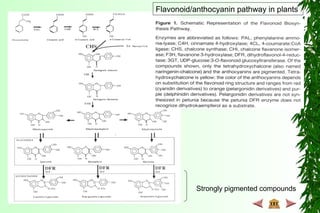
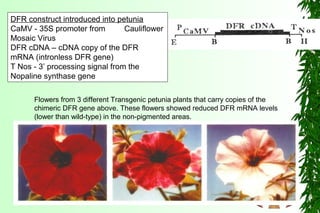
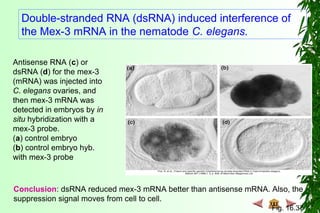
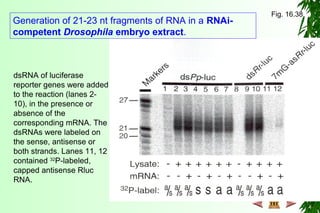
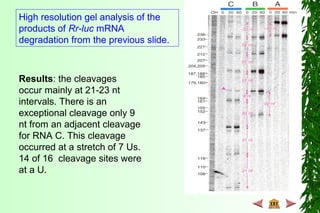
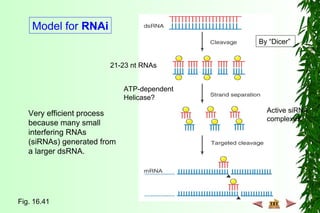
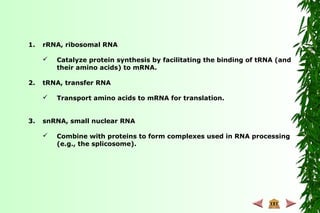
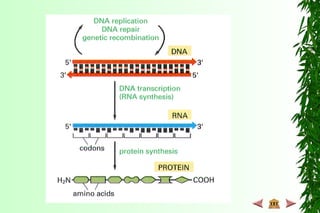
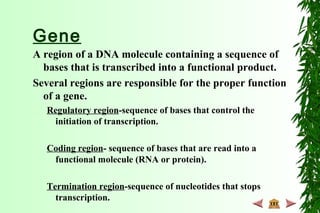
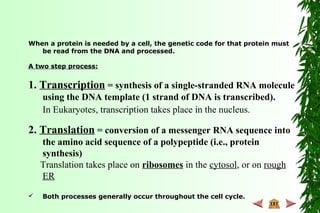
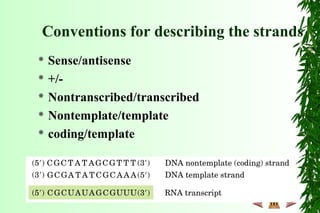
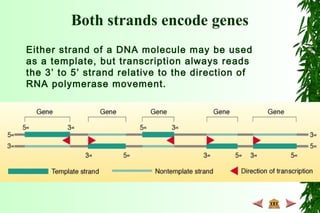
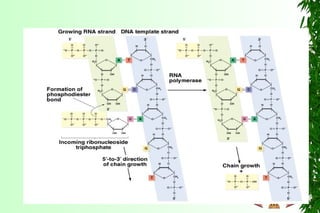
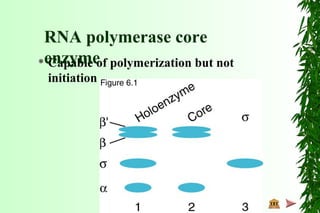
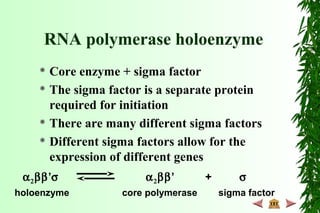
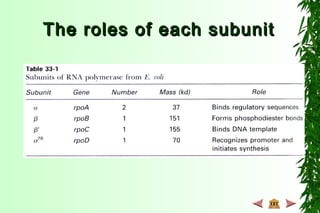
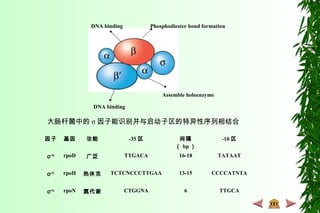
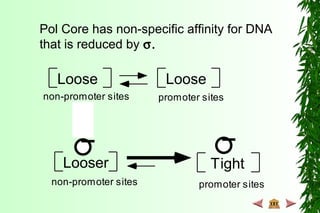
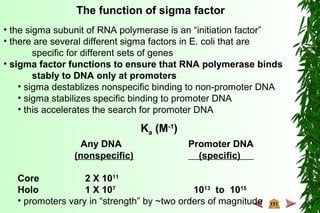
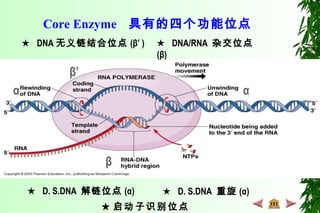
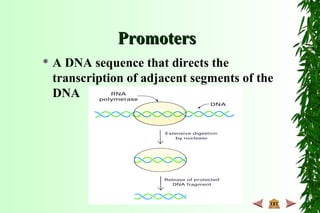
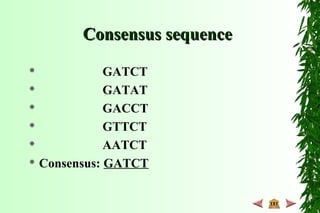
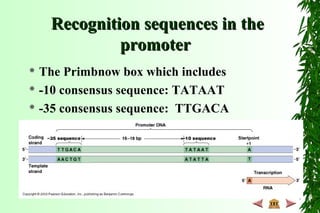
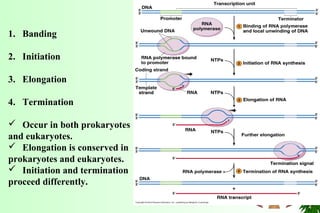
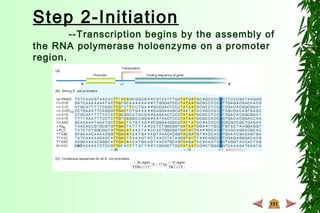
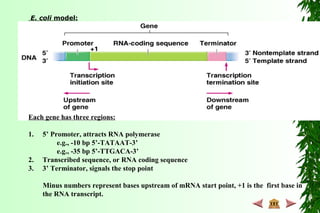
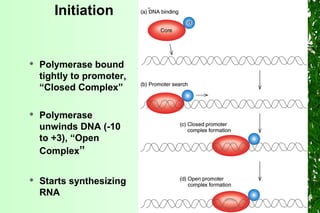
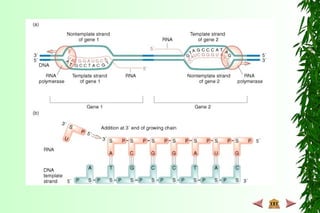
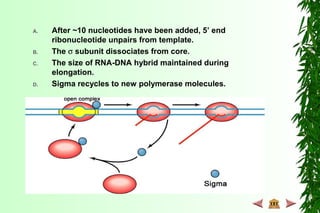
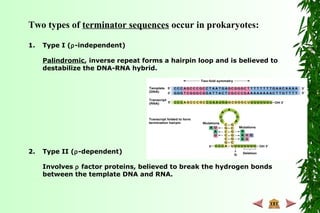
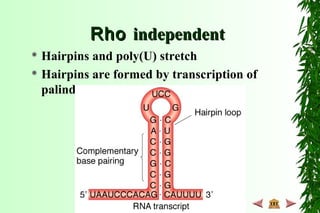
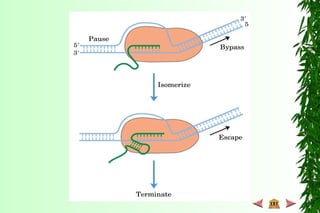
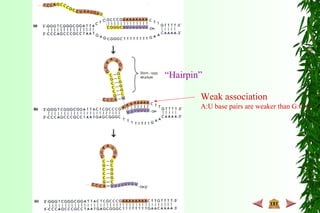
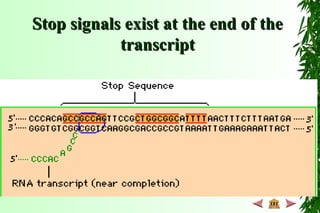
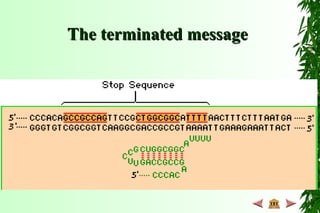
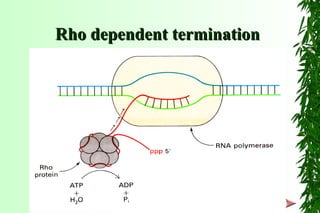
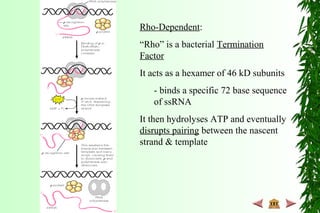
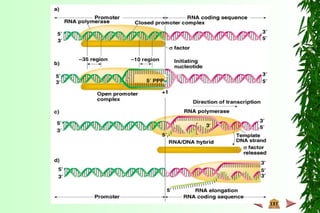
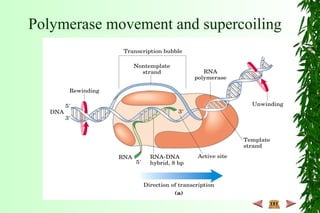
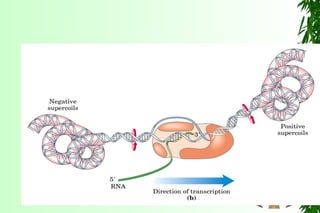
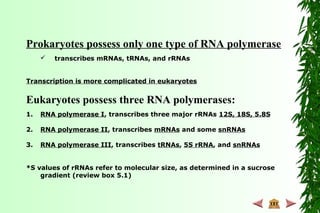
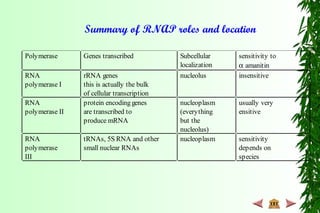
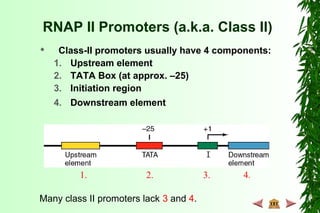
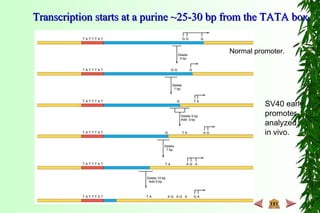
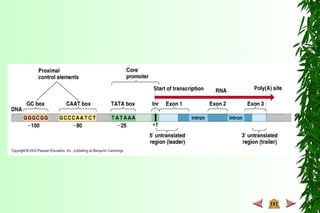
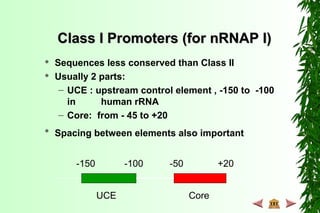
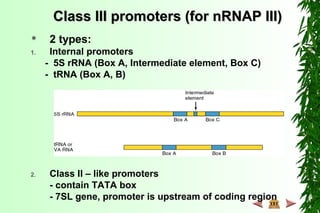
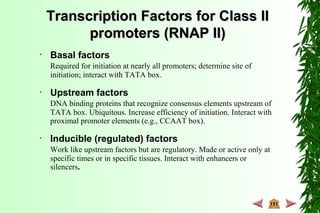
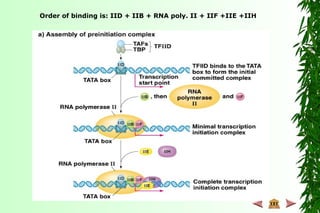
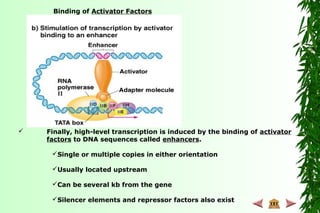
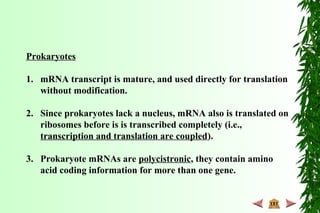
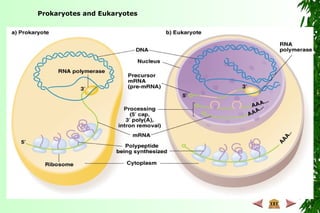
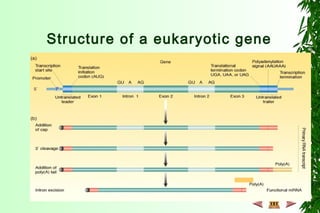
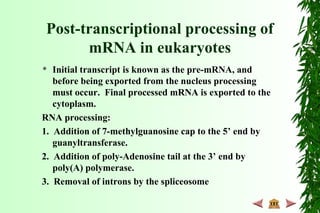
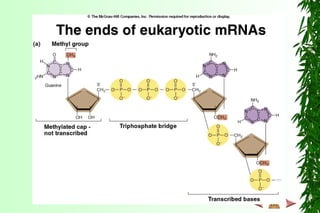
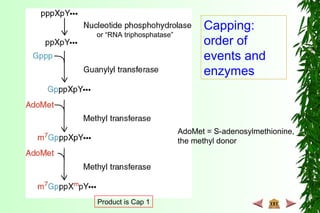
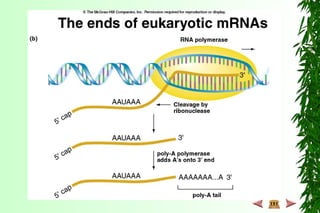
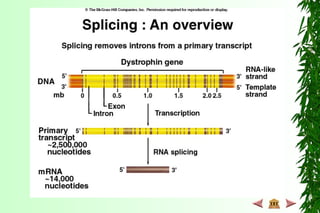
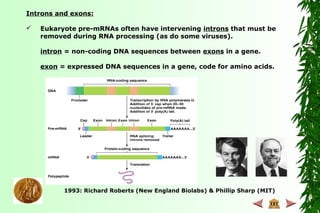
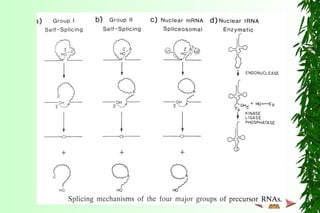
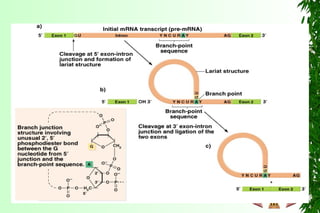
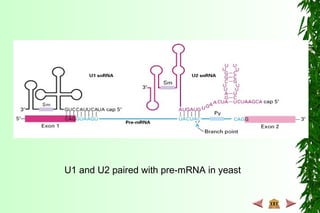
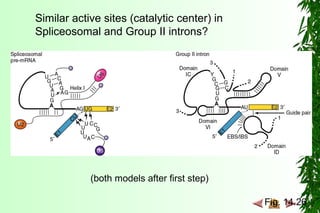
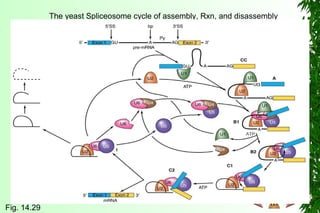
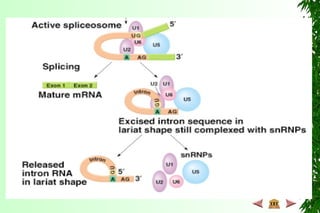
This document discusses transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, transcription is carried out by RNA polymerase, which associates with sigma factors to form holoenzymes that recognize specific promoter sequences. The process involves initiation at promoters, elongation, and termination. In eukaryotes, there are three nuclear RNA polymerases that transcribe different genes. RNA polymerase II transcribes protein-coding genes using promoters that often contain TATA boxes and other recognition elements.














































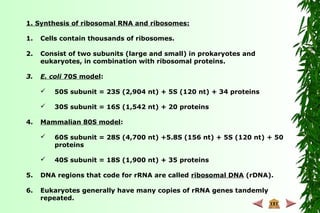
![Other Systems with RNA Editing
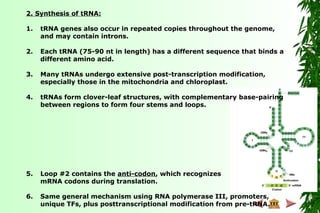
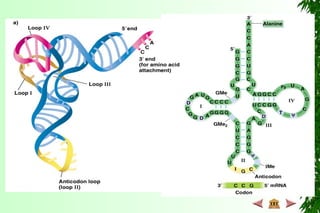
Land plant (C U) and Physarum (slime
mold) mitochondria (nt insertions)
Chloroplasts of angiosperms (C U)
A few nuclear genes in mammals
– Apolipoprotein B (C U)
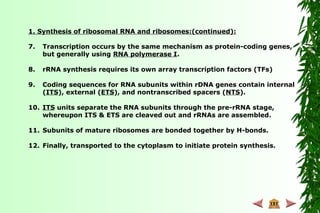
– Glutamate receptor [A I (inosine)]
Hepatitus delta virus (A I)
Paramyxovirus (G insertions)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-130517090022-phpapp01/85/3-125-320.jpg)