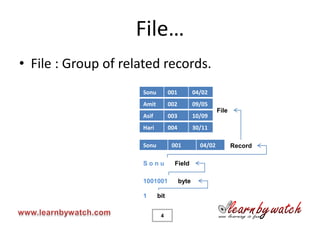
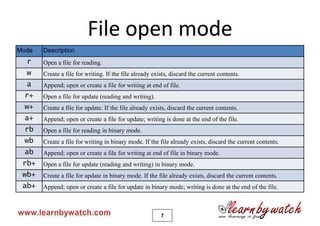
C programming language tutorial covering file input/output (I/O) operations in C such as opening, reading, writing, and closing files. Key points include:
1) Files are used to permanently store data on disk while variables are stored temporarily in RAM.
2) The FILE pointer and fopen/fclose functions are used to open/close files. Modes like r, w, a specify read/write/append.
3) Common file I/O functions are fgetc, fputs, fscanf to read/write text files sequentially. Fwrite, fread, fseek access binary files randomly by record.
4) Examples demonstrate opening files, reading/