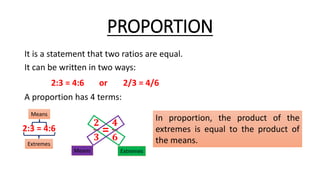
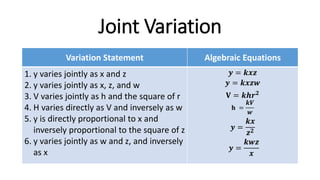
This document provides examples and explanations of different types of variation problems involving ratios, proportions, direct variation, inverse variation, and joint variation. It defines key terms like ratio, proportion, direct variation, inverse variation, and joint variation. It shows how to write algebraic equations to represent different variation statements and provides sample problems to practice determining unknown variables based on given variation relationships.