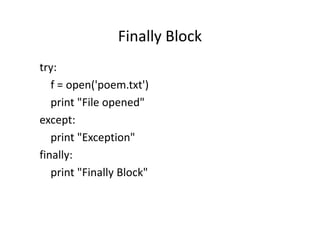
This document discusses Python files, modules, exceptions, and tasks. It covers reading and writing files in different modes, creating custom modules, handling exceptions using try/except blocks, and includes tasks to reverse a string and find the sum and factorial of numbers in a list.