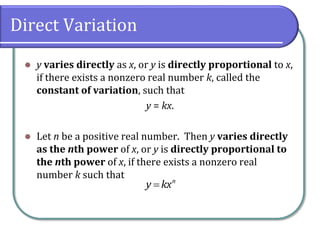
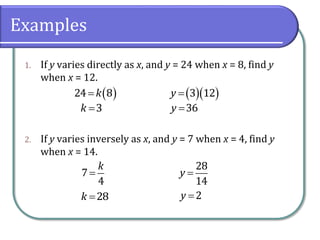
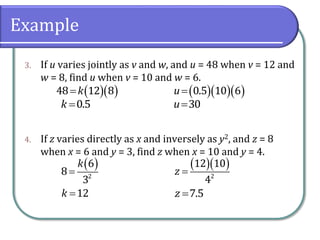
This document discusses different types of variation, including direct variation, inverse variation, and joint variation. It provides examples of solving variation problems by writing the general relationship as an equation using the constant of variation k, substituting given values to find k, and then substituting values into the original equation to solve for the unknown. Types of problems include direct variation where y varies directly with x, inverse variation where y varies inversely with x, and joint variation where y varies jointly as functions of x and z.