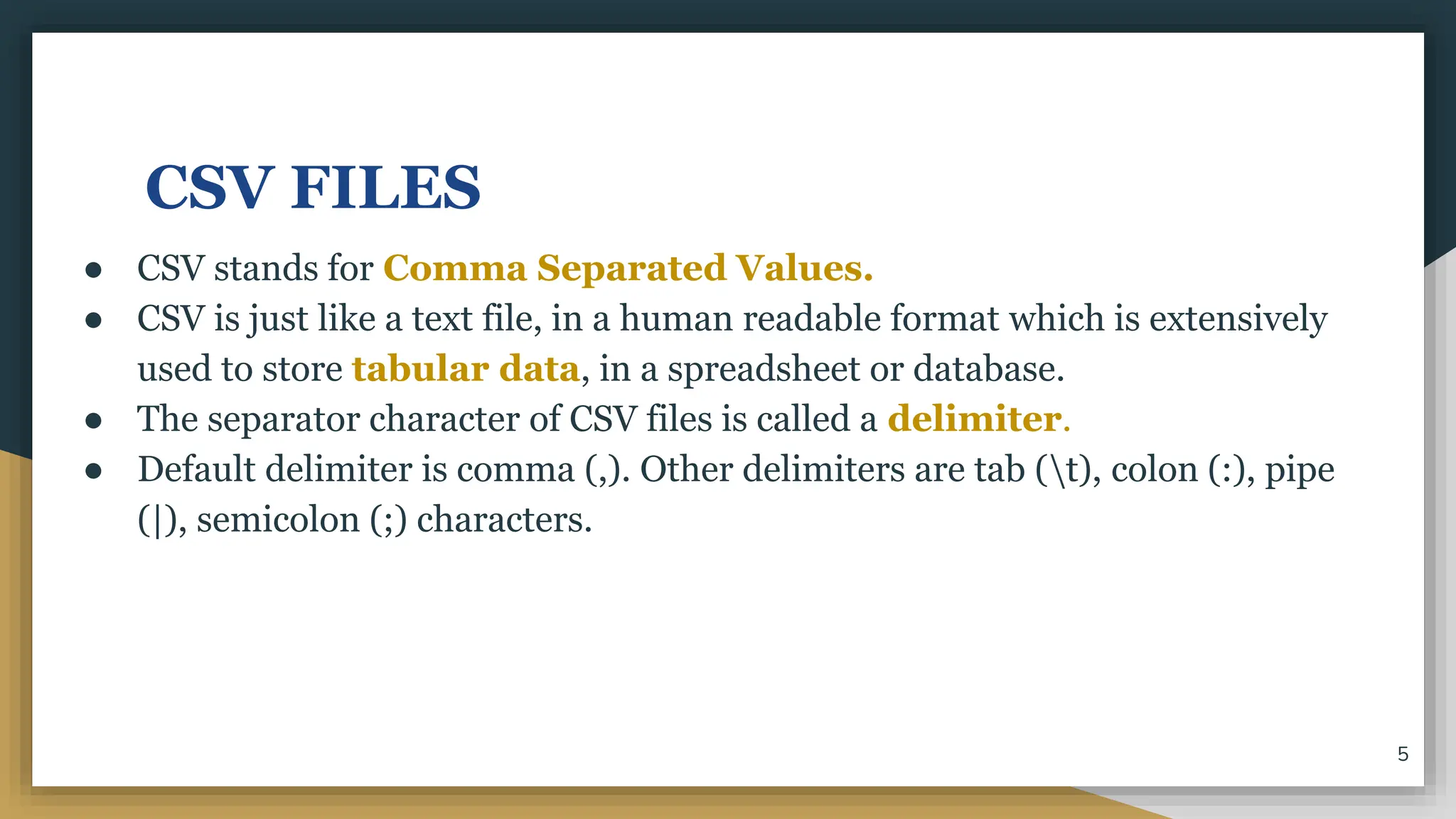
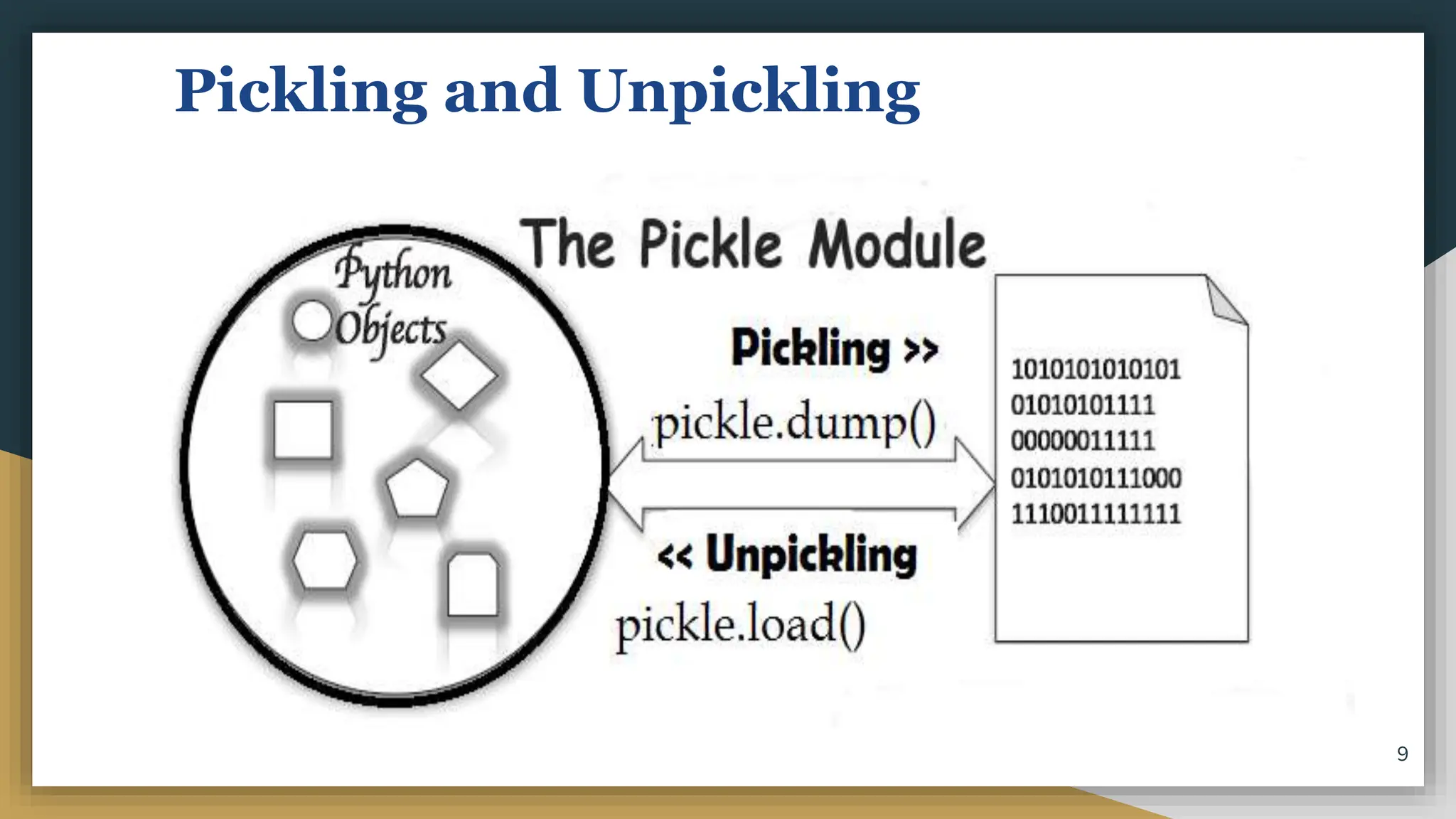
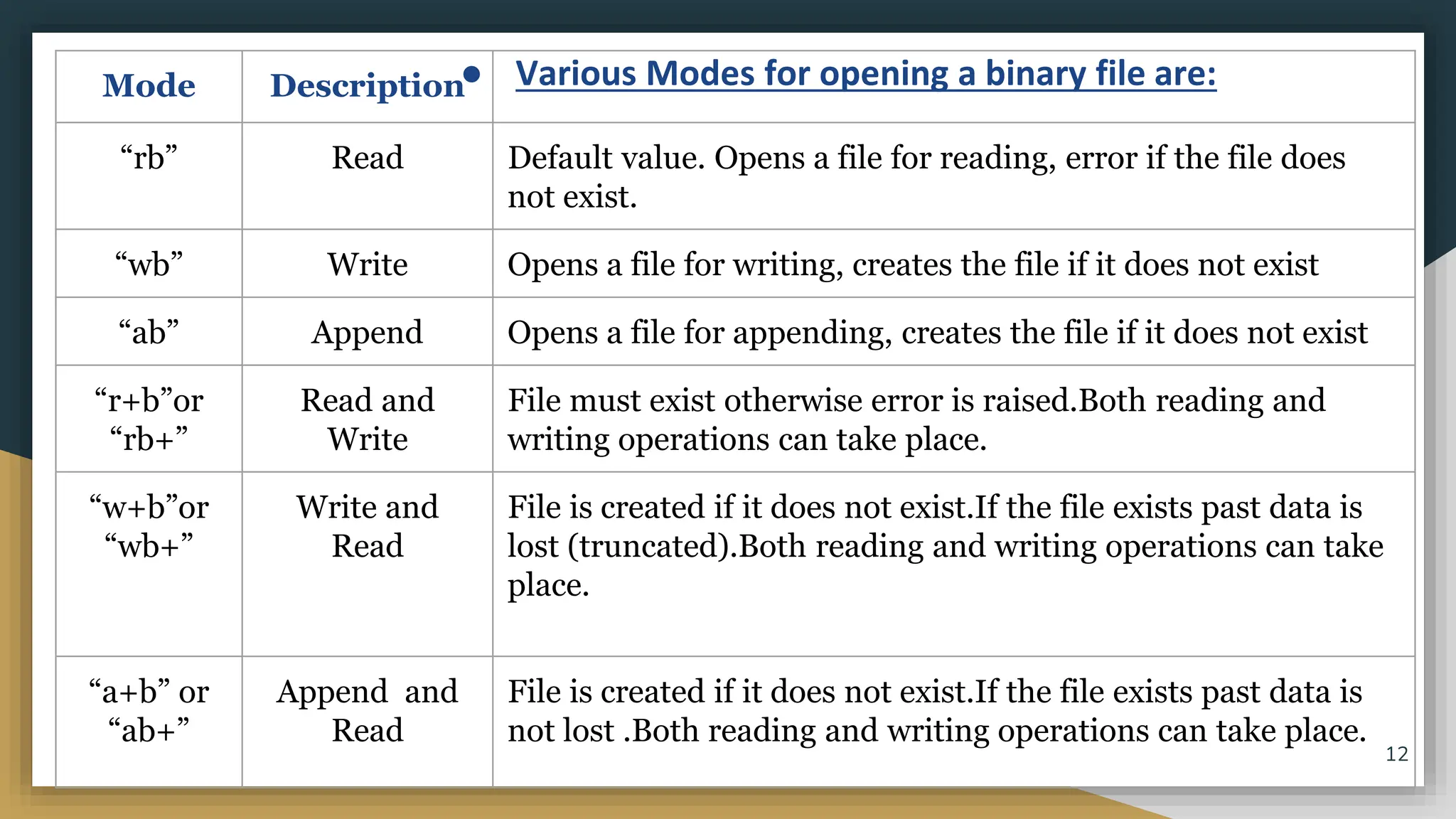
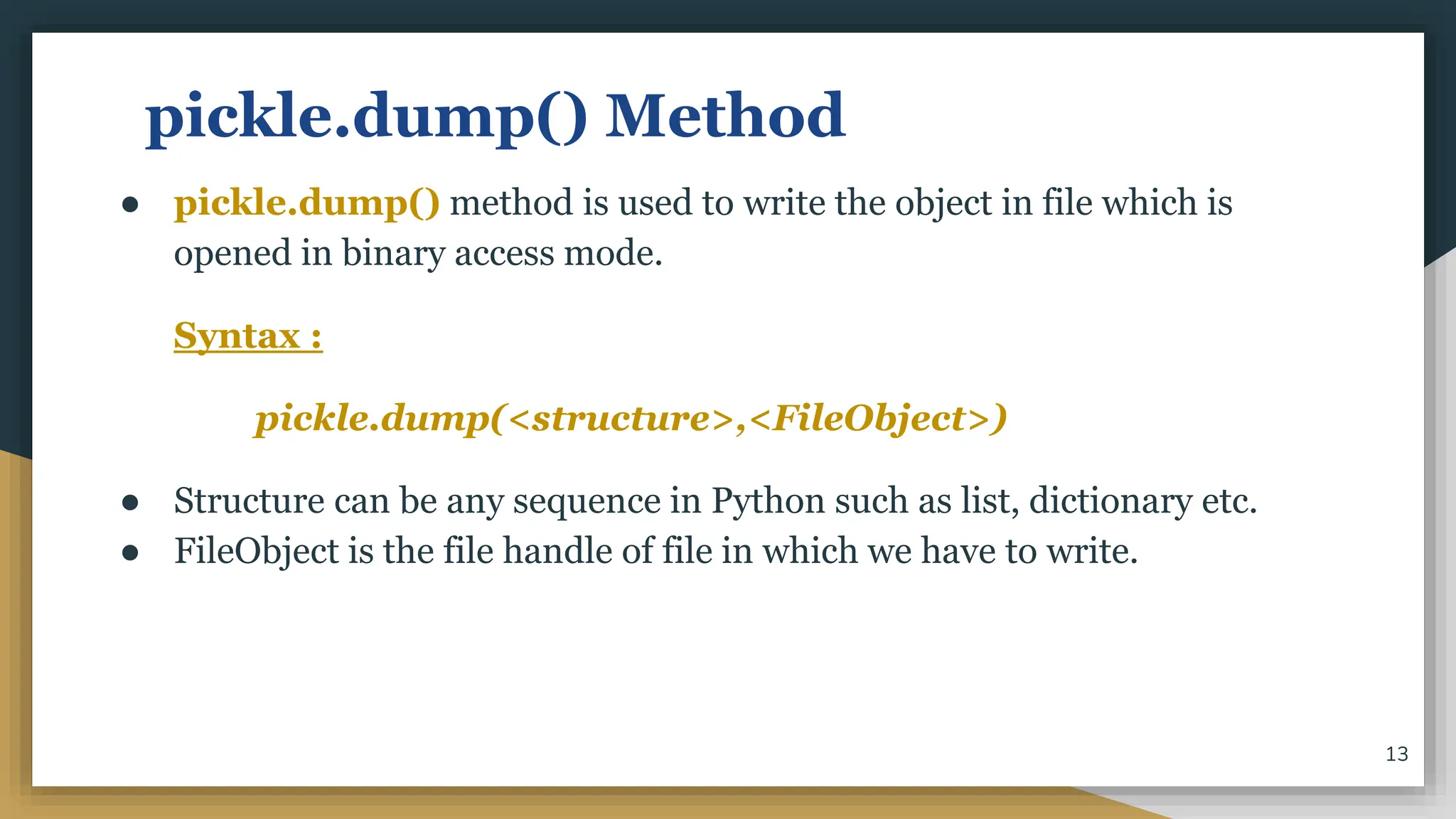
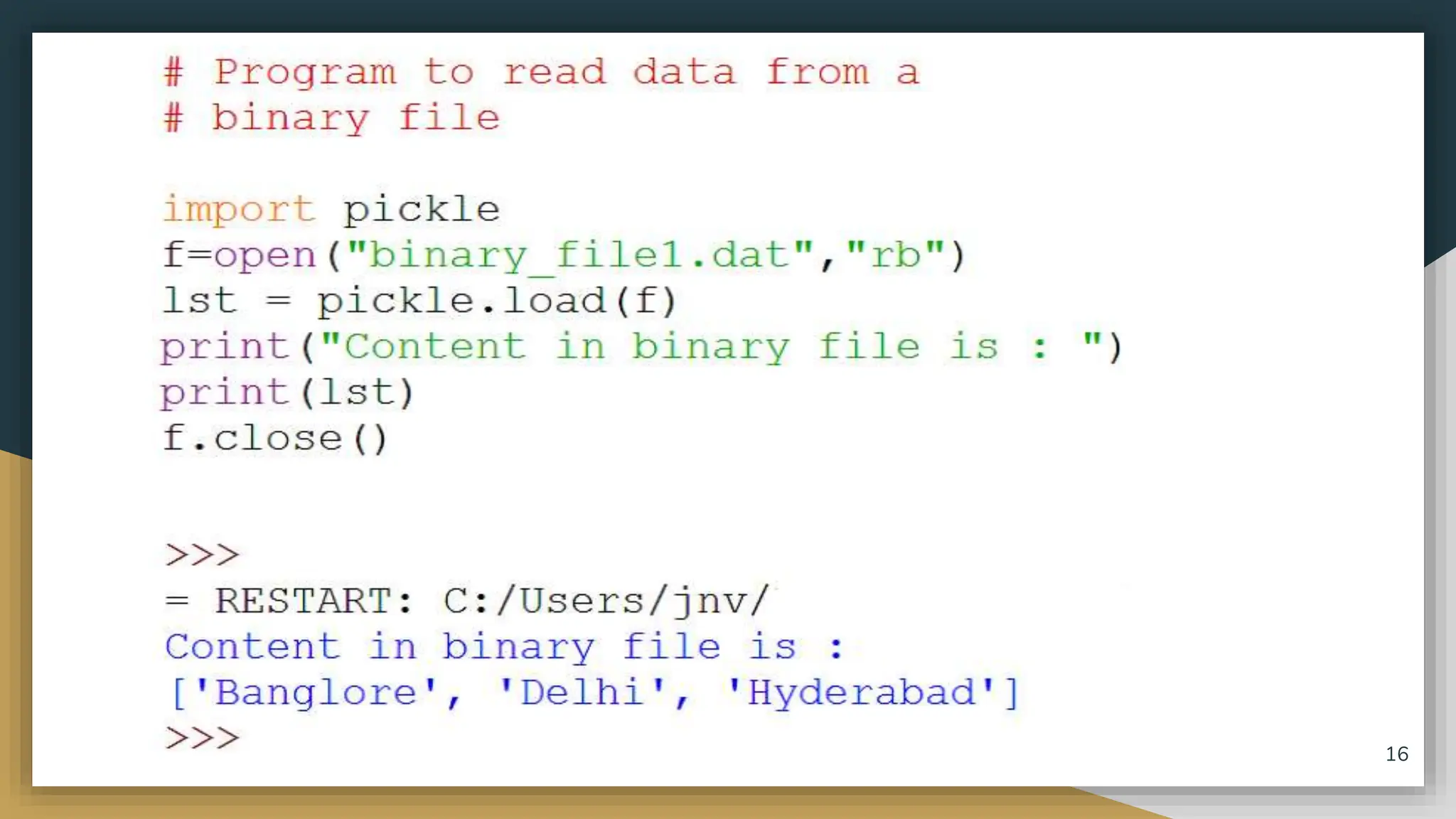
This document discusses file handling in Python. It explains that files are used to permanently store data as variables are volatile. There are three main types of files - text, binary, and CSV files. Text files store human-readable text while binary files contain arbitrary binary data. CSV files store tabular data with commas as the default delimiter. The document outlines the steps to process a file which include opening the file, performing operations, and closing the file. It specifically discusses binary files, noting they are encoded as byte streams and Python's pickle module is used to convert data to bytes for writing and back for reading. The pickle methods dump() and load() are used to write and read pickled data to and from binary files.