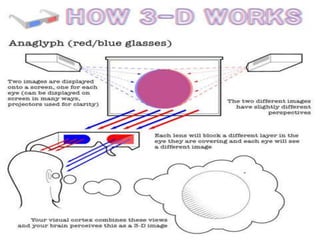
Three dimensional displays create the illusion of depth by presenting offset images to each eye. Stereoscopy refers to the technique of using two slightly different images to create this 3D effect. There are two main types of 3D displays - active 3D requires powered glasses while passive 3D uses polarized filters. Active 3D provides better image quality but passive 3D glasses are lighter and cheaper. Volumetric displays can actually create 3D images without glasses. Auto-stereoscopic displays also don't require glasses by using lenses or barriers to direct different pixels to each eye. 3D is now being applied to movies, TVs, gaming, and upcoming mobile phones as the technology advances.