Here are the answers to your questions:
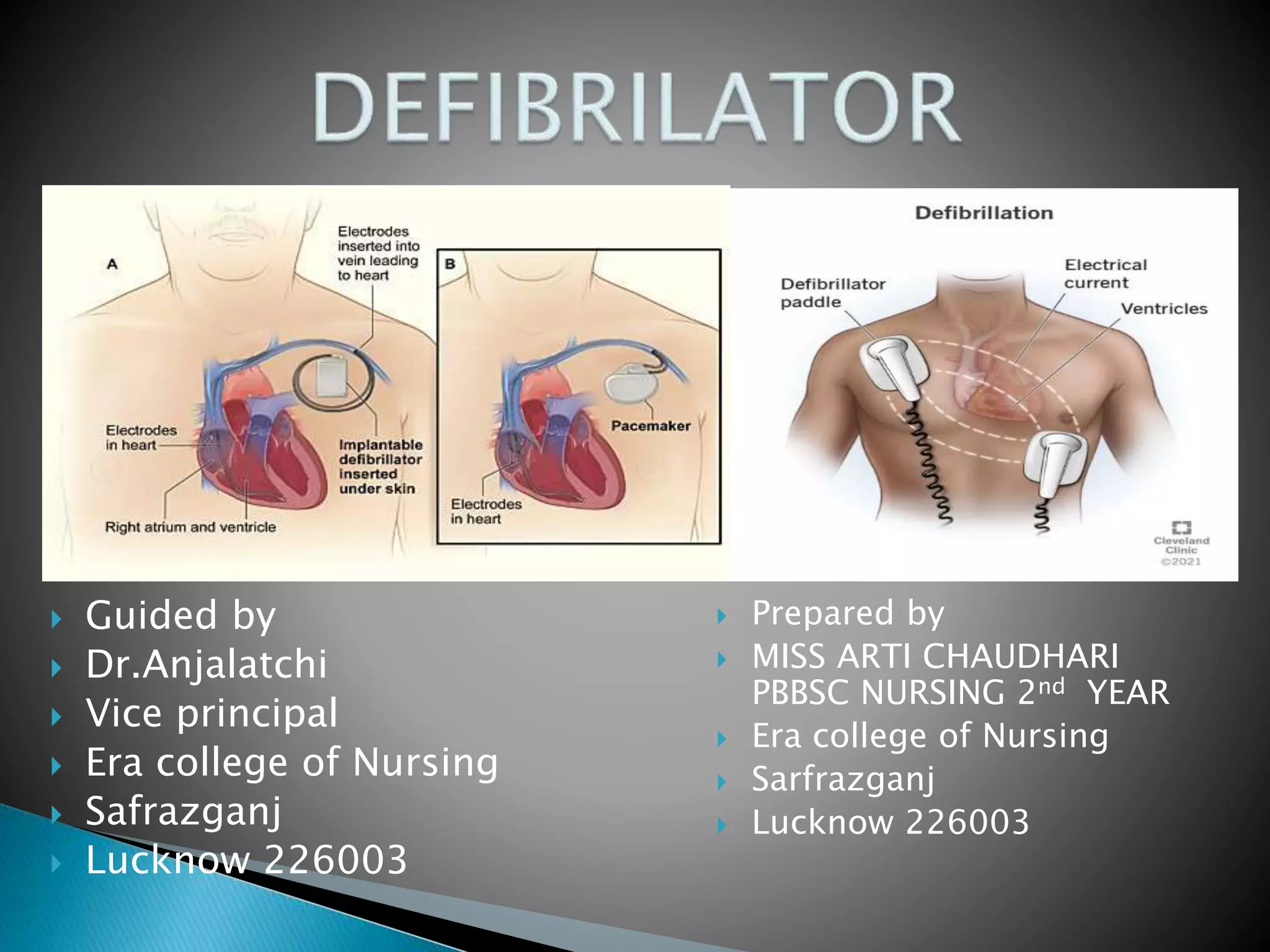
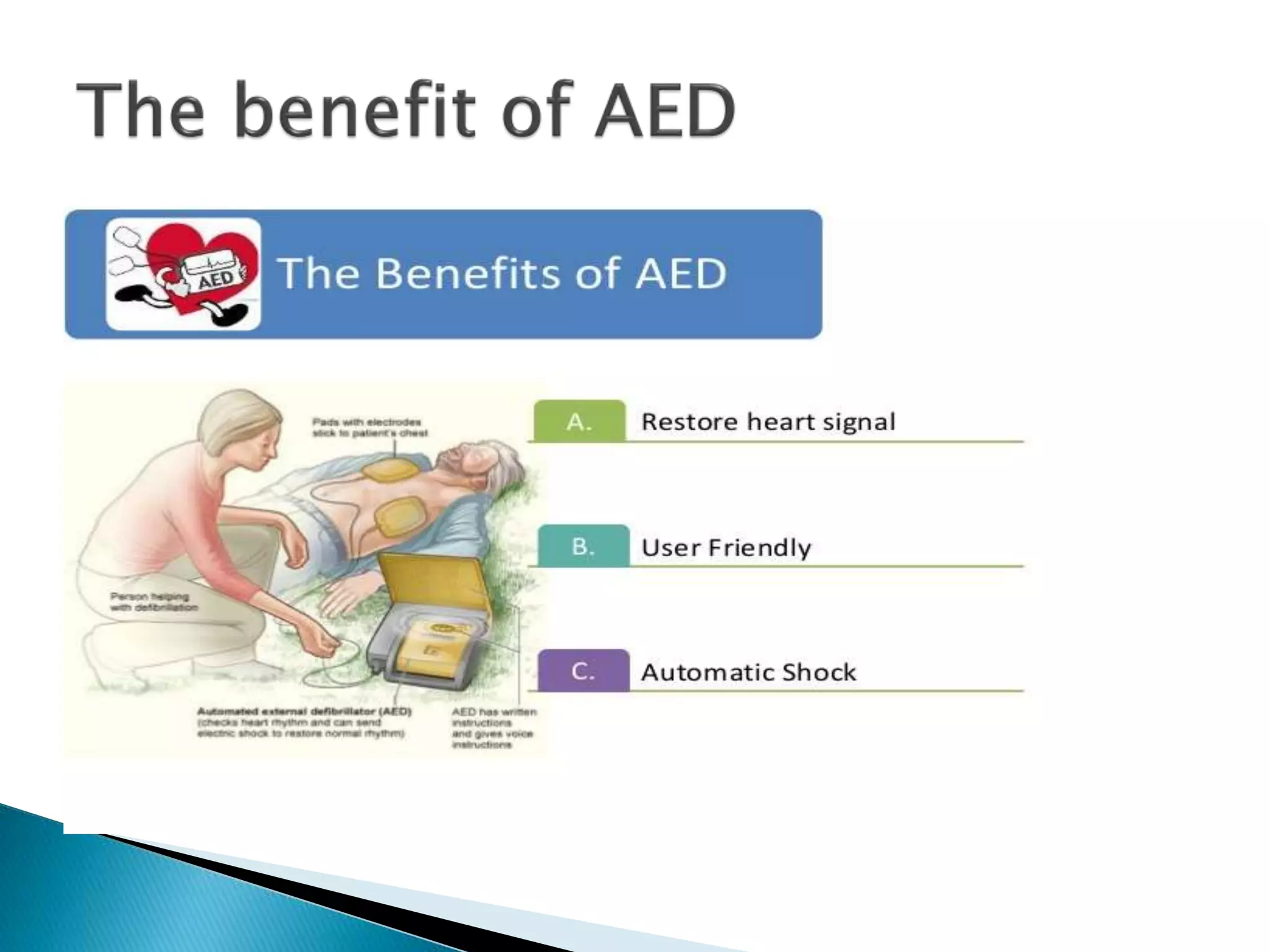
1. A defibrillator is a device that gives a high energy electric shock to the heart to treat potentially life threatening abnormal heart rhythms called arrhythmias.
2. The purpose of a defibrillator is to deliver a therapeutic dose of electric current to the heart with the aim of depolarizing a critical mass of the heart muscle and terminating the arrhythmia, allowing for spontaneous organized cardiac depolarization and contraction to resume.
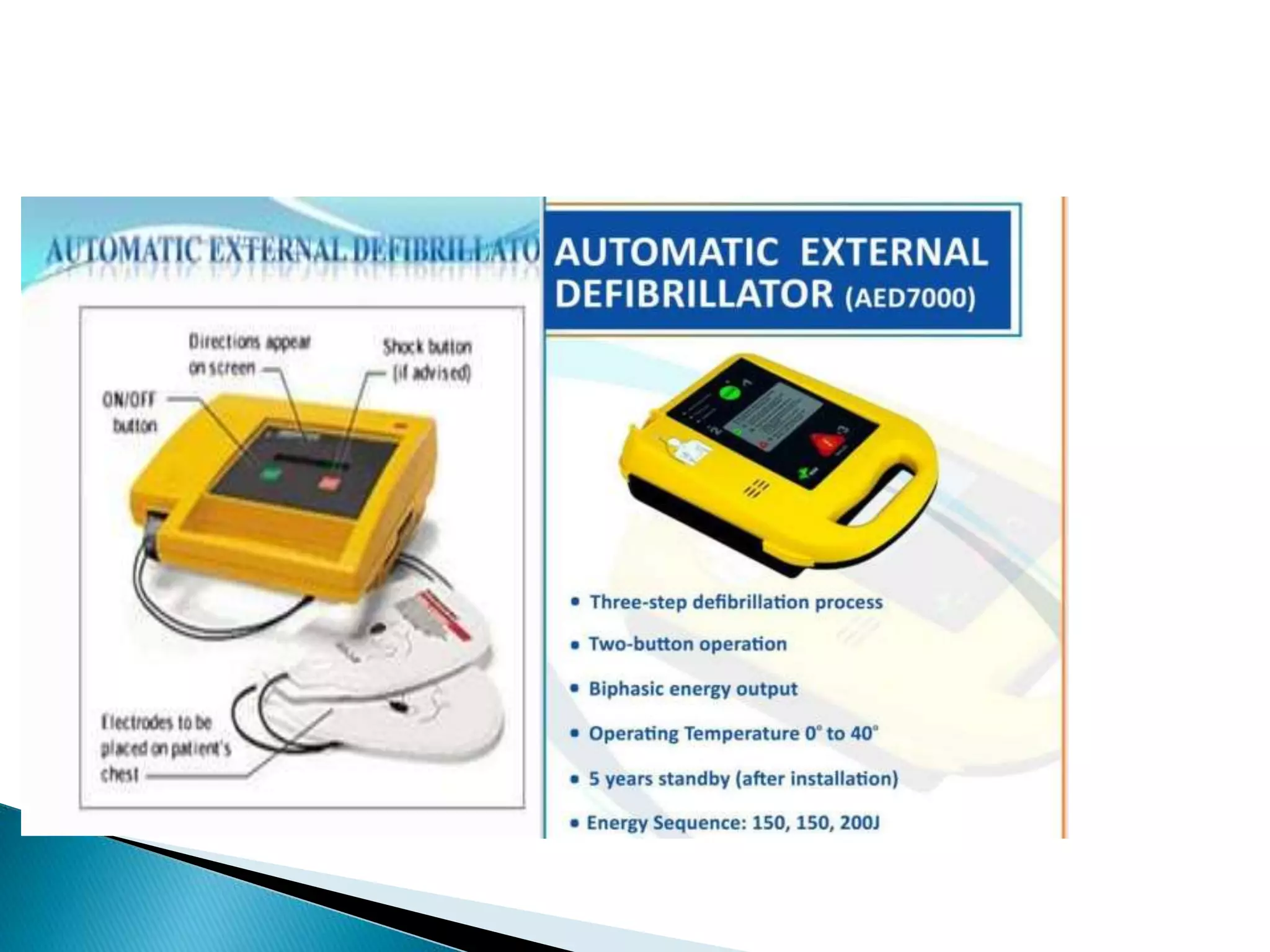
3. The typical joules delivered by a defibrillator range from 120-360 joules depending on whether it is a monophasic or biphasic defibrillator.
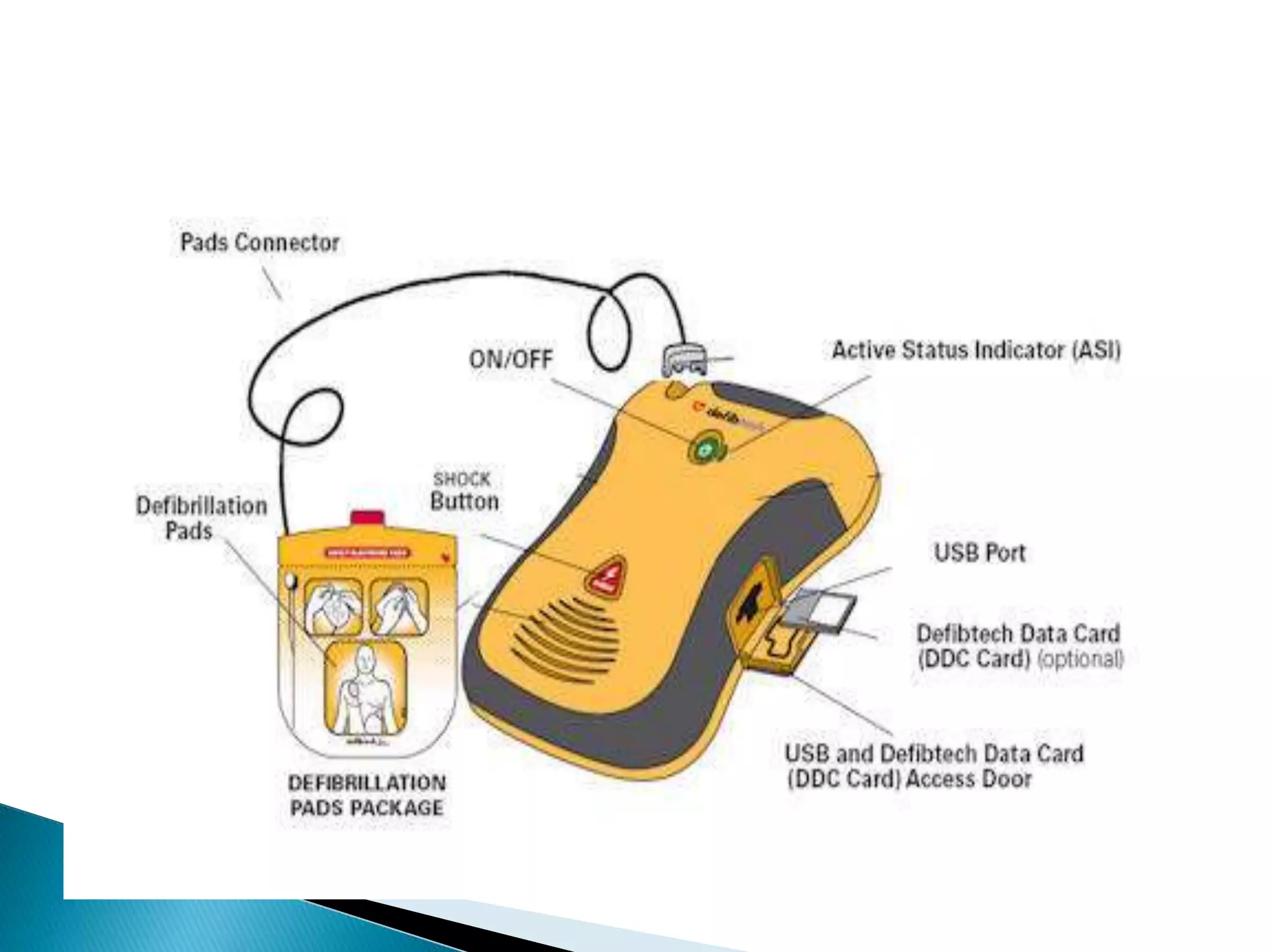
4. Defibrillator pads are placed on the patient