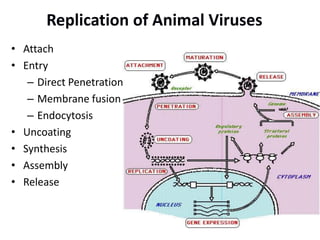
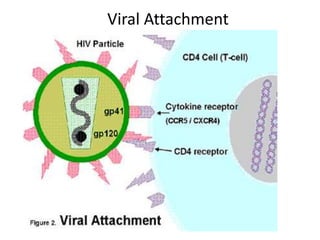
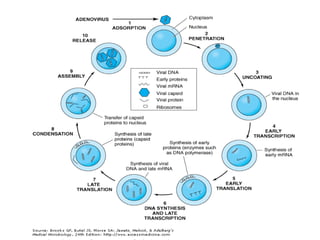
Viruses replicate inside host cells using the cell's machinery. There are typically six phases to viral replication: 1) attachment to host cell receptors, 2) penetration of the host cell, 3) uncoating of the viral genome from the capsid, 4) expression of viral genes and synthesis of new viral components, 5) assembly of new virus particles, and 6) release of progeny virus from the host cell. The replication cycles of DNA and RNA viruses differ in some of the intermediate steps but generally follow this overall pattern of attachment, entry, genome expression/replication, assembly and release.