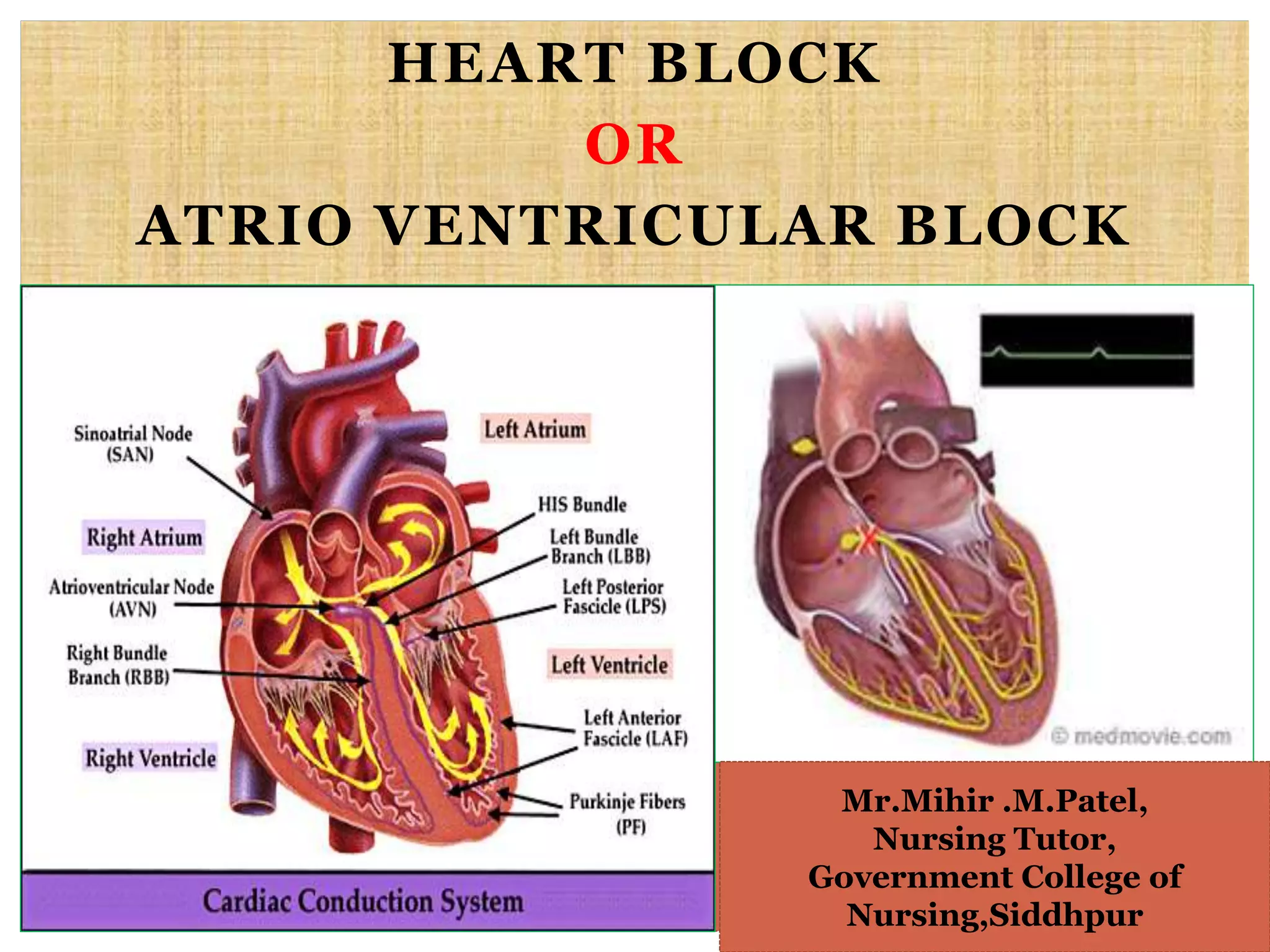
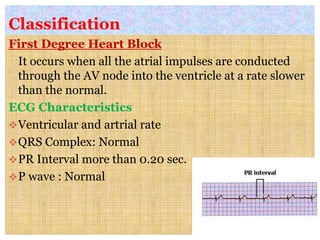
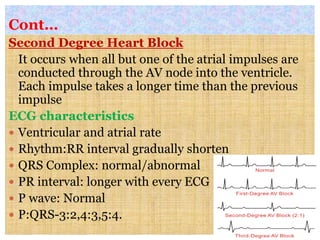
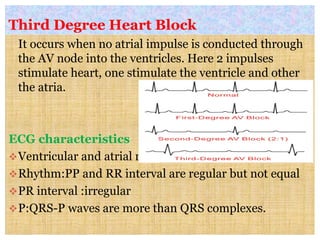
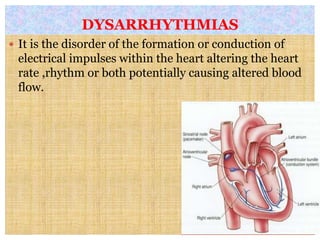
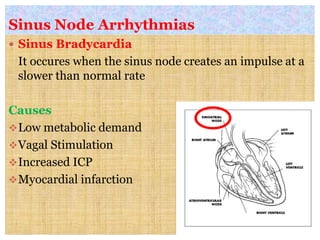
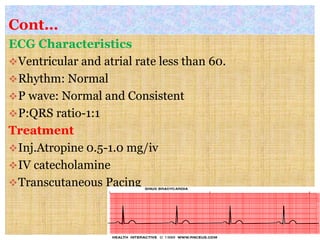
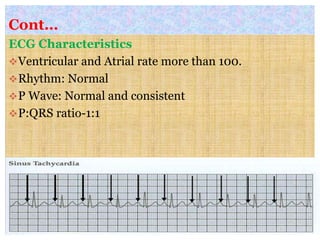
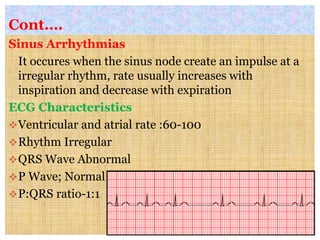
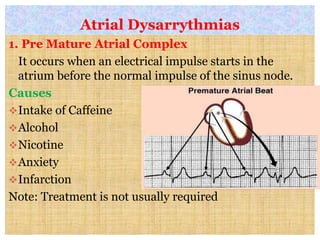
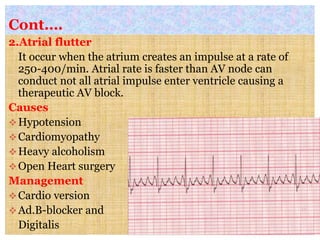
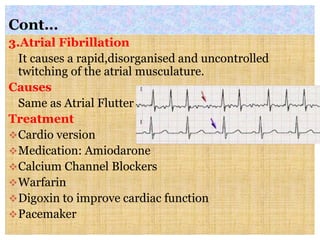
This document discusses different types of heart block and arrhythmias. It defines first, second, and third degree heart block and their characteristic ECG patterns. It also covers different types of arrhythmias including sinus, atrial, junctional, and ventricular arrhythmias. For each type of arrhythmia, it discusses causes, ECG characteristics, clinical manifestations, and potential treatments. The document provides an overview of heart block and various cardiac arrhythmias for medical professionals.