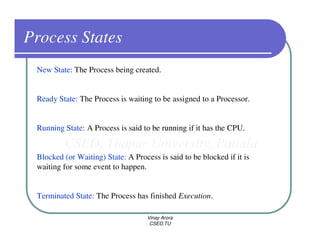
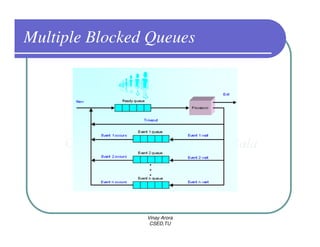
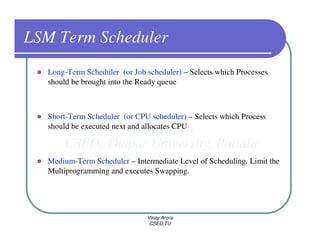
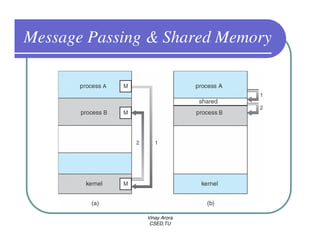
This document provides an overview of processes in operating systems. It defines a process as a program in execution and notes that a process includes the program counter, stack, data section, and other resources. It describes the different states a process can be in like new, ready, running, blocked, and terminated. Process scheduling and context switching are also summarized. The document outlines techniques for process creation and termination. It discusses interprocess communication methods like shared memory and message passing. In summary, the document defines processes and key concepts regarding their management in an operating system.