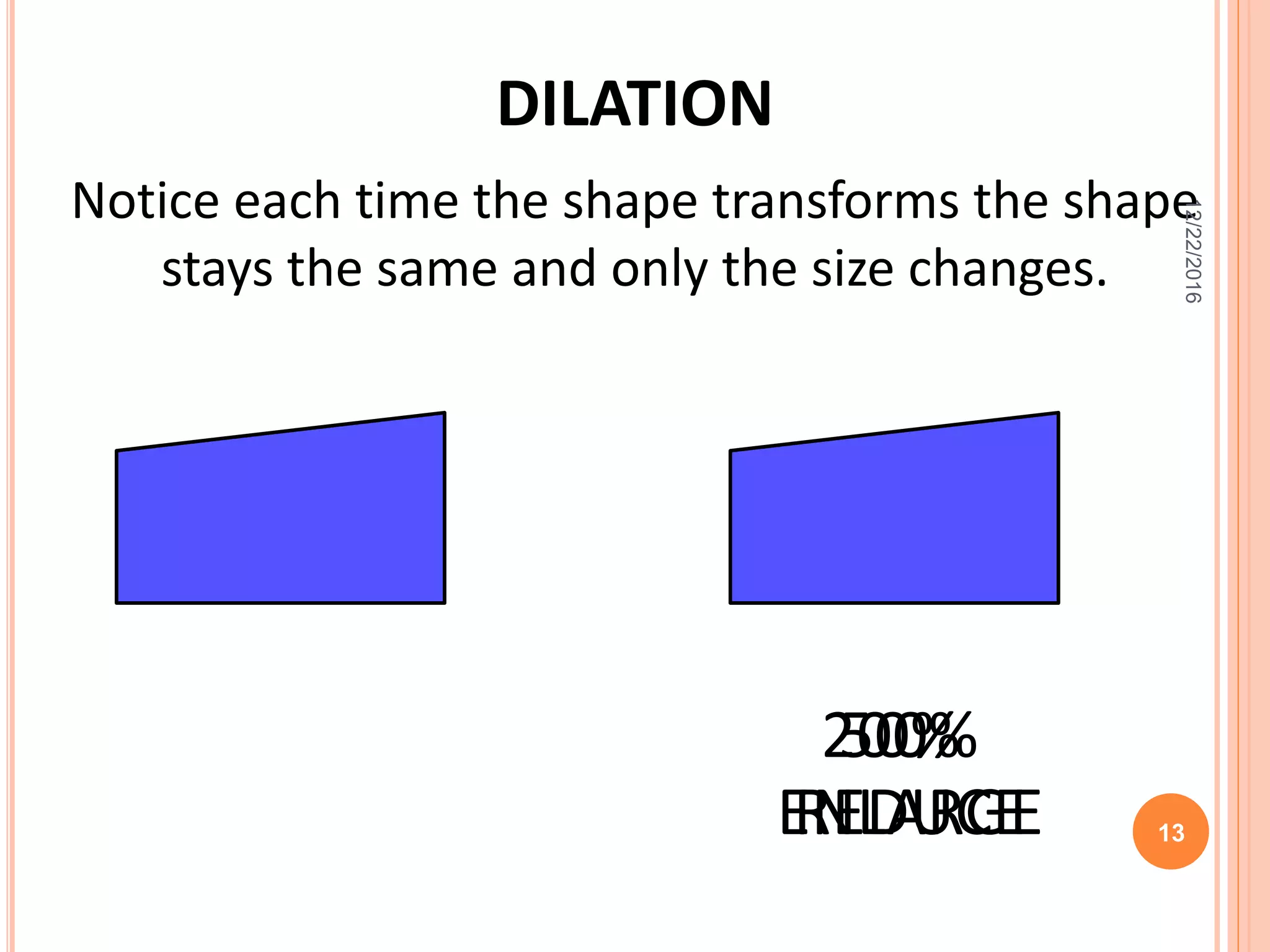
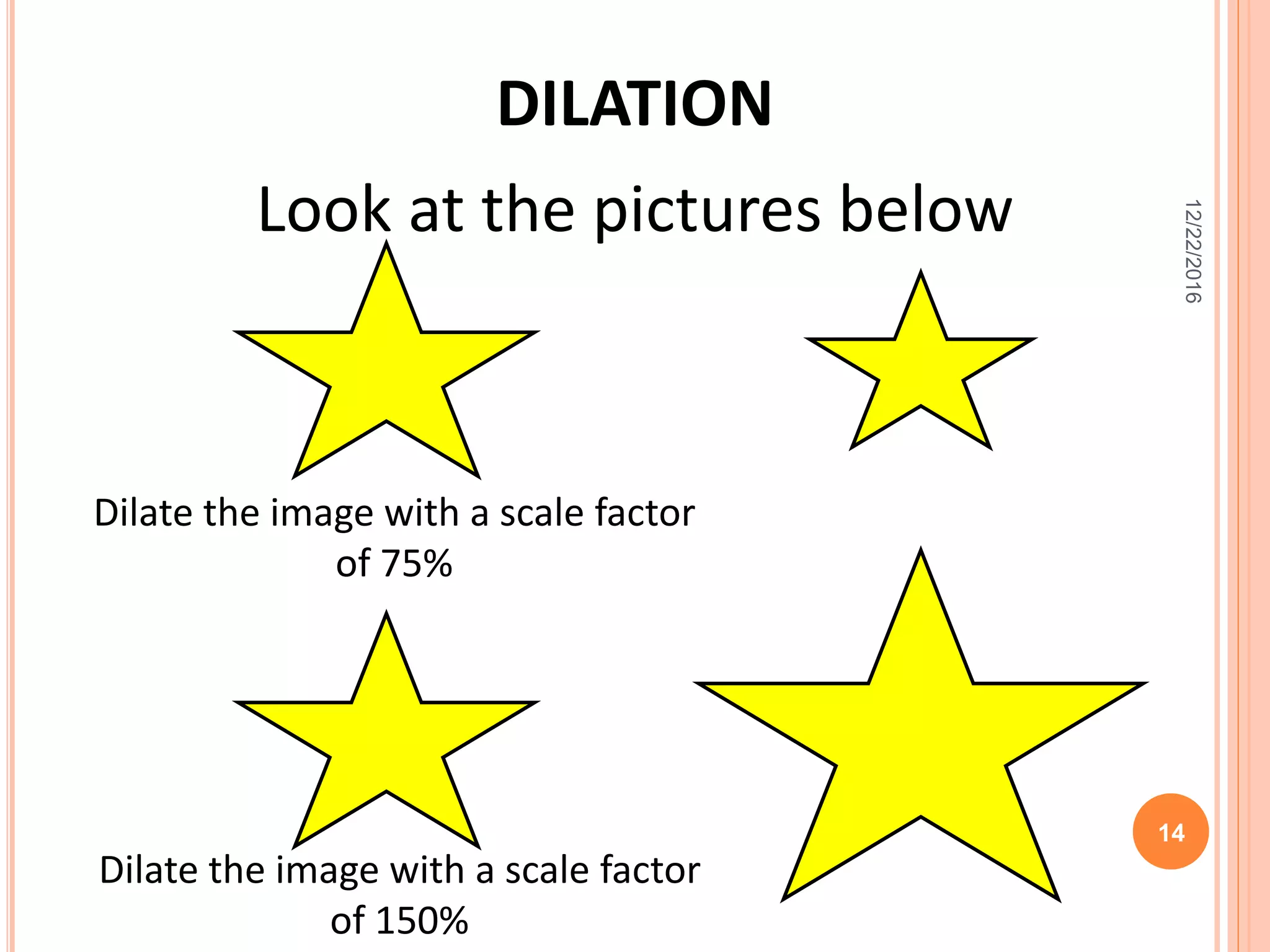
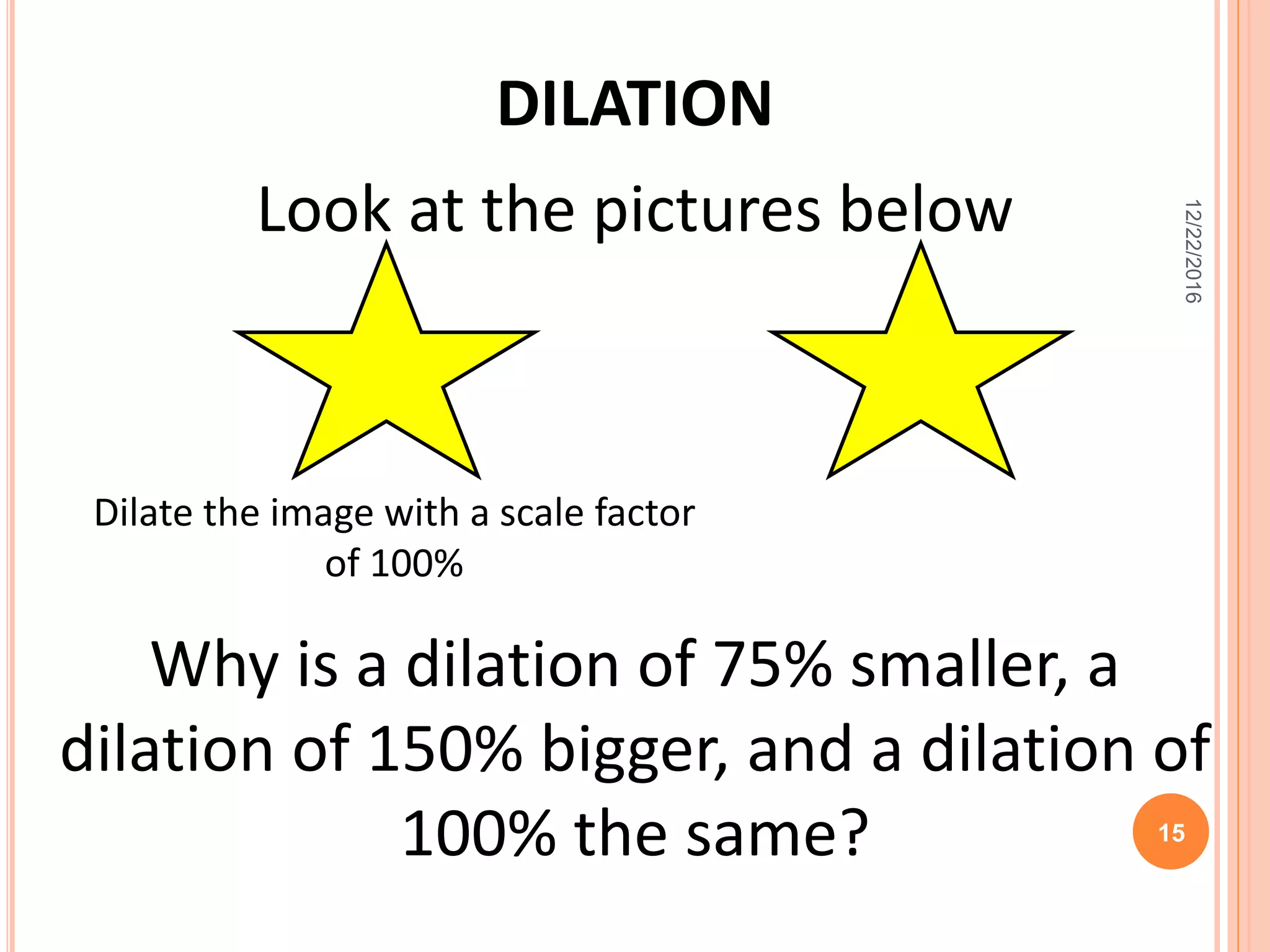
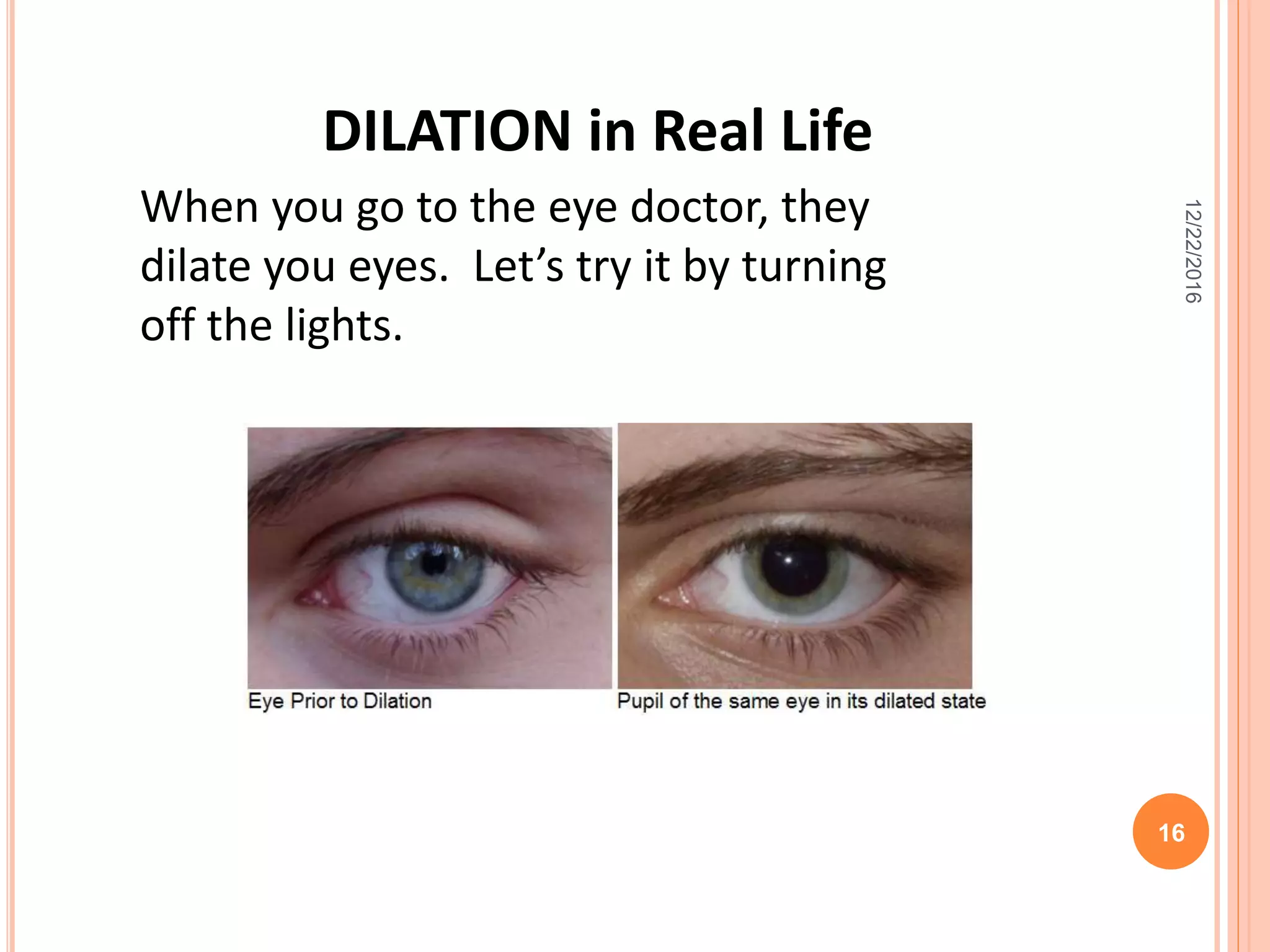
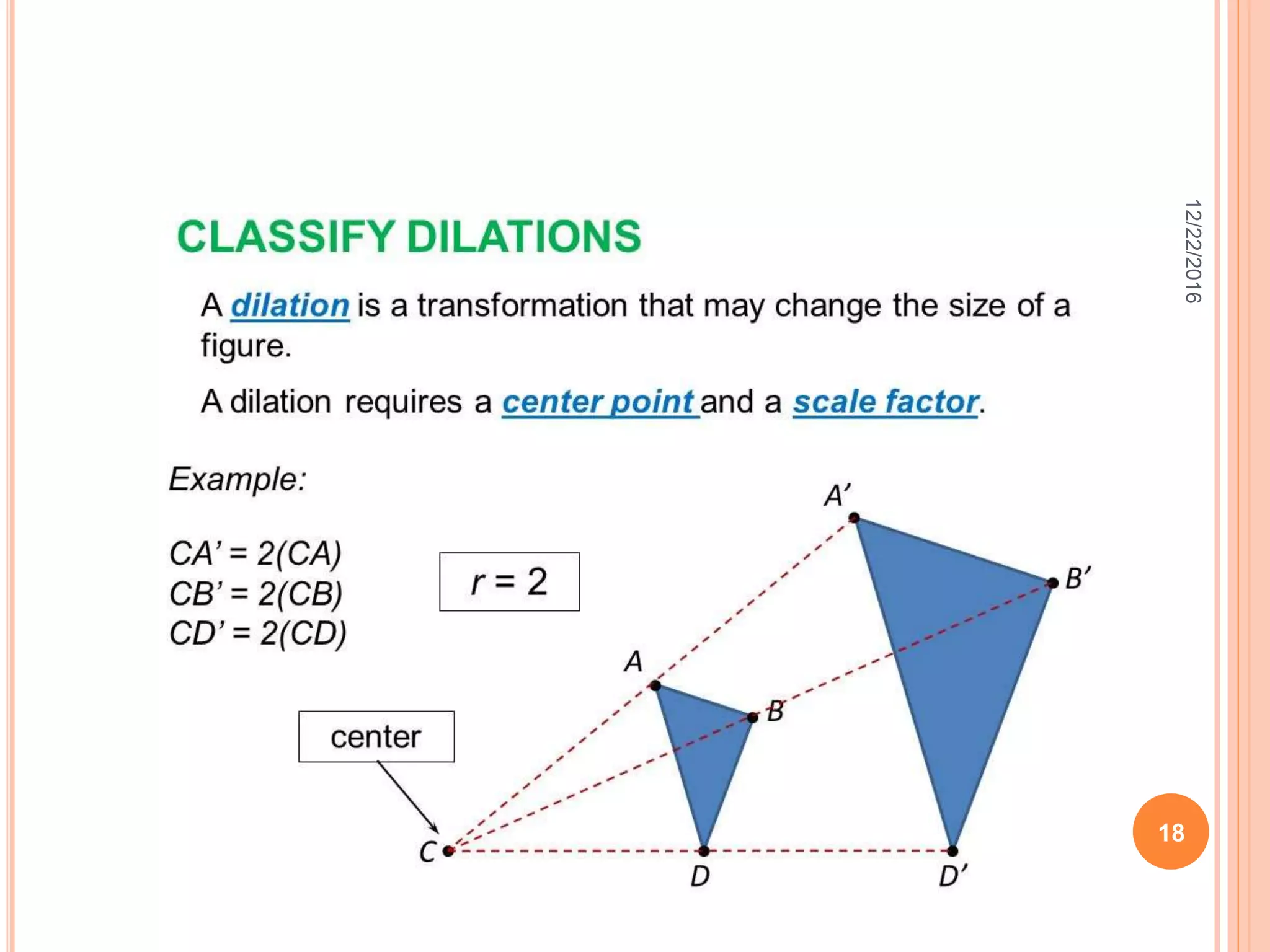
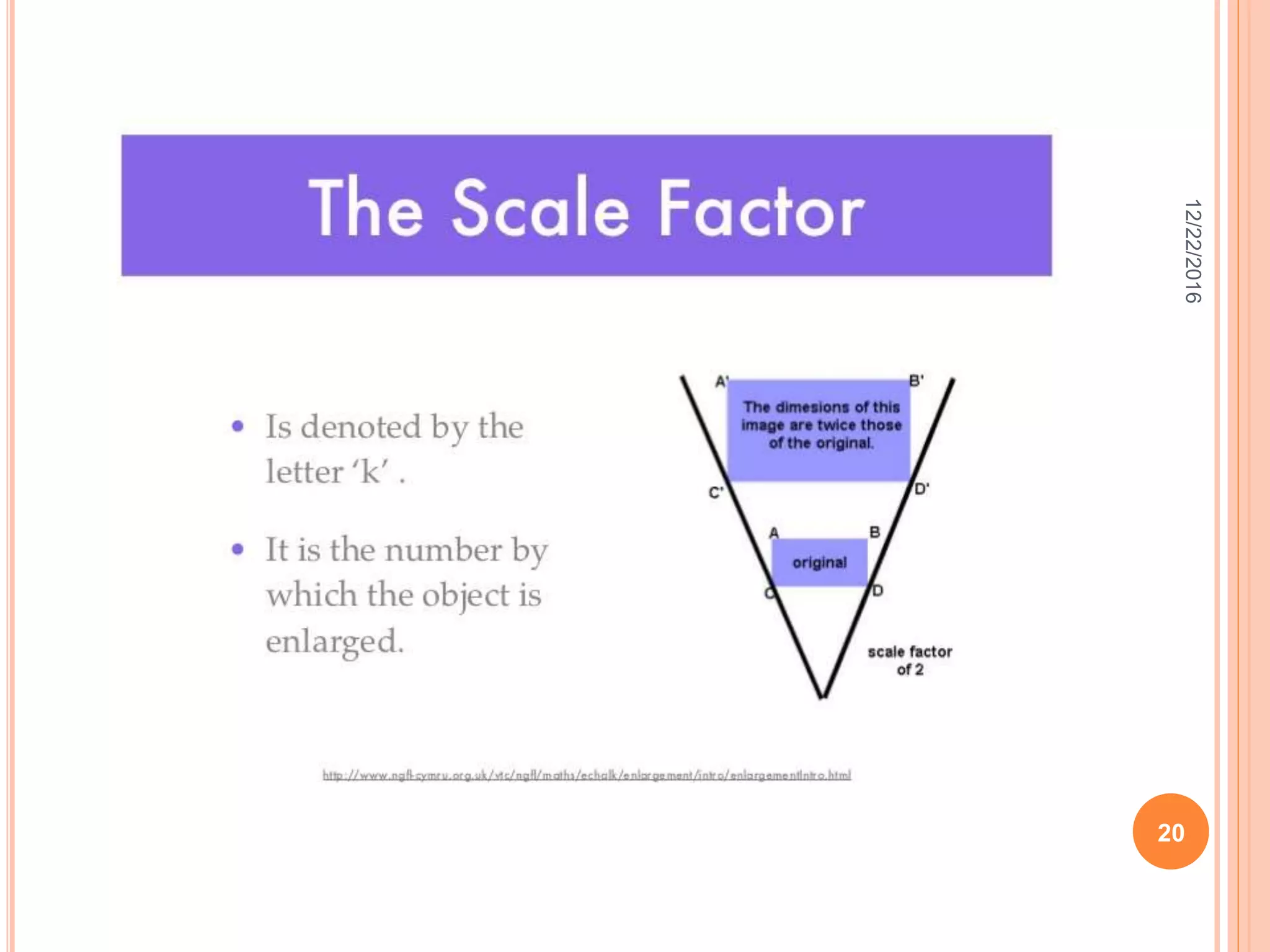
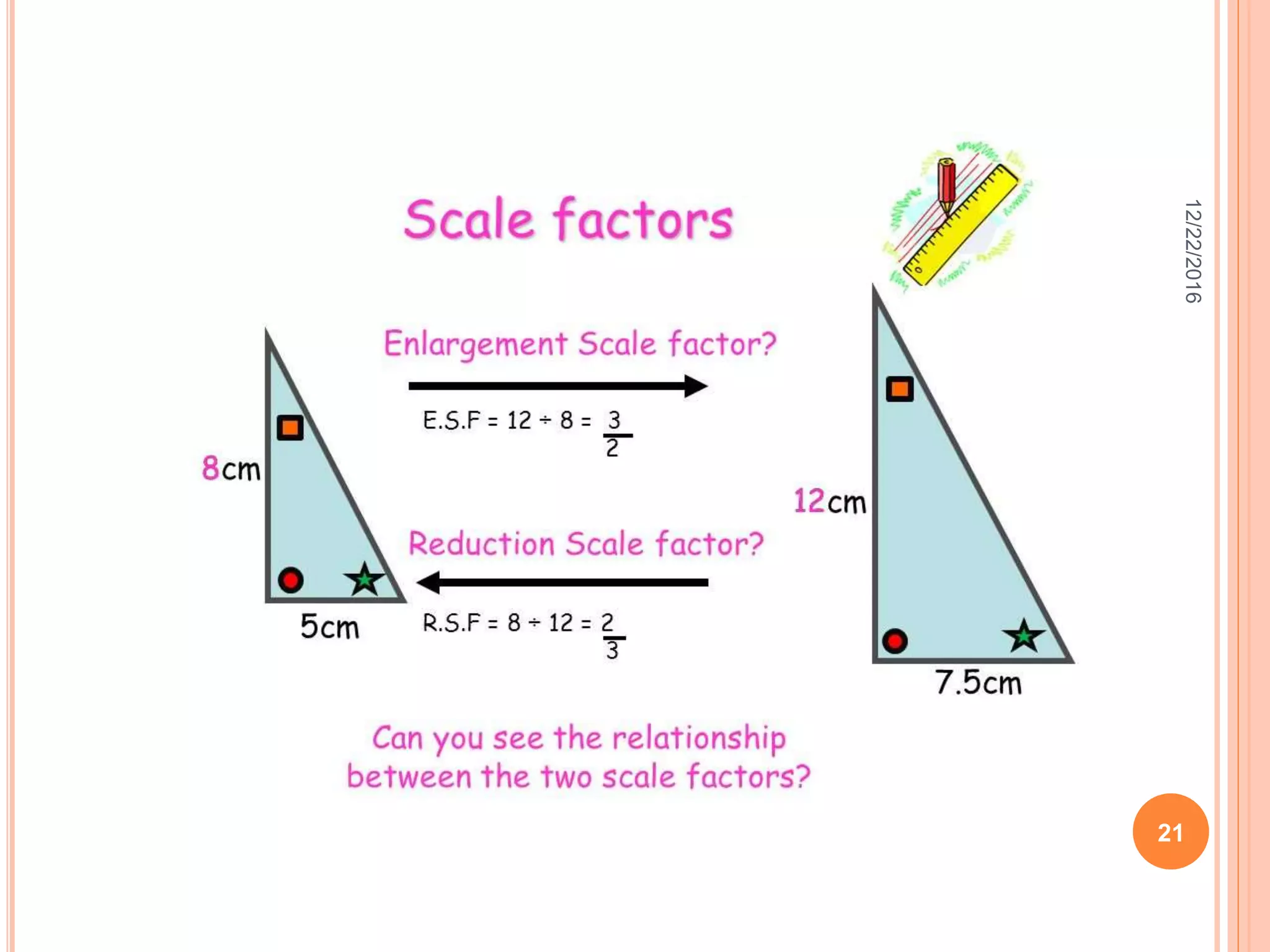
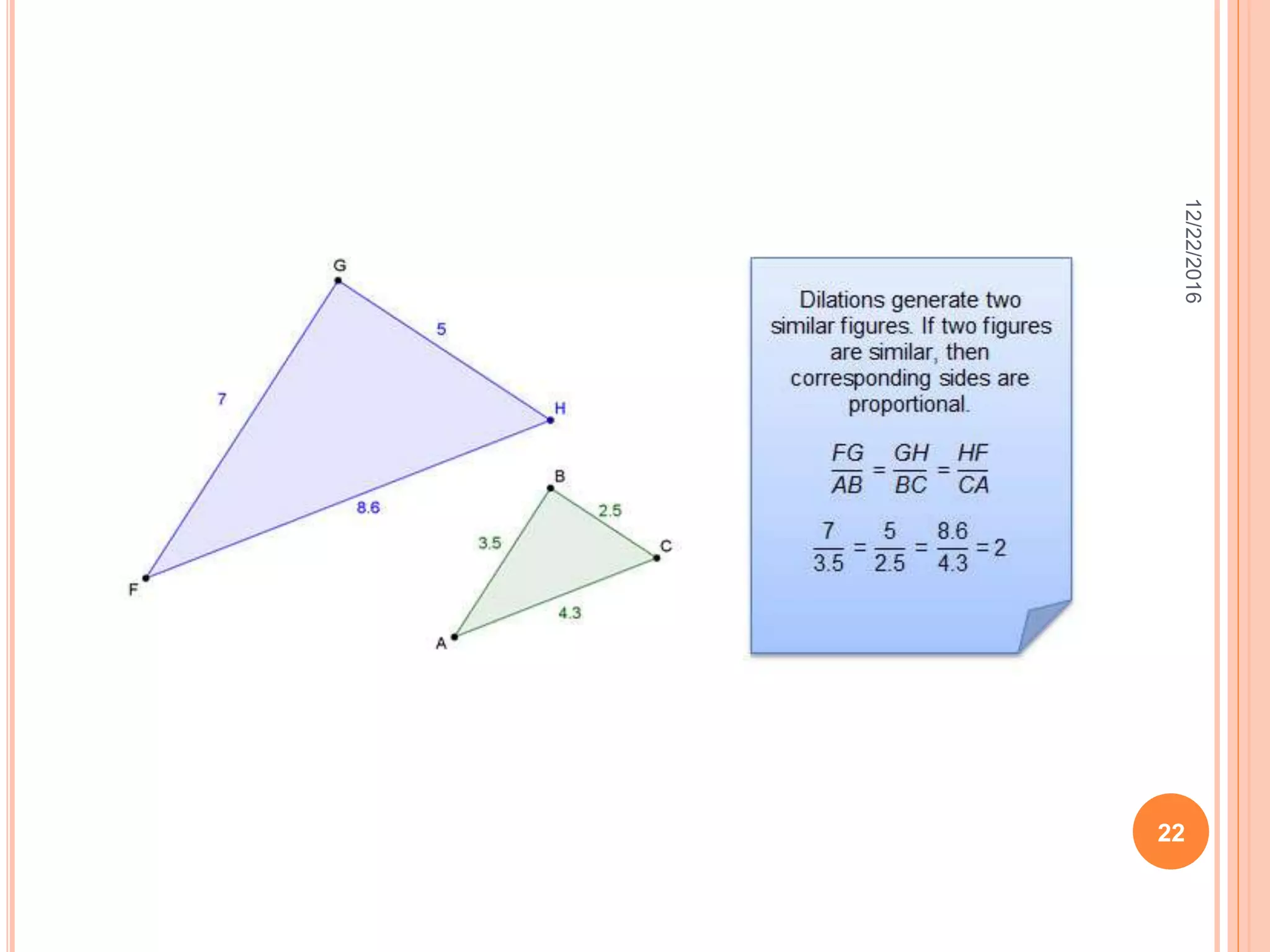
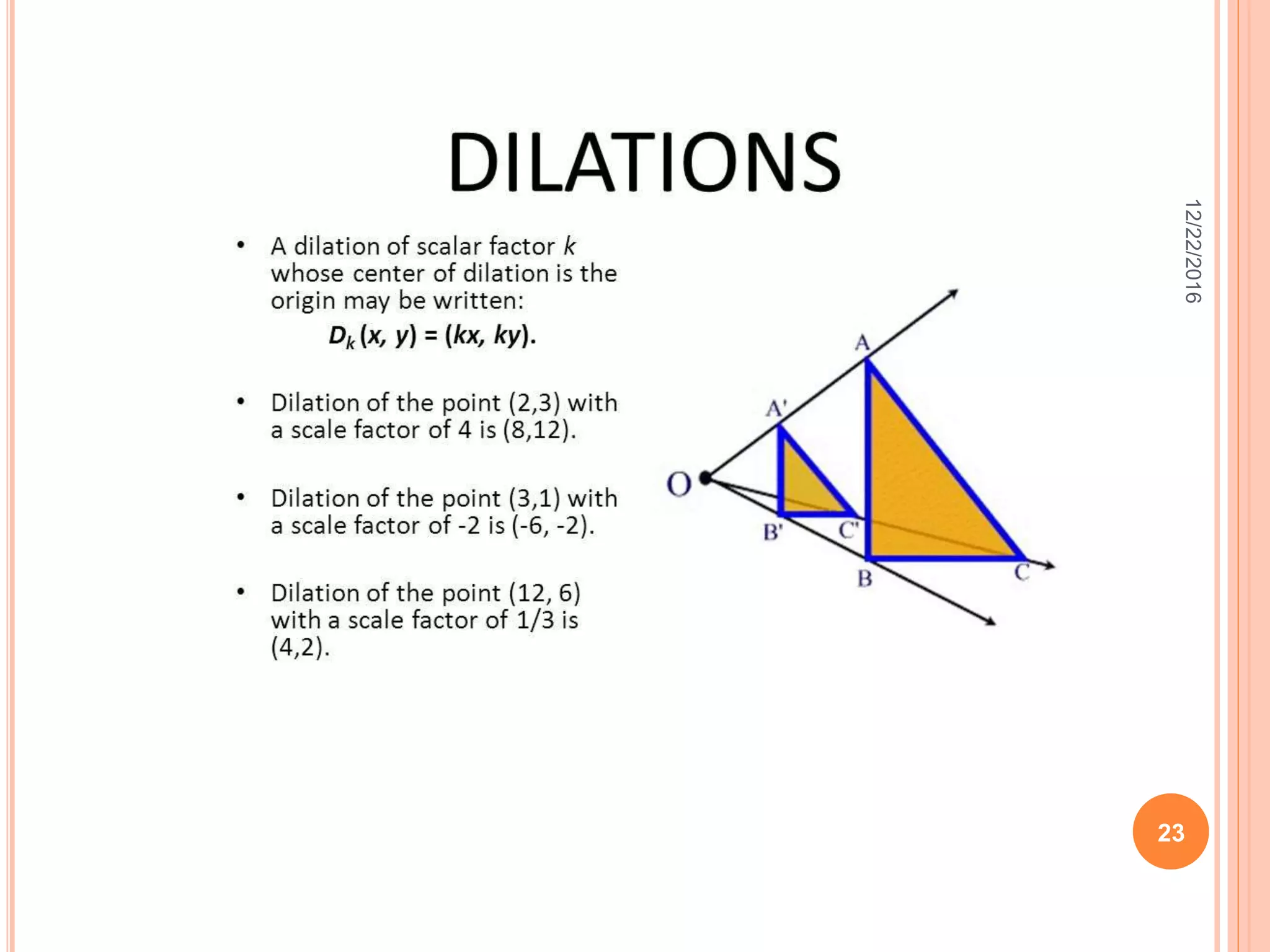
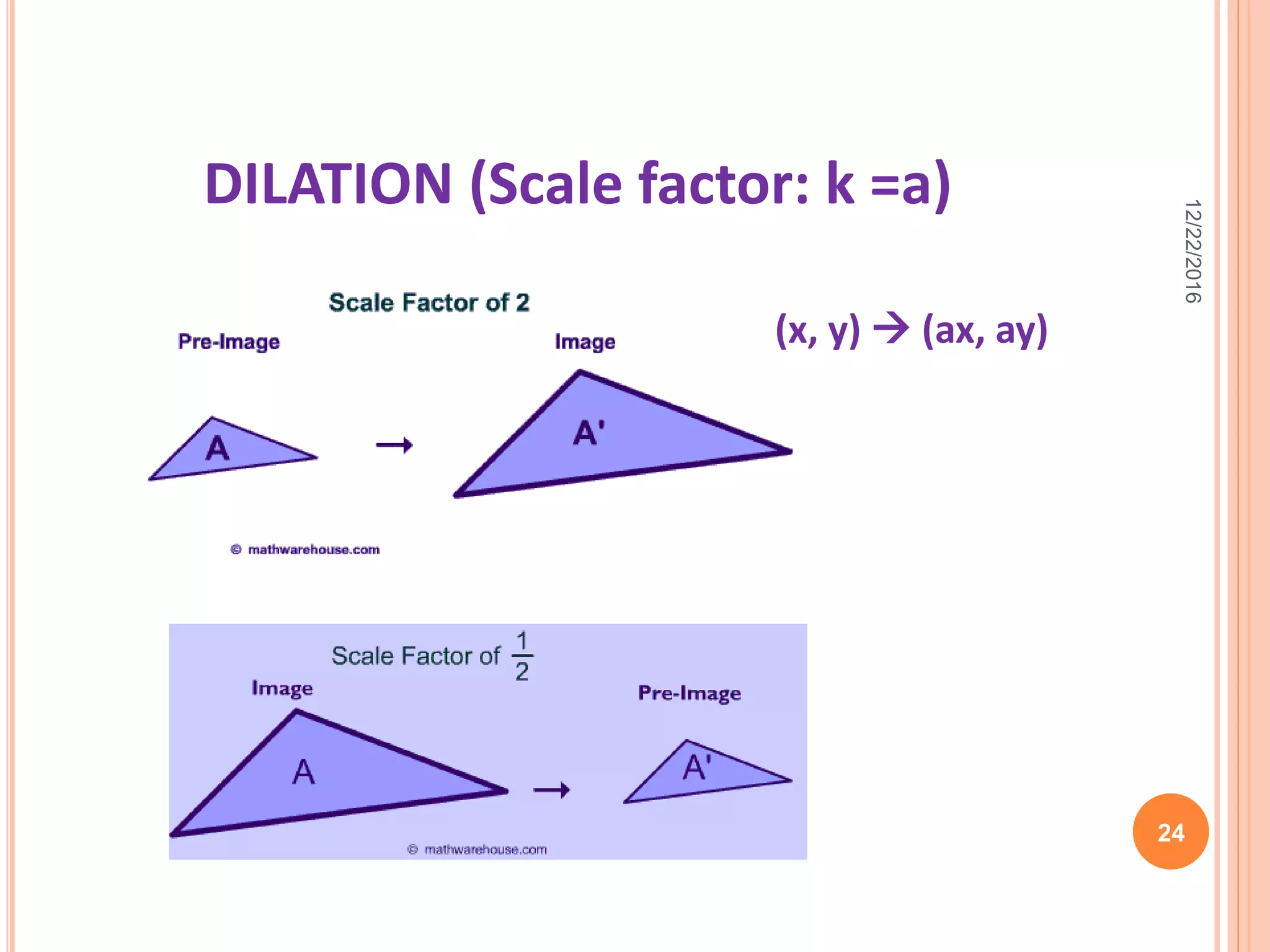
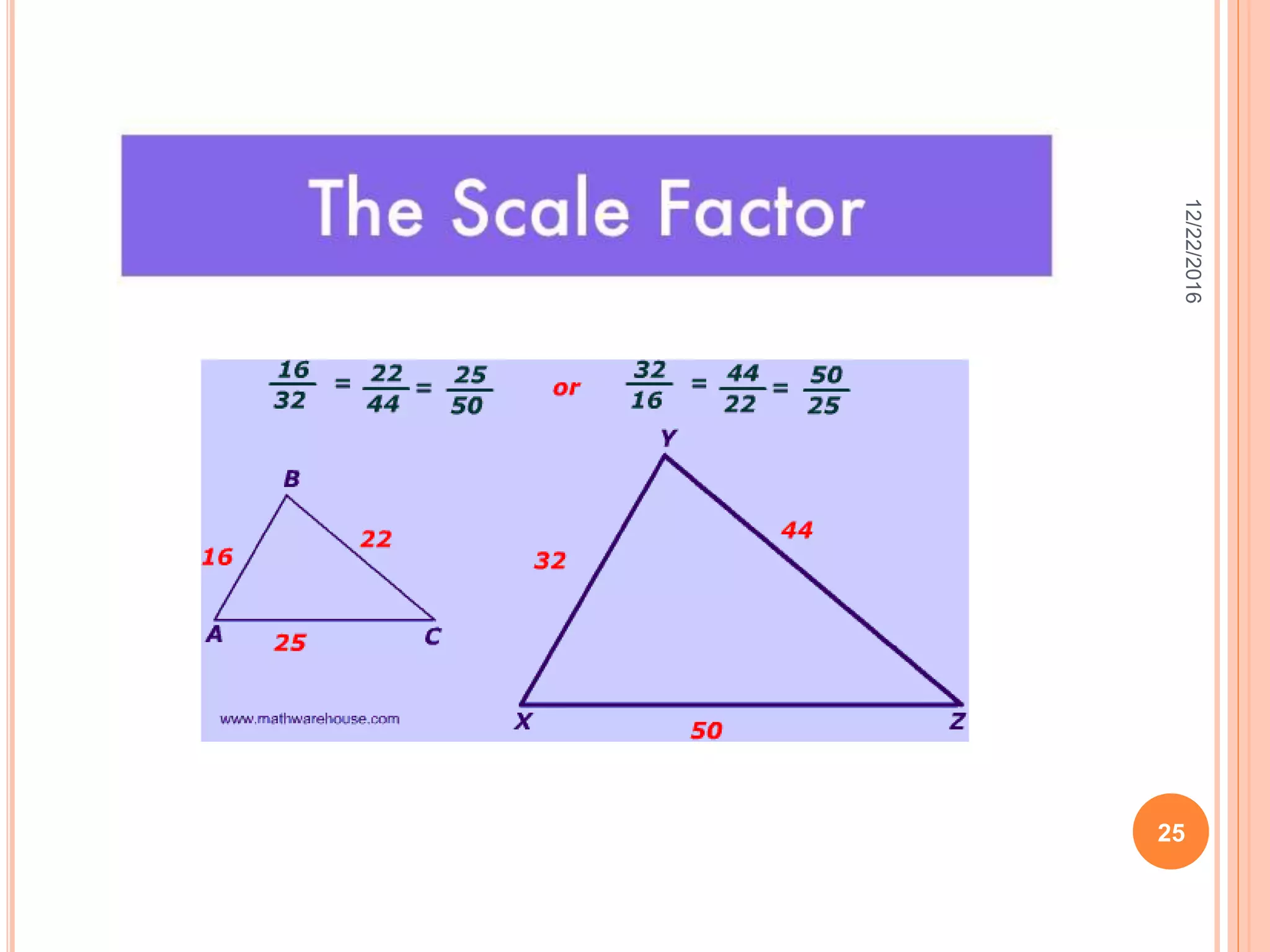
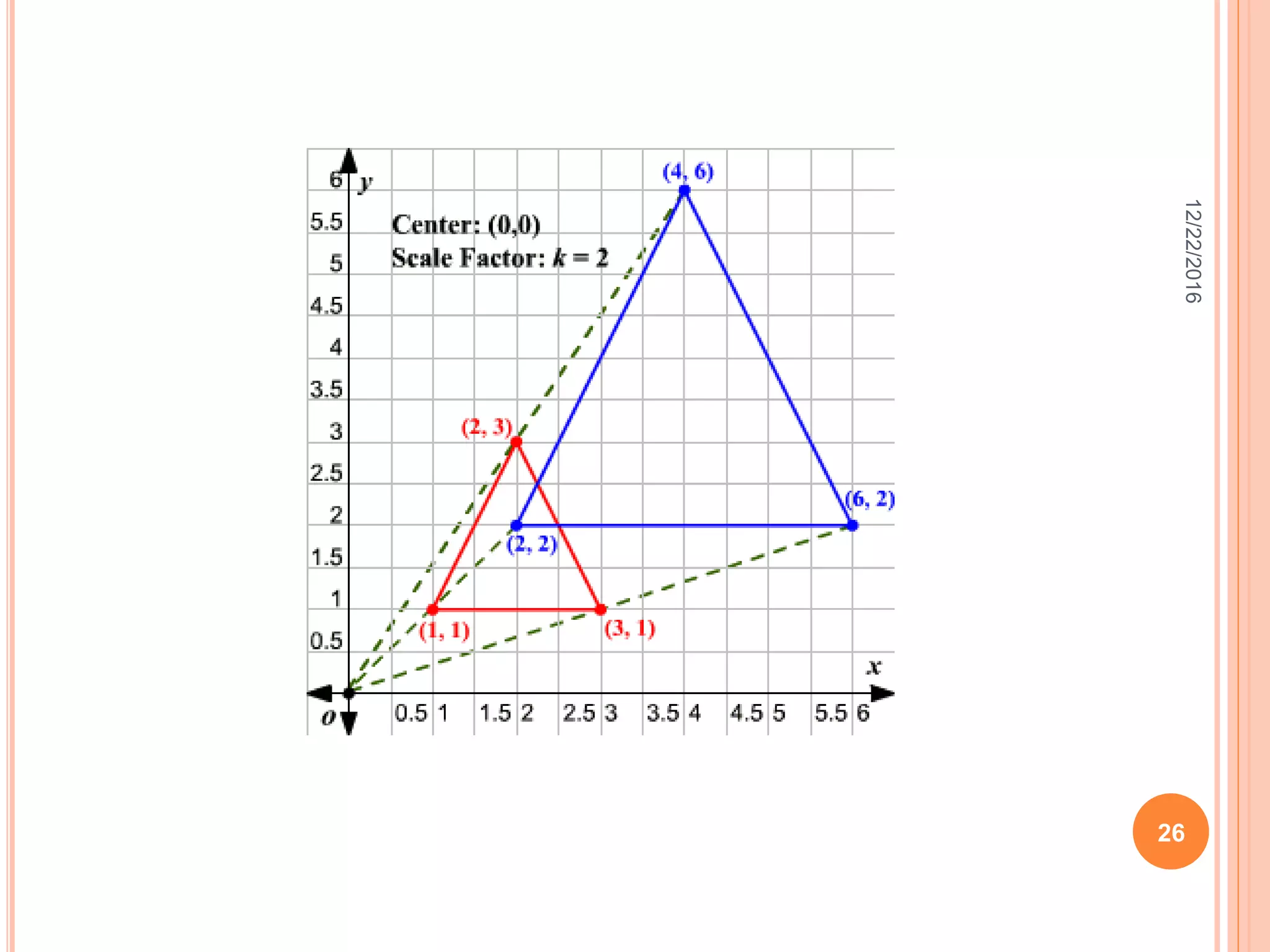
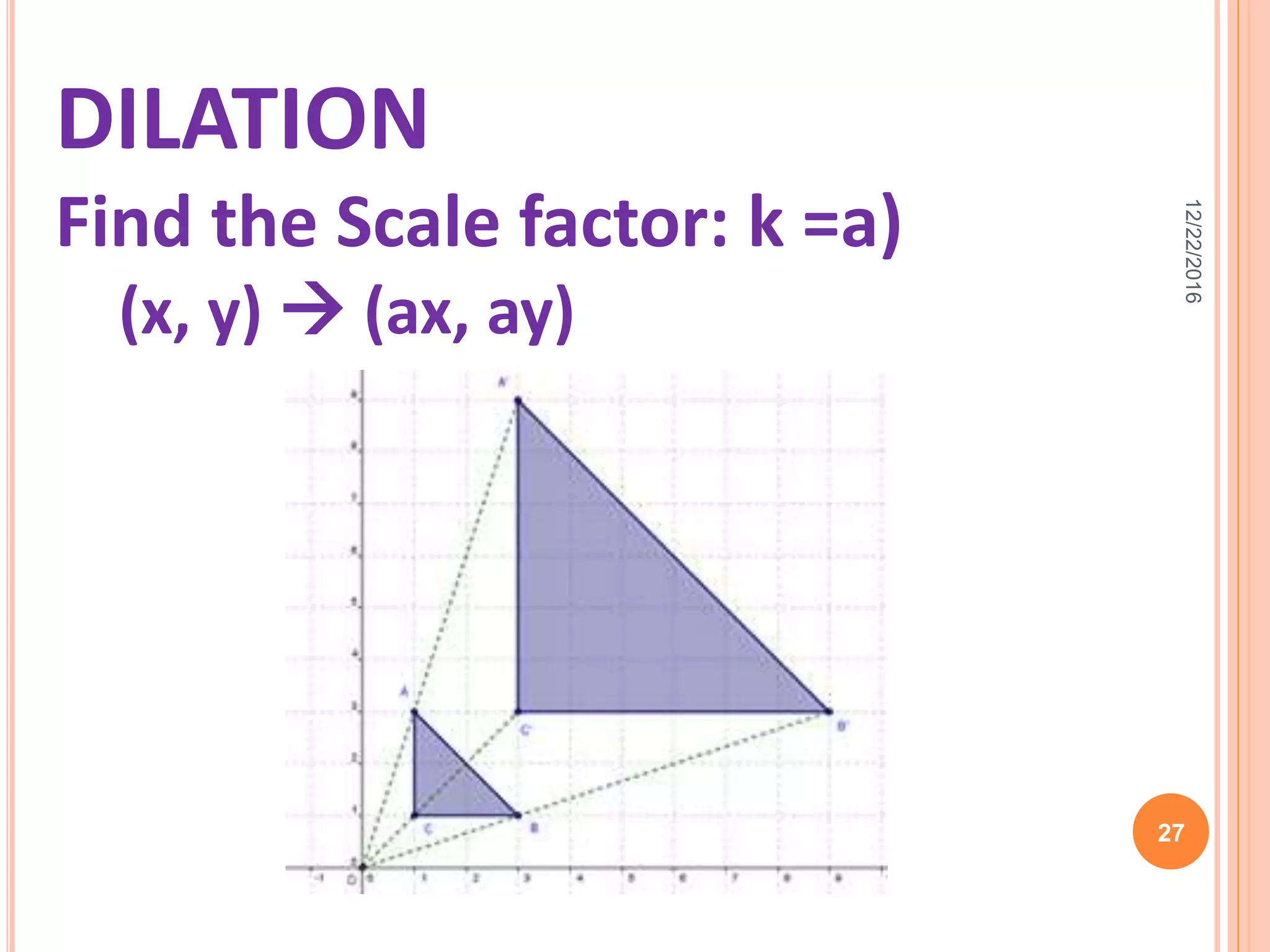
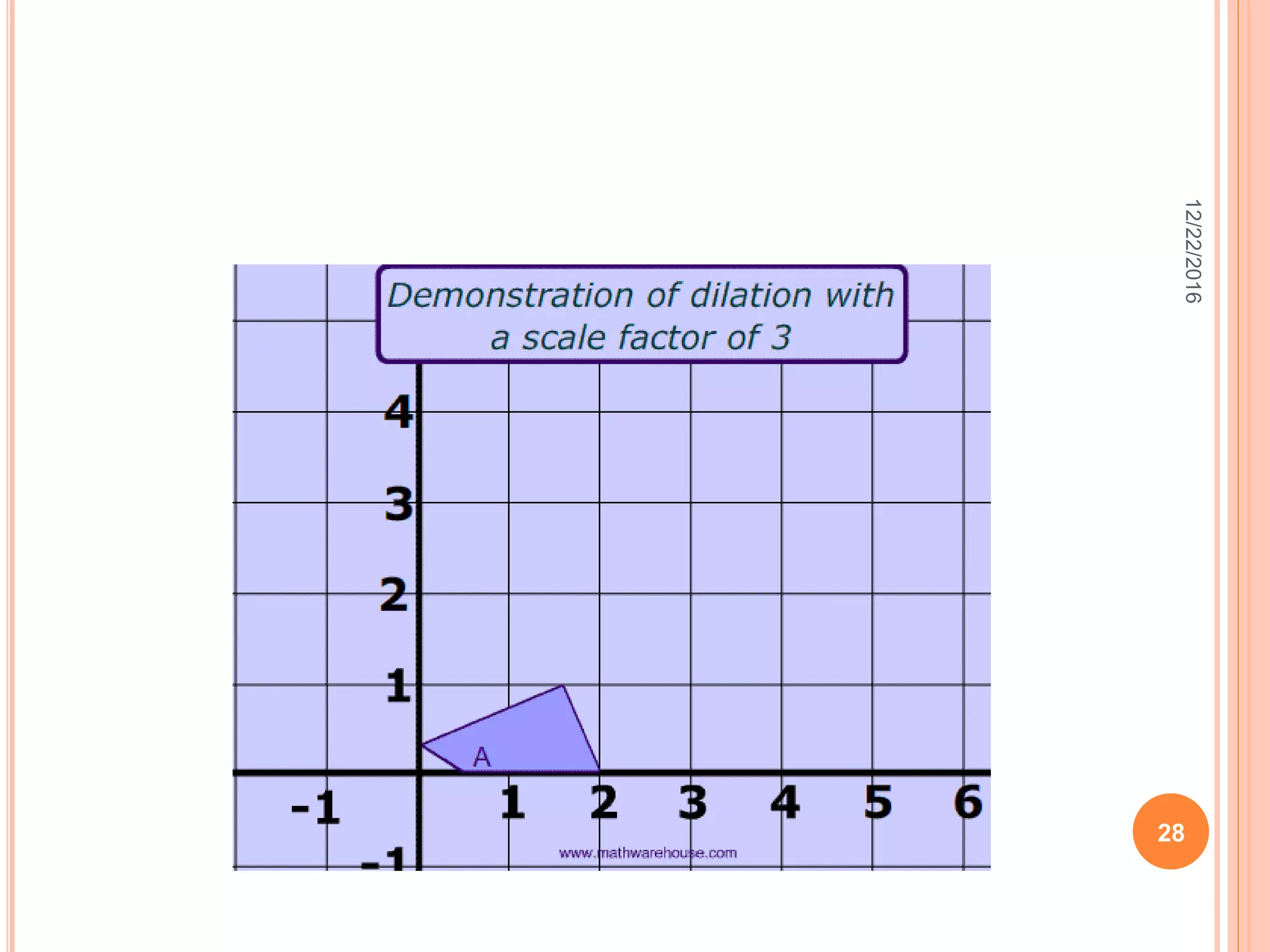
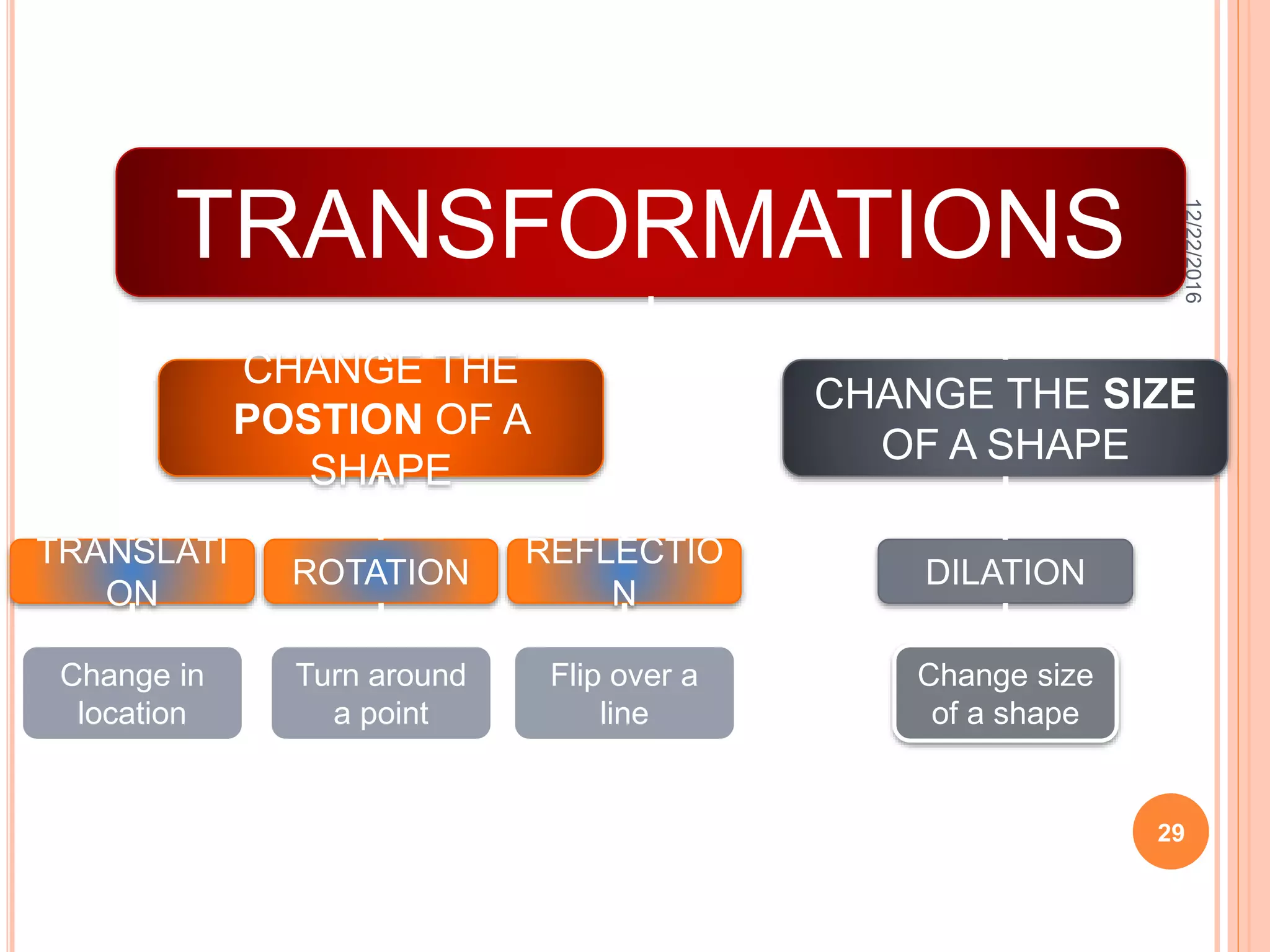
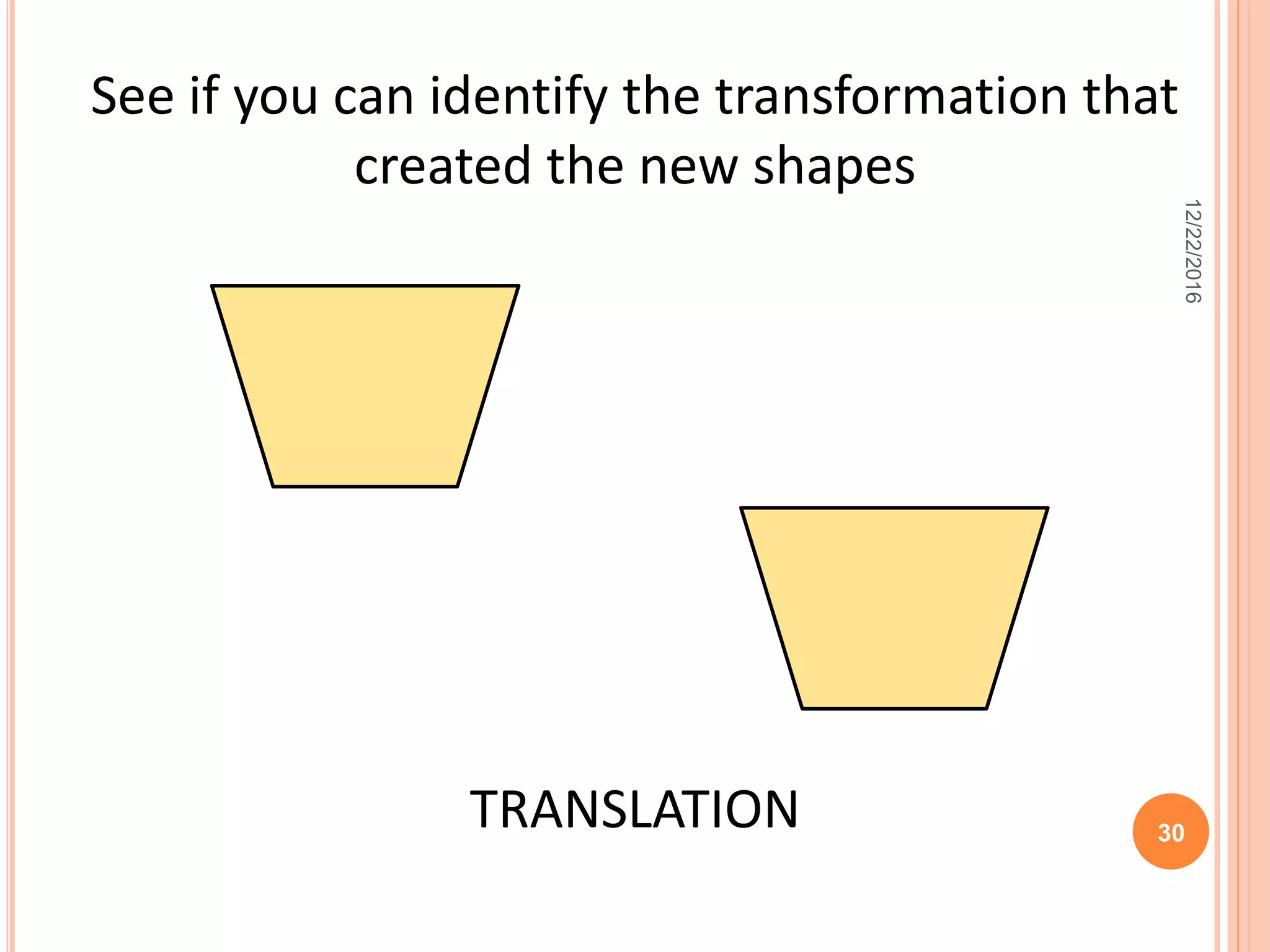
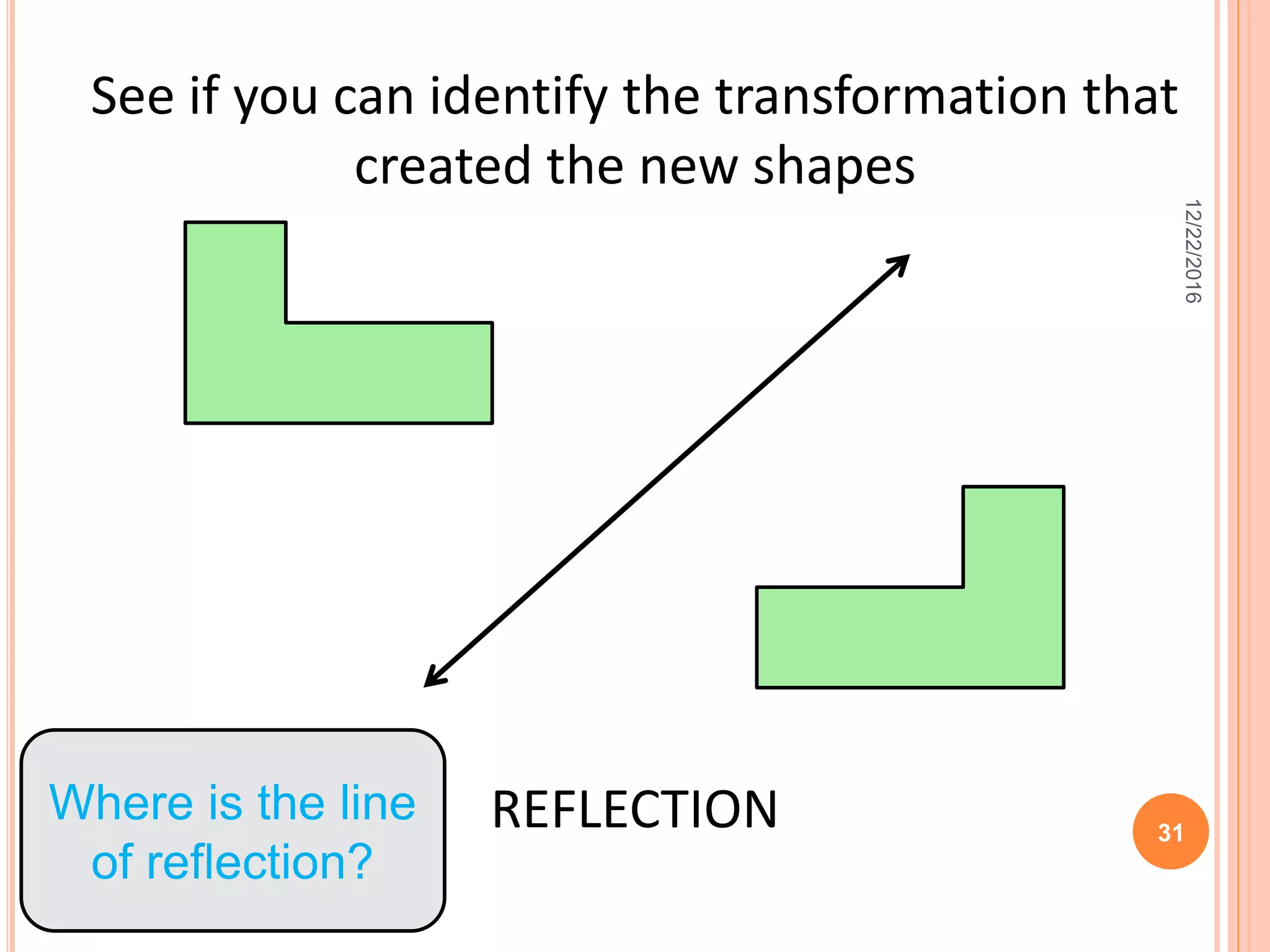
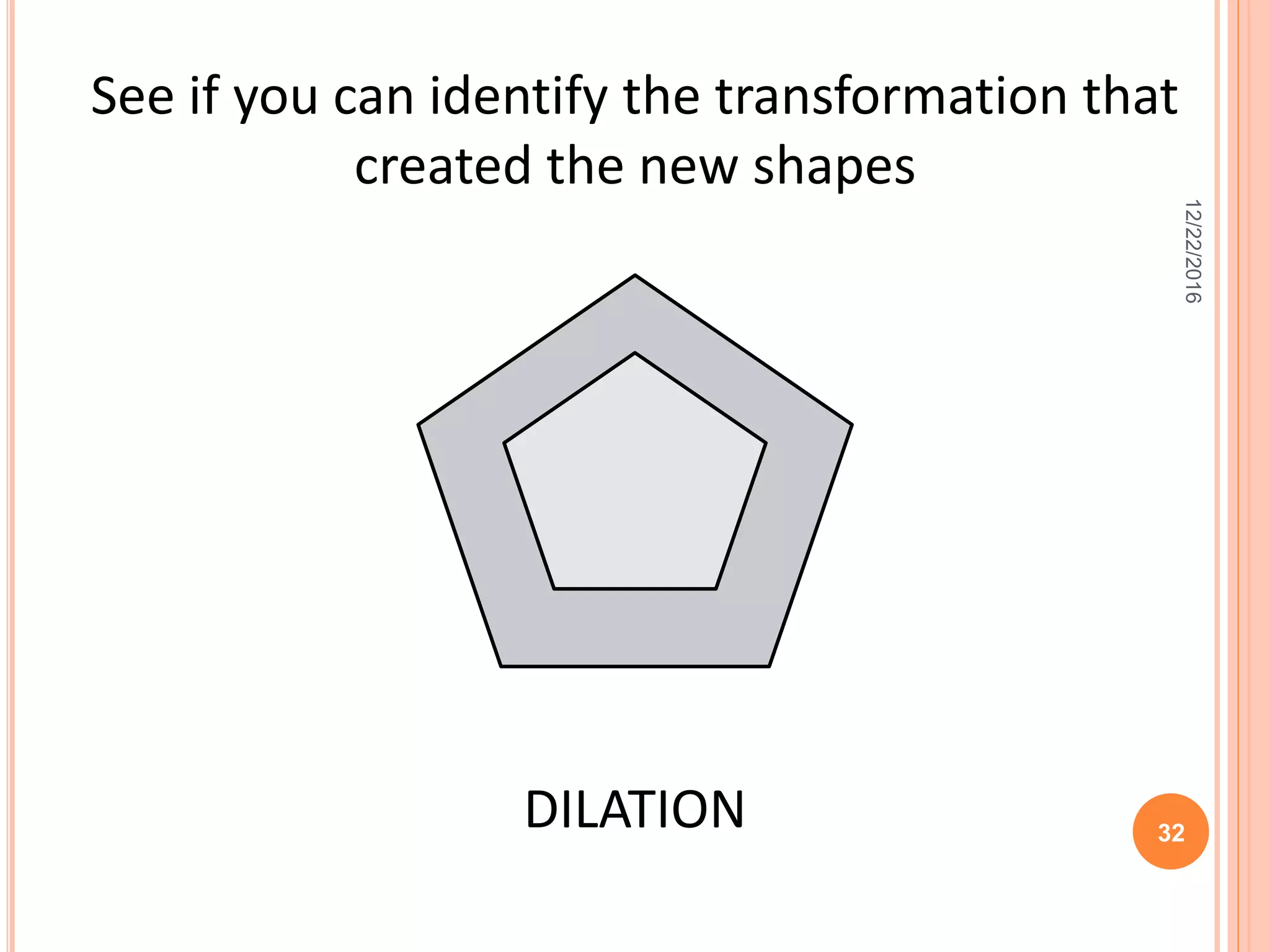
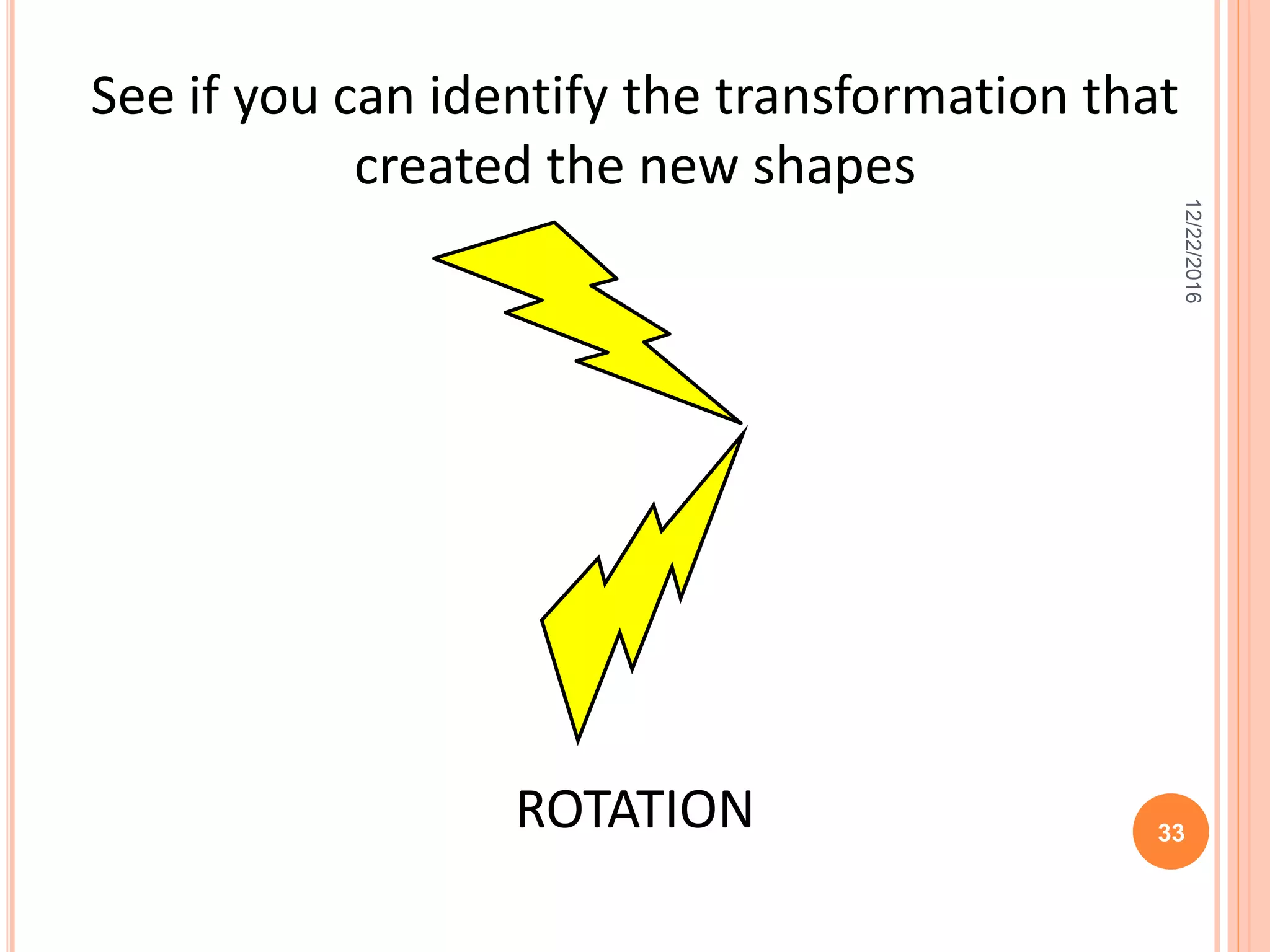
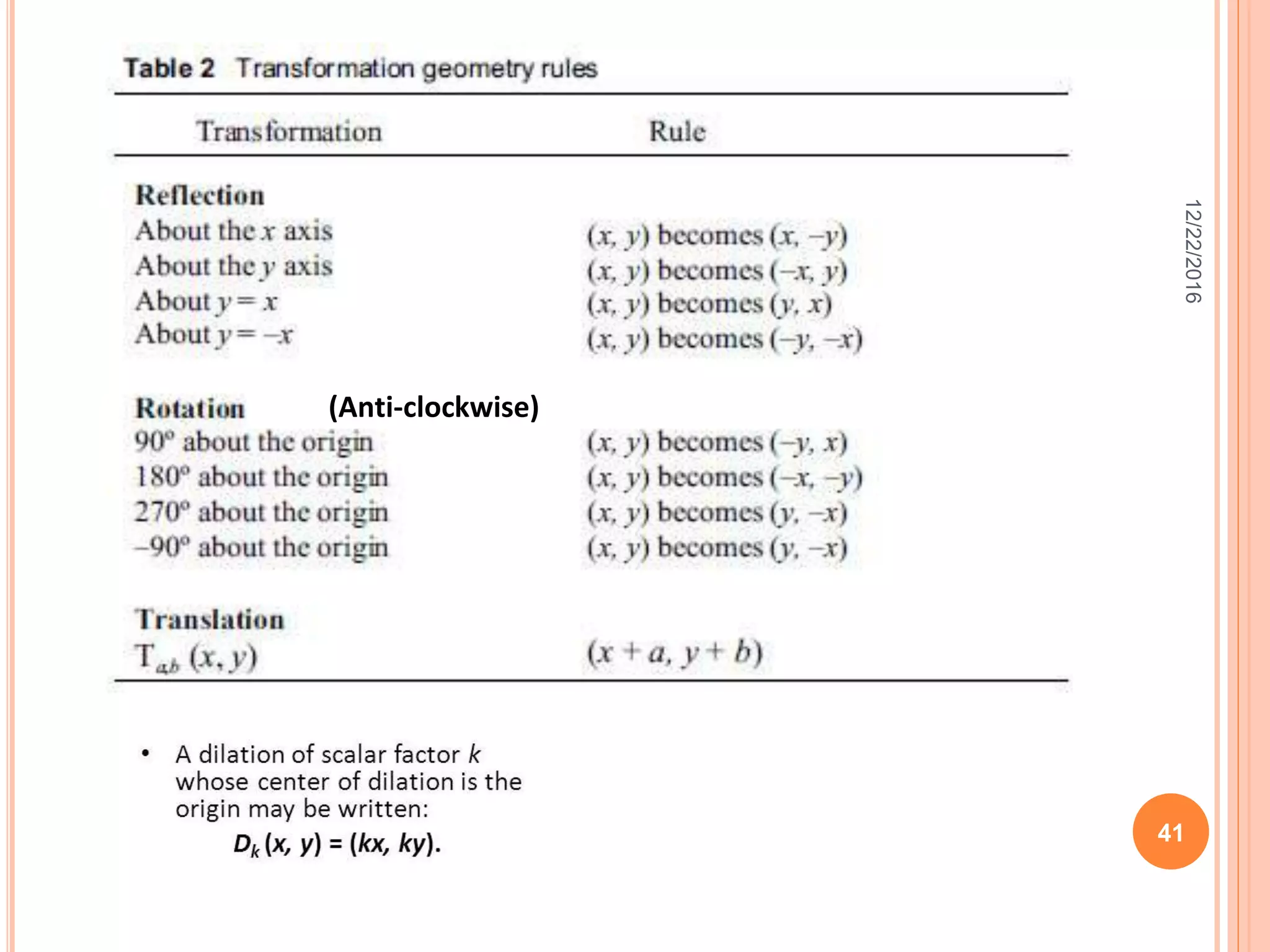
This document discusses the geometric transformation of dilation. Dilation changes the size of a shape but not its shape. Dilation is specified by a scale factor, where a scale factor greater than 1 enlarges the shape and less than 1 reduces the shape. Examples are given of dilating shapes at scale factors of 75%, 150%, and 100%. Real-world examples of dilation include enlarging photographs and reducing maps on a photocopier. The key aspects of dilation are explained, including that it changes the size but not the shape using a scale factor to specify the amount of enlargement or reduction.