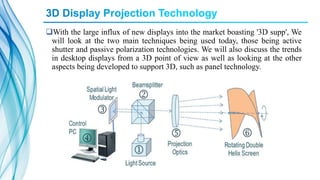
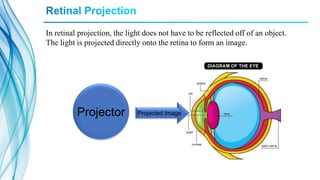
The document discusses screenless display technology, including its origins, types (such as Google Glass and SixthSense), components, advantages, and effects. Screenless displays transmit visual information without the use of a screen through methods like retinal projection, projected air interfaces, and direct brain interfaces. This technology has benefits like higher resolution and portability compared to traditional screens, and could improve access to information for visually impaired individuals. However, challenges remain regarding device costs, dependence on hardware, and potential issues from component failures.